Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial disparities in the mortality burden of the covid-19 pandemic across 569 European regions (2020-2021)
Spatial disparities in the mortality burden of the covid-19 pandemic across 569 European regions (2020-2021)
Excess mortality can be used as an indicator of the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, the authors estimate excess mortality in 569 European regions in 25 countries for 2020 and 2021 and describe how impacts changed over time.
- Florian Bonnet
- , Pavel Grigoriev
- & Carlo-Giovanni Camarda
-
Article
| Open Access Wide range of possible trajectories of North Atlantic climate in a warming world
Wide range of possible trajectories of North Atlantic climate in a warming world
This study reveals a widening range of projected North Atlantic climate states in the mid-twenty-first century. The distinct trajectories seen in sea surface temperatures are activated by global warming and may enable skillful long-lead decadal predictions.
- Qinxue Gu
- , Melissa Gervais
- & Shang-Ping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Early planetesimal differentiation and late accretion shaped Earth’s nitrogen budget
Early planetesimal differentiation and late accretion shaped Earth’s nitrogen budget
The late veneer impacts Earth’s nitrogen budget while exhibiting limited effects on other volatile elements, according to first-principles calculations of N-isotope fractionation during Earth’s accretion and differentiation.
- Wenzhong Wang
- , Michael J. Walter
- & Shichun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access On the potential of vehicle-to-grid and second-life batteries to provide energy and material security
On the potential of vehicle-to-grid and second-life batteries to provide energy and material security
Europe is becoming increasingly dependent on battery material imports. Here, authors show that electric vehicle batteries could fully cover Europe’s need for stationary battery storage by 2040, through either vehicle-to-grid or second-life-batteries, and reduce battery material demand by up to 7.5%.
- Fernando Aguilar Lopez
- , Dirk Lauinger
- & Daniel B. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon pricing and system reliability impacts on pathways to universal electricity access in Africa
Carbon pricing and system reliability impacts on pathways to universal electricity access in Africa
This study investigates the role of off-grid solar in achieving SDG7 in Africa, focusing on understanding the impact of carbon pricing and supply reliability. It uses high-resolution spatial analysis and demand modelling to explore policy interventions for universal electricity access.
- Hamish Beath
- , Shivika Mittal
- & Ajay Gambhir
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic review and meta-analysis of ex-post evaluations on the effectiveness of carbon pricing
Systematic review and meta-analysis of ex-post evaluations on the effectiveness of carbon pricing
Carbon pricing policies are adopted in many countries around the world to mitigate climate change. This systematic review shows that significant emission reductions of between 5 and 21% are achieved by at least 17 out of 21 reviewed policy schemes.
- Niklas Döbbeling-Hildebrandt
- , Klaas Miersch
- & Jan C. Minx
-
Article
| Open Access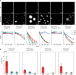 Physiological basis for atmospheric methane oxidation and methanotrophic growth on air
Physiological basis for atmospheric methane oxidation and methanotrophic growth on air
Atmospheric methane-oxidizing bacteria constitute the sole biological sink for atmospheric methane. Here, Schmider et al. assess the ability and strategies of seven methanotrophic species to grow with air as sole energy, carbon, and nitrogen source, showing that these bacteria can grow on the trace concentrations of methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen present in air.
- Tilman Schmider
- , Anne Grethe Hestnes
- & Alexander T. Tveit
-
Article
| Open Access Public engagement for inclusive and sustainable governance of climate interventions
Public engagement for inclusive and sustainable governance of climate interventions
Meaningful public engagement is key to sustainable governance of carbon removal and solar radiation modification. A study across 22 countries emphasizes tailored approaches sensitive to local contexts, technological nuances, power dynamics and trust.
- Livia Fritz
- , Chad M. Baum
- & Benjamin K. Sovacool
-
Article
| Open Access Ion pair sites for efficient electrochemical extraction of uranium in real nuclear wastewater
Ion pair sites for efficient electrochemical extraction of uranium in real nuclear wastewater
Electrochemical uranium extraction from real nuclear wastewater is appealing but challenging. Herein, Lin et al develop a strategy of ion pair site for enhanced binding of dominant uranium fluoride species in real wastewater, achieving efficient recycling of uranium as powder product.
- Tao Lin
- , Tao Chen
- & Rong He
-
Article
| Open Access Geologically younger ecosystems are more dependent on soil biodiversity for supporting function
Geologically younger ecosystems are more dependent on soil biodiversity for supporting function
This study demonstrates that soil BEF relationships diminish during long-term pedogenesis, highlighting the importance of soil biodiversity in sustaining multiple ecosystem functions in younger, drier soils.
- Jiao Feng
- , Yu-Rong Liu
- & Manuel Delgado-Baquerizo
-
Article
| Open Access Severe drought exposure in utero associates to children’s epigenetic age acceleration in a global climate change hot spot
Severe drought exposure in utero associates to children’s epigenetic age acceleration in a global climate change hot spot
The study suggests a positive association between in utero drought exposure and faster biological aging in children in a global climate change hot spot. Drought experienced during pregnancy may reduce life expectancy.
- Xi Qiao
- , Bilinda Straight
- & Belinda L. Needham
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon storage through China’s planted forest expansion
Carbon storage through China’s planted forest expansion
The dynamics of planted forests in China over the past three decades have contributed ~1198tg of above-ground carbon storage.
- Kai Cheng
- , Haitao Yang
- & Qinghua Guo
-
Article
| Open Access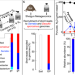 Sustained bacterial N2O reduction at acidic pH
Sustained bacterial N2O reduction at acidic pH
Microbial reduction of nitrous oxide to dinitrogen is considered negligible under acidic conditions. However, Guang He et al. show that a co-culture of two bacterial species derived from acidic tropical forest soil can reduce nitrous oxide at pH 4.5.
- Guang He
- , Gao Chen
- & Frank E. Löffler
-
Article
| Open Access Financial markets value skillful forecasts of seasonal climate
Financial markets value skillful forecasts of seasonal climate
Traders of financial options bet that firms’ stock prices will be affected by forecasts of seasonal climate produced by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Firms are exposed throughout the economy, and traders spend more to hedge the news from more skillful forecasts
- Derek Lemoine
- & Sarah Kapnick
-
Article
| Open Access A HIMU-like component in Mariana Convergent Margin magma sources during initial arc rifting revealed by melt inclusions
A HIMU-like component in Mariana Convergent Margin magma sources during initial arc rifting revealed by melt inclusions
HIMU-type seamounts may be subducted elsewhere beneath the Mariana arc, but obvious HIMU-type components appear only in the initial stages of arc rifting due to the low melting degree and being consumed during the process of back-arc spreading.
- Xiaohui Li
- , Osamu Ishizuka
- & Hongxia Yu
-
Article
| Open Access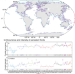 Global mapping and evolution of persistent fronts in Large Marine Ecosystems over the past 40 years
Global mapping and evolution of persistent fronts in Large Marine Ecosystems over the past 40 years
A global digital atlas of persistent fronts in Large Marine Ecosystems reveals a rapid increase in subtropical and polar regions, and stable conditions or a slight decrease in tropical regions, a pattern not captured by climate projections and ocean models.
- Qinwang Xing
- , Haiqing Yu
- & Hui Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Stratospheric influence on surface ozone pollution in China
Stratospheric influence on surface ozone pollution in China
The authors analyze the frequency, duration and intensity of stratospheric intrusions to the surface in China over 2015-2022 and find that such intrusions enhance surface ozone pollution, especially in spring and autumn, followed by summer.
- Zhixiong Chen
- , Jane Liu
- & Zhou Zang
-
Article
| Open Access Global projections of heat exposure of older adults
Global projections of heat exposure of older adults
By 2050 > 23% of the global population aged 69 + will live in climates with acute heat exposure– the 95th percentile of the distribution of maximum daily temperatures–greater than the critical threshold of 37.5C, compared with 14% in 2020, an increase of 177–246 million older adults exposed to dangerous acute heat.
- Giacomo Falchetta
- , Enrica De Cian
- & Deborah Carr
-
Article
| Open Access Long-read powered viral metagenomics in the oligotrophic Sargasso Sea
Long-read powered viral metagenomics in the oligotrophic Sargasso Sea
The Sargasso Sea is a natural laboratory for understanding future conditions of warmer oceans and associated nutrient limitation. Here, the authors combined short- and long-read sequencing to survey Sargasso Sea viral communities.
- Joanna Warwick-Dugdale
- , Funing Tian
- & Ben Temperton
-
Article
| Open Access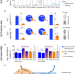 Ammonium-derived nitrous oxide is a global source in streams
Ammonium-derived nitrous oxide is a global source in streams
NH4+-derived pathways, rather than NO3--derived pathway, are the dominant hyporheic N2O sources in lower-order streams. These findings provide insights into better estimation of N2O emissions in global models of riverine ecosystems and emphasize the importance of managing ammonium.
- Shanyun Wang
- , Bangrui Lan
- & Yong-Guan Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic detection of methane emissions in multispectral satellite imagery using a vision transformer
Automatic detection of methane emissions in multispectral satellite imagery using a vision transformer
Accurate monitoring of methane emissions is essential to understand its contribution to global warming. The authors here employ multi-spectral satellite data to create a methane detection tool with global coverage and high temporal and spatial resolution.
- Bertrand Rouet-Leduc
- & Claudia Hulbert
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of nearly 3000 archaeal genomes from terrestrial geothermal springs sheds light on interconnected biogeochemical processes
Analysis of nearly 3000 archaeal genomes from terrestrial geothermal springs sheds light on interconnected biogeochemical processes
Here, Qi et al. assembled ~3000 archaeal genomes from hot springs, capturing temporal dynamics and environmental diversity, and systematically explored functional niches and metabolic handoffs, shedding light on Archaea’s role in biogeochemical cycling.
- Yan-Ling Qi
- , Ya-Ting Chen
- & Zheng-Shuang Hua
-
Article
| Open Access Anthropogenic forcings reverse a simulated multi-century naturally-forced Northern Hemisphere Hadley cell intensification
Anthropogenic forcings reverse a simulated multi-century naturally-forced Northern Hemisphere Hadley cell intensification
The authors find an unprecedented human-induced weakening of the Northern Hemisphere Hadley circulation in recent and coming decades, contrasting with the naturally-forced simulated strengthening over the preindustrial last millennium.
- Or Hess
- & Rei Chemke
-
Article
| Open Access Urban development pattern’s influence on extreme rainfall occurrences
Urban development pattern’s influence on extreme rainfall occurrences
Cities that experience compact development tend to witness more extreme rainfall over downtown than their rural surroundings, while the anomalies in extreme rainfall frequency diminish for cities with dispersed development patterns.
- Long Yang
- , Yixin Yang
- & Dev Niyogi
-
Article
| Open Access Overlooked shelf sediment reductive sinks of dissolved rhenium and uranium in the modern ocean
Overlooked shelf sediment reductive sinks of dissolved rhenium and uranium in the modern ocean
The sources and sinks of Re and U in the modern ocean may be imbalanced, according to sedimentary porewater analysis and assessment of reductive Re and U removal on the continental shelf
- Qingquan Hong
- , Yilin Cheng
- & Tianyu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access High carbon dioxide emissions from Australian estuaries driven by geomorphology and climate
High carbon dioxide emissions from Australian estuaries driven by geomorphology and climate
Australian estuaries shown to emit more CO2 per unit area than global estuaries due to the dominance of macrotidal subtropical and tropical tidal systems, while disturbance effects were minimal due to low overall disturbance.
- Jacob Z.-Q. Yeo
- , Judith A. Rosentreter
- & Bradley D. Eyre
-
Article
| Open Access Human-induced intensified seasonal cycle of sea surface temperature
Human-induced intensified seasonal cycle of sea surface temperature
The authors reveal a 3.9% intensification in the sea surface temperature seasonal cycle over the past four decades, with hotspot regions experiencing intensification of up to 10%. This intensification extends throughout the mixed layer, amplifying the seasonal cycle of upper-ocean oxygenation.
- Fukai Liu
- , Fengfei Song
- & Yiyong Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature alters the predator-prey size relationships and size-selectivity of Southern Ocean fish
Temperature alters the predator-prey size relationships and size-selectivity of Southern Ocean fish
Using prey size measurements from ten Southern Ocean lanternfish species sampled across >10° of latitude, this study shows that higher temperatures were associated with smaller fish and an overall decrease in the size of fish relative to their prey. Ocean warming may therefore alter the diversity and size structuring of trophic interactions, reducing the stability of marine ecosystems.
- Patrick Eskuche-Keith
- , Simeon L. Hill
- & Eoin J. O’Gorman
-
Article
| Open Access Drivers and implications of alternative routes to fuels decarbonization in net-zero energy systems
Drivers and implications of alternative routes to fuels decarbonization in net-zero energy systems
Assumptions about the use of biomass and CO2 sequestration drive key differences in how emissions from remaining fuels are mitigated in net-zero energy systems, with potentially significant tradeoffs that will need to be evaluated and managed.
- Bryan K. Mignone
- , Leon Clarke
- & Aranya Venkatesh
-
Article
| Open Access Western US intraplate deformation controlled by the complex lithospheric structure
Western US intraplate deformation controlled by the complex lithospheric structure
The lithospheric structure controls crustal deformation in the western US. Particularly, its abrupt thickness change along the eastern boundary of the Basin and Range leads to enhanced lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction and localized earthquakes.
- Zebin Cao
- & Lijun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access East European sedimentary basins long heated by a fading mantle upwelling
East European sedimentary basins long heated by a fading mantle upwelling
Since the Jurassic, East European basins have likely been situated over a weakening mantle upwelling, which heated the basins and created suitable conditions for hydrocarbon maturation, according to geodata combined with modelling.
- Alik Ismail-Zadeh
- , Anne Davaille
- & Yuri Volozh
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean internal tides suppress tropical cyclones in the South China Sea
Ocean internal tides suppress tropical cyclones in the South China Sea
The authors show that the presence of strong ocean internal tides in the South China Sea suppresses tropical cyclone intensification, mitigating their impacts on the highly populated surrounding regions.
- Shoude Guan
- , Fei-Fei Jin
- & Jinbao Song
-
Article
| Open Access Levitation and dynamics of bodies in supersaturated fluids
Levitation and dynamics of bodies in supersaturated fluids
When a solid object is placed in a supersaturated environment, it can exhibit interesting dynamics. Spagnolie et al. conducted an experiment using raisins and 3D-printed bodies in carbonated water and found that the motion of the solid object is influenced by the accumulation and release of bubbles as they reach the surface.
- Saverio E. Spagnolie
- , Samuel Christianson
- & Carsen Grote
-
Article
| Open Access A unifying modelling of multiple land degradation pathways in Europe
A unifying modelling of multiple land degradation pathways in Europe
This study presents an unprecedented analysis of agricultural land multi-degradation in 40 European countries, using twelve dataset-based processes that were modelled as land degradation convergence and combination pathways across the continent.
- Remus Prăvălie
- , Pasquale Borrelli
- & Marius-Victor Birsan
-
Article
| Open Access The differential impact of climate interventions along the political divide in 60 countries
The differential impact of climate interventions along the political divide in 60 countries
A major barrier to climate mitigation is the political polarization of climate change. Here, the authors examine which of several interventions increase people’s climate policy support and climate action across ideological boundaries.
- Michael Berkebile-Weinberg
- , Danielle Goldwert
- & Madalina Vlasceanu
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient recovery and recycling/upcycling of precious metals using hydrazide-functionalized star-shaped polymers
Efficient recovery and recycling/upcycling of precious metals using hydrazide-functionalized star-shaped polymers
Despite the use of amine-functionalized polymers as metal adsorbents, they are generally ineffective at recovering precious metals. Here the authors prepare a star-shaped, hydrazide-functionalized polymer as a recoverable standalone adsorbent with high precious metal adsorption capability/selectivity and practical feasibility.
- Seung Su Shin
- , Youngkyun Jung
- & Jung-Hyun Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing fossil-based plastics, chemicals and fertilizers production in China
Tracing fossil-based plastics, chemicals and fertilizers production in China
Plastics, chemical production, and fertilizers commonly rely on fossil fuels. Here the authors examine these uses in China and find that in 2017, 5%, 15%, and 7% of China’s total coal, crude oil, and natural gas were used as feedstocks in the chemical industry.
- Meng Jiang
- , Yuheng Cao
- & Bing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Compensating affected parties necessary for rapid coal phase-out but expensive if extended to major emitters
Compensating affected parties necessary for rapid coal phase-out but expensive if extended to major emitters
When countries phase out coal, they compensate affected companies, communities and workers. Today more than $200 billion are allocated for such payoff, but much larger amount will be needed if China and India also phase out coal to tackle climate change.
- Lola Nacke
- , Vadim Vinichenko
- & Jessica Jewell
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of management practices on the ecosystem-service multifunctionality of temperate grasslands
Effects of management practices on the ecosystem-service multifunctionality of temperate grasslands
Sustainable agricultural policies need to be practically assessed. Here, the authors assess how management practices affect ecosystem services in Swiss agricultural grasslands showing that organic farming has a lesser impact than the eco-scheme and the use as pasture or meadow.
- Franziska J. Richter
- , Matthias Suter
- & Valentin H. Klaus
-
Article
| Open Access Early warning signals of the termination of the African Humid Period(s)
Early warning signals of the termination of the African Humid Period(s)
The end of the green Sahara in the mid-Holocene was gradual, but punctuated by rapidly changing episodes of extreme drought and wetness, to which human societies were exposed and had to adapt to, as a lake record from southern Ethiopia suggests.
- Martin H. Trauth
- , Asfawossen Asrat
- & Paul J. Valdes
-
Article
| Open Access Lower Ordovician synziphosurine reveals early euchelicerate diversity and evolution
Lower Ordovician synziphosurine reveals early euchelicerate diversity and evolution
Here, the authors describe an early synziphosurine from the Lower Ordovician Fezouata Shale of Morocco, which exhibits traits that elucidate the long-contentious relationships between crown euchelicerates and their sister taxa, and also clarifies euchelicerate body plan evolution.
- Lorenzo Lustri
- , Pierre Gueriau
- & Allison C. Daley
-
Article
| Open Access Contextual and combinatorial structure in sperm whale vocalisations
Contextual and combinatorial structure in sperm whale vocalisations
Sperm whales use sequences of clicks to communicate. Here, the authors show that these vocalizations are significantly more complex than previously believed-the “sperm whale phonetic alphabet" has both combinatorial structure and call modulation dependent on the conversational context.
- Pratyusha Sharma
- , Shane Gero
- & Jacob Andreas
-
Article
| Open Access Hot Cordilleran hinterland promoted lower crust mobility and decoupling of Laramide deformation
Hot Cordilleran hinterland promoted lower crust mobility and decoupling of Laramide deformation
Researchers test geodynamic models for far-field continental deformation during the Laramide orogeny. New and existing thermal data show that the hot hinterland crust promoted lower crust mobility and crust-mantle decoupling during flat-slab traction.
- Dominik R. Vlaha
- , Andrew V. Zuza
- & Matthieu Harlaux
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of emissions caps on the costs and feasibility of low-carbon hydrogen in the European ammonia industry
Effects of emissions caps on the costs and feasibility of low-carbon hydrogen in the European ammonia industry
Decarbonizing the European ammonia industry: Less stringent emissions caps for electrolytic hydrogen production can significantly reduce costs and land use while still achieving more than 90% reduction in emissions relative to fossil-based hydrogen.
- Stefano Mingolla
- , Paolo Gabrielli
- & Zhongming Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Recent collisional history of (65803) Didymos
Recent collisional history of (65803) Didymos
The fast-spinning primary of the Didymos near-earth asteroid binary system was found to have a degraded top shape by the DART (NASA) mission. Here, authors find that these surface features observed in the asteroid are more likely to have been caused by collisional effects than by the YORP effect.
- Adriano Campo Bagatin
- , Aldo Dell’Oro
- & Jean-Baptiste Vincent
-
Article
| Open Access Globally occurring pelagiphage infections create ribosome-deprived cells
Globally occurring pelagiphage infections create ribosome-deprived cells
SAR11 bacteria and their phages are abundant in the oceans. Here the authors quantify the number of phage-infected SAR11 cells using microscopy techniques and discover phage-infected cells without any detectable ribosomes. They hypothesize that ribosomal RNA may be used for the synthesis of phage genomes.
- Jan D. Brüwer
- , Chandni Sidhu
- & Bernhard M. Fuchs
-
Article
| Open Access The environmental sustainability of digital content consumption
The environmental sustainability of digital content consumption
The average Internet user spends over 40% of their waking hours online, yet the environmental footprint remains poorly understood. This study suggests that digital content consumption could exacerbate the pressure on the finite Earth’s carrying capacity.
- Robert Istrate
- , Victor Tulus
- & Gonzalo Guillén-Gosálbez
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution impact-based early warning system for riverine flooding
High-resolution impact-based early warning system for riverine flooding
A hindcast experiment of the 2021 summer flood in West Germany unveils a 17-hour lead time for preparedness and advisable action, holding promise for impact-based forecasting of inundated roads, railways and building footprint in real-time.
- Husain Najafi
- , Pallav Kumar Shrestha
- & Luis Samaniego
-
Article
| Open Access Timing the evolution of phosphorus-cycling enzymes through geological time using phylogenomics
Timing the evolution of phosphorus-cycling enzymes through geological time using phylogenomics
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient which may have influenced Earth’s early biosphere. This study interrogates genomic records, finding potentially phosphate depleted conditions toward the end of the Archean when enzymes for scavenging reduced phosphorus compounds spread throughout the tree of life.
- Joanne S. Boden
- , Juntao Zhong
- & Eva E. Stüeken

 Establishing flood thresholds for sea level rise impact communication
Establishing flood thresholds for sea level rise impact communication