Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of growing carbon nanotube interfaces probed by machine learning-enabled molecular simulations
Dynamics of growing carbon nanotube interfaces probed by machine learning-enabled molecular simulations
There is a lack of atomic level insight on the role of defects on carbon nanotubes' growth. Here, authors present a machine learning force field to drive near-microsecond simulations the entire growth process of this material, unveiling mechanisms of defect formation and healing.
- Daniel Hedman
- , Ben McLean
- & Feng Ding
-
Article
| Open Access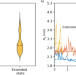 Tertiary structure and conformational dynamics of the anti-amyloidogenic chaperone DNAJB6b at atomistic resolution
Tertiary structure and conformational dynamics of the anti-amyloidogenic chaperone DNAJB6b at atomistic resolution
Adupa et al show how the anti-amyloidogenic molecular chaperone DNAJB6 adopts three conformational states that determine the accessibility of its substrate binding domain. In all states, interactions with HSP70 are shielded, suggesting that functional interactions only may occur upon substrate binding.
- Vasista Adupa
- , Elizaveta Ustyantseva
- & Patrick R. Onck
-
Article
| Open Access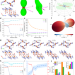 Unconventional mechanical and thermal behaviours of MOF CALF-20
Unconventional mechanical and thermal behaviours of MOF CALF-20
CALF-20 MOF is considered a benchmark sorbent for industrial scale CO2 capture. Here authors use machine-learning potential simulations to show that CALF-20 exhibits anomalous structural responses to temperature and strain stimuli, with potential applications in mechanical/thermal sensing.
- Dong Fan
- , Supriyo Naskar
- & Guillaume Maurin
-
Article
| Open Access Layer-by-layer phase transformation in Ti3O5 revealed by machine-learning molecular dynamics simulations
Layer-by-layer phase transformation in Ti3O5 revealed by machine-learning molecular dynamics simulations
Reconstructive phase transitions in materials are usually slow due to large activation energy barriers. Here, the authors show a kinetically favorable layer-by-layer mechanism in Ti3O5 transformations using machine-learning molecular dynamics simulations.
- Mingfeng Liu
- , Jiantao Wang
- & Xing-Qiu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insight into the initial hydration of tricalcium aluminate
Molecular insight into the initial hydration of tricalcium aluminate
The hydration of tricalcium aluminate is an important initial step in the structural build-up of Portland cement. Here the authors use ab initio and accelerated dynamics to describe the reactions and dynamics of this process at the molecular level.
- Xing Ming
- , Wen Si
- & Zongjin Li
-
Article
| Open Access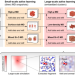 Modelling atomic and nanoscale structure in the silicon–oxygen system through active machine learning
Modelling atomic and nanoscale structure in the silicon–oxygen system through active machine learning
Understanding the silicon-oxygen system is crucial for various applications. Here, the authors present an interatomic potential covering a wide range of the Si-O configurational space and showcase applications to silica and Si-SiO2 interfaces.
- Linus C. Erhard
- , Jochen Rohrer
- & Volker L. Deringer
-
Article
| Open Access Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
Electrofreezing of liquid water at ambient conditions
By performing long ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of water under external electric fields, for up to 500 picoseconds, the authors identify a transition to a ferroelectric amorphous phase at ambient conditions.
- Giuseppe Cassone
- & Fausto Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access Amorphous alloys surpass E/10 strength limit at extreme strain rates
Amorphous alloys surpass E/10 strength limit at extreme strain rates
Magnitude of the ideal strength achievable in experiments for metals remains to be known. Here, the authors show that the spall strength of Cu50Zr50 amorphous alloy exceeds the E/10 limit at extreme strain rates, showing the void nucleation and growth as the primary failure mechanism.
- Wenqing Zhu
- , Zhi Li
- & Xiaoding Wei
-
Article
| Open Access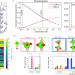 Ca-dimers, solvent layering, and dominant electrochemically active species in Ca(BH4)2 in THF
Ca-dimers, solvent layering, and dominant electrochemically active species in Ca(BH4)2 in THF
Alternatives to lithium-ion electrochemistry present challenges due to undesirable phenomena at the electrode-electrolyte interface. Through simulations, the authors find that the performance of a calcium-based electrolyte is driven entirely by molecular-scale processes within approximately 1 nm of the electrode.
- Ana Sanz Matias
- , Fabrice Roncoroni
- & David Prendergast
-
Article
| Open Access Ripples in the bottom of the potential energy landscape of metallic glass
Ripples in the bottom of the potential energy landscape of metallic glass
Little is known about how the states in glass are connected to each other. Here, the authors perform molecular dynamics simulation of relaxation in a prototypical metallic glass to show that the energy barriers separating these states are very low, and even be overcome by quantum fluctuations.
- Leo Zella
- , Jaeyun Moon
- & Takeshi Egami
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular understanding of the critical role of alkali metal cations in initiating CO2 electroreduction on Cu(100) surface
Molecular understanding of the critical role of alkali metal cations in initiating CO2 electroreduction on Cu(100) surface
Alkali metal cations affect CO2 electroreduction performance. Here, the authors provide a comprehensive molecular understanding of the alkali metal cation effects on both CO2 activation and competing hydrogen evolution based on explicit solvation models.
- Zhichao Zhang
- , Hengyu Li
- & Jia Li
-
Article
| Open Access Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Understanding the surface growth mechanism of carbon nanostructures would help designing better catalysts. Here, the authors combine active machine learning force fields with time-stamped Monte Carlo methods, to dynamically predict carbon growth on metal surfaces.
- Di Zhang
- , Peiyun Yi
- & Hao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic paddle-wheels in a solid-state electrolyte
Electronic paddle-wheels in a solid-state electrolyte
Conduction in solid-state electrolytes composed of monatomic ions is found to be analogous to the paddle-wheel mechanism in molecular solid electrolytes, facilitated by rotational motion of lone pair electrons, helping unify understanding of mechanisms.
- Harender S. Dhattarwal
- , Rahul Somni
- & Richard C. Remsing
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous temperature dependence of elastic limit in metallic glasses
Anomalous temperature dependence of elastic limit in metallic glasses
It is still challenging to study the atomistic mechanism of inelastic deformation in metallic glasses owing to their amorphous structure. Here, the authors report an anomalous temperature dependence of the onset of plasticity in metallic glasses at low temperature.
- Yifan Wang
- , Jing Liu
- & Wei Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments
Ultrafast spectroscopy enables characterization and control of non-equilibrium states. Here the authors introduce a stochastic thermodynamics approach to calculate entropy production in a material under ultrafast excitation, using ionic displacement data from time-resolved X-ray scattering experiments.
- Lorenzo Caprini
- , Hartmut Löwen
- & R. Matthias Geilhufe
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
The nucleation of calcium silicate hydrate is a crucial step in cement hydration, but is still a poorly understood process. Here the authors use atomistic simulations to study primary particles and their aggregation, revealing a potential C-S-H “basic building block”.
- Xabier M. Aretxabaleta
- , Jon López-Zorrilla
- & Hegoi Manzano
-
Article
| Open Access Self-activated superhydrophilic green ZnIn2S4 realizing solar-driven overall water splitting: close-to-unity stability for a full daytime
Self-activated superhydrophilic green ZnIn2S4 realizing solar-driven overall water splitting: close-to-unity stability for a full daytime
A superhydrophilic green hollow ZnIn2S4 was fabricated to realize unassisted photocatalytic overall water splitting. This work could provide an innovative aperture for efficient solar-driven green hydrogen production to achieve carbon neutrality.
- Wei-Kean Chong
- , Boon-Junn Ng
- & Siang-Piao Chai
-
Article
| Open Access Cation-induced changes in the inner- and outer-sphere mechanisms of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction
Cation-induced changes in the inner- and outer-sphere mechanisms of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction
The underlying mechanism of cation effects on CO2RR remains debated. Combining constrained density function theory, Marcus theory, and slow-growth sampling approaches, we resolve how cations modulate the inner- and outer-sphere pathways of CO2RR at solid-liquid interfaces.
- Xueping Qin
- , Heine A. Hansen
- & Marko M. Melander
-
Article
| Open Access What dictates soft clay-like lithium superionic conductor formation from rigid salts mixture
What dictates soft clay-like lithium superionic conductor formation from rigid salts mixture
Soft clay-like superionic conductors are integral for realising all-solid-state batteries. Here the authors provide fundamental insights into how a soft clay-like Li-superionic conductor, and soft clays in general can be created from a rigid-salts mixture.
- Sunny Gupta
- , Xiaochen Yang
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering the formation of spin-defects from first principles
Engineering the formation of spin-defects from first principles
Spin defects in semiconductors are promising for quantum technologies but understanding of defect formation processes in experiment remains incomplete. Here the authors present a computational protocol to study the formation of spin defects at the atomic scale and apply it to the divacancy defect in SiC.
- Cunzhi Zhang
- , Francois Gygi
- & Giulia Galli
-
Article
| Open Access Material symmetry recognition and property prediction accomplished by crystal capsule representation
Material symmetry recognition and property prediction accomplished by crystal capsule representation
Learning global crystal symmetry and interpreting equivariance are crucial for developing ML model to predict electronic properties. Here authors propose a symmetry-enhanced model to simulate cluster interactions and to predict materials properties.
- Chao Liang
- , Yilimiranmu Rouzhahong
- & Huashan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying disorder one atom at a time using an interpretable graph neural network paradigm
Quantifying disorder one atom at a time using an interpretable graph neural network paradigm
Level of atomic disorder in materials is critical to understanding the effect of local structure on materials properties. Here the authors present a workflow combining structure-aware graph neural networks and physics-inspired order parameter to characterize structural disorder on a per atom basis.
- James Chapman
- , Tim Hsu
- & Brandon C. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Realistic phase diagram of water from “first principles” data-driven quantum simulations
Realistic phase diagram of water from “first principles” data-driven quantum simulations
The molecular modelling of water has been a long sought-after goal in computational sciences for more than 50 years. Here, the authors show that the data-driven many-body MB-pol potential can provide a realistic representation of the phase diagram of water.
- Sigbjørn Løland Bore
- & Francesco Paesani
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-enabled exploration of the electrochemical stability of real-scale metallic nanoparticles
Machine learning-enabled exploration of the electrochemical stability of real-scale metallic nanoparticles
Surface Pourbaix diagrams are critical to understanding the stability of nanomaterials. Here, the authors develop a bond-type embedded crystal graph convolutional neural network model and construct reliable Pourbaix diagrams for real-scale nanoparticles.
- Kihoon Bang
- , Doosun Hong
- & Hyuck Mo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Lithium crystallization at solid interfaces
Lithium crystallization at solid interfaces
In solid-state lithium metal batteries, the crystallization of Li-ions deposited at interfaces remains unclear. Here, authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal lithium crystallization pathways and energy barriers, guiding improved interfacial engineering and accelerated crystal growth.
- Menghao Yang
- , Yunsheng Liu
- & Yifei Mo
-
Article
| Open Access Topology of vibrational modes predicts plastic events in glasses
Topology of vibrational modes predicts plastic events in glasses
It remains challenging to understand the relation between mechanical properties of glasses close to the yielding point and plastic behaviors at microscales. Wu et al. examine the plasticity using topological properties of the vibrational modes and identify a correlation between defects and plastic events.
- Zhen Wei Wu
- , Yixiao Chen
- & Limei Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven prediction of complex crystal structures of dense lithium
Data-driven prediction of complex crystal structures of dense lithium
Recent experiments reveal undetermined crystalline phases near the melting minimum region in lithium. Here, the authors use a crystal structure search method combined with machine learning to explore the energy landscape of lithium and predict complex crystal structures.
- Xiaoyang Wang
- , Zhenyu Wang
- & Yanming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic binding sites in a metal-organic framework for the optical sensing of nitrogen dioxide
Synergistic binding sites in a metal-organic framework for the optical sensing of nitrogen dioxide
Luminescent metal-organic frameworks are an emerging class of optical sensors capable to capture and detect toxic gases. Here, the authors report the incorporation of synergistic binding sites in MOF-808 through post-synthetic modification with copper for optical sensing of NO2 at remarkably low concentrations.
- Isabel del Castillo-Velilla
- , Ahmad Sousaraei
- & Ana E. Platero-Prats
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic signatures of Lorentzian dynamics and charge fluctuations in lithiated graphite structures
Electronic signatures of Lorentzian dynamics and charge fluctuations in lithiated graphite structures
Lithium graphite intercalation compounds are important for developing Li-ion batteries. Here authors simulate the interaction of high energy X-rays with Li ions intercalated in graphite and show that Li ions behave in an unexpected non-Gaussian fashion, leading to increasingly chaotic behaviour as the ion concentration reduces.
- Sasawat Jamnuch
- & Tod A. Pascal
-
Article
| Open Access Magnesium oxide-water compounds at megabar pressure and implications on planetary interiors
Magnesium oxide-water compounds at megabar pressure and implications on planetary interiors
Magnesium Oxide and water are abundant in the interior of planets. Here, the authors predict three new MgO-H2O compounds: Mg2O3H2, MgO3H4 and MgO4H6, and they exhibit superionic behavior in planetary interior conditions.
- Shuning Pan
- , Tianheng Huang
- & Jian Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Learning local equivariant representations for large-scale atomistic dynamics
Learning local equivariant representations for large-scale atomistic dynamics
The paper presents a method that allows scaling machine learning interatomic potentials to extremely large systems, while at the same time retaining the remarkable accuracy and learning efficiency of deep equivariant models. This is obtained with an E(3)- equivariant neural network architecture that combines the high accuracy of equivariant neural networks with the scalability of local methods.
- Albert Musaelian
- , Simon Batzner
- & Boris Kozinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical insights into the Peierls plasticity in SrTiO3 ceramics via dislocation remodelling
Theoretical insights into the Peierls plasticity in SrTiO3 ceramics via dislocation remodelling
Many ceramics and semiconductors are brittle at moderate temperatures, which can be a concern for applications. Here authors present a theoretical approach based on local misfit energy to accurately derive the Peierls stress and model the dislocation process in SrTiO3, which provides insights into the plasticity around room temperature.
- Yi Li
- , Xiangyang Liu
- & Chunlei Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor
Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor
Improving the efficiency of light-driven molecular rotary motors is a challenging task. Here, the authors combine theoretical modeling, synthesis and spectroscopy to prepare a prototype molecular motor capable of avoiding inefficient thermally activated motion; thus offering prospects to implement a 2-stroke photon-only molecular motor.
- Michael Filatov(Gulak)
- , Marco Paolino
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article
| Open Access An unconstrained approach to systematic structural and energetic screening of materials interfaces
An unconstrained approach to systematic structural and energetic screening of materials interfaces
Predicting structures and stabilities of solid-solid interfaces presents an ongoing and increasingly important challenge for development of new technologies. Here authors report an unconstrained and generally applicable non-periodic screening method for systematic exploration of material´s interfaces.
- Giovanni Di Liberto
- , Ángel Morales-García
- & Stefan T. Bromley
-
Article
| Open Access Vacancy driven surface disorder catalyzes anisotropic evaporation of ZnO (0001) polar surface
Vacancy driven surface disorder catalyzes anisotropic evaporation of ZnO (0001) polar surface
Evaporation and crystal growth occur at different rates on different surfaces. Here authors show dissociative evaporation from ZnO (0001) polar surfaces is accelerated by the formation of a Zn-deficient quasi-liquid layer derived from the formation and inward diffusion of Zn vacancies that stabilize the polar surface.
- Zhen Wang
- , Jinho Byun
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
The effect of aliovalent doping on grain boundary is not yet fully understood at the atomic level. Here, the authors report grain boundary structural transformation in α-Al2O3 is induced by co-segregation of multiple dopants using atomic-resolution electron microscopy and theoretical calculations.
- Toshihiro Futazuka
- , Ryo Ishikawa
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Transition metal migration and O2 formation underpin voltage hysteresis in oxygen-redox disordered rocksalt cathodes
Transition metal migration and O2 formation underpin voltage hysteresis in oxygen-redox disordered rocksalt cathodes
The oxygen-redox mechanism in lithium-rich disordered rocksalt cathode materials is still not well understood. Here, the authors show that in Li2MnO2F, molecular oxygen forms in the bulk during charge and is re-incorporated into the structure as oxygen anions on discharge, but this process is associated with irreversible Mn migration, causing voltage hysteresis.
- Kit McColl
- , Robert A. House
- & M. Saiful Islam
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental investigations on the sodium-ion transport properties of mixed polyanion solid-state battery electrolytes
Fundamental investigations on the sodium-ion transport properties of mixed polyanion solid-state battery electrolytes
Battery solid-state electrolytes rely on mixed polyanion networks to attain high ionic conductivities. Here, the authors investigate the effect of polyanion mixing on the solid-state electrolyte ion conductivity via theoretical calculations and electrochemical measurements.
- Zeyu Deng
- , Tara P. Mishra
- & Pieremanuele Canepa
-
Article
| Open Access BIGDML—Towards accurate quantum machine learning force fields for materials
BIGDML—Towards accurate quantum machine learning force fields for materials
Most machine-learning force fields dismiss long-range interactions. Here the authors demonstrate the BIGDML approach for building materials’ potential energy surfaces that enables a broad range of materials simulations within accuracies better than 1 meV/atom using just 10–200 structures for training.
- Huziel E. Sauceda
- , Luis E. Gálvez-González
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the failure of two-dimensional silica glasses
Predicting the failure of two-dimensional silica glasses
The sheer number of parameters in deep learning makes the physical interpretation of failure predictions in glasses challenging. Here the authors use Grad-CAM to reveal the role of topological defects and local potential energies in failure predictions.
- Francesc Font-Clos
- , Marco Zanchi
- & Stefano Zapperi
-
Article
| Open Access E(3)-equivariant graph neural networks for data-efficient and accurate interatomic potentials
E(3)-equivariant graph neural networks for data-efficient and accurate interatomic potentials
An E(3)-equivariant deep learning interatomic potential is introduced for accelerating molecular dynamics simulations. The method obtains state-of-the-art accuracy, can faithfully describe dynamics of complex systems with remarkable sample efficiency.
- Simon Batzner
- , Albert Musaelian
- & Boris Kozinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Argyrodite-type advanced lithium conductors and transport mechanisms beyond paddle-wheel effect
Argyrodite-type advanced lithium conductors and transport mechanisms beyond paddle-wheel effect
Fundamental mechanisms governing the superionic behaviour in solid-state Li-ion batteries are under debate. Here the authors investigate computationally the mechanism of superionic lithium-ion conduction and predict new advanced lithium superionic conductors.
- Hong Fang
- & Puru Jena
-
Article
| Open Access Hypervalency in amorphous chalcogenides
Hypervalency in amorphous chalcogenides
The current study explores by ab-initio molecular dynamics simuations the concept of hypervalency in amorphous chalcogenide materials, from which a unified conceptual framework for understanding chemical bonding, microscopic structures, and structure-property relationships is established.
- T. H. Lee
- & S. R. Elliott
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast visualization of incipient plasticity in dynamically compressed matter
Ultrafast visualization of incipient plasticity in dynamically compressed matter
Understanding incipient plasticity has been experimentally limited by spatial and temporal resolution. Here the authors report ultra-fast, in situ electron diffraction measurement of dislocation defect dynamics in the early stage of plastic deformation in Al under laser-driven compression.
- Mianzhen Mo
- , Minxue Tang
- & Siegfried Glenzer
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of twelve-fold iodine coordination at high pressure
Formation of twelve-fold iodine coordination at high pressure
High pressure can modify the chemical properties of the elements, giving rise to exotic bonding. Here the authors report the prediction of a nitrogen-rich iodine nitride compound IN6 where the iodine atom has an unusual twelve-fold coordination, stable above 100 GPa.
- Yan Liu
- , Rui Wang
- & Tian Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial-intelligence-driven discovery of catalyst genes with application to CO2 activation on semiconductor oxides
Artificial-intelligence-driven discovery of catalyst genes with application to CO2 activation on semiconductor oxides
Here the authors demonstrate an artificial-intelligence based approach to identify catalytic materials features that correlate with mechanisms that trigger, facilitate, or hinder CO2 catalytic reactions.
- Aliaksei Mazheika
- , Yang-Gang Wang
- & Matthias Scheffler
-
Article
| Open Access Learning in continuous action space for developing high dimensional potential energy models
Learning in continuous action space for developing high dimensional potential energy models
Reinforcement learning algorithms are emerging as powerful machine learning approaches. This paper introduces a novel machine-learning approach for learning in continuous action space and applies this strategy to the generation of high dimensional potential models for a wide variety of materials.
- Sukriti Manna
- , Troy D. Loeffler
- & Subramanian K. R. S. Sankaranarayanan
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization and validation of twin nucleation and early-stage growth in magnesium
Visualization and validation of twin nucleation and early-stage growth in magnesium
The origins of deformation twins in Mg have remained unclear in the past. Here the authors, by combining in situ experimental observations and atomistic simulations, capture the rapid twinning phenomena in Mg crystals and show that twinning occurs through pure atomic shuffle.
- Lin Jiang
- , Mingyu Gong
- & Julie M. Schoenung
-
Article
| Open Access In-plane quasi-single-domain BaTiO3 via interfacial symmetry engineering
In-plane quasi-single-domain BaTiO3 via interfacial symmetry engineering
In-plane polarized ferroelectric thin films typically exhibit complicated multidomain states, not desirable for optoelectronic device performance. Here, the authors combine interfacial symmetry engineering and anisotropic strain to design single-domain in-plane polarized ferroelectric BaTiO3 films.
- J. W. Lee
- , K. Eom
- & C. B. Eom

 A reactive neural network framework for water-loaded acidic zeolites
A reactive neural network framework for water-loaded acidic zeolites