Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access RecG and UvsW catalyse robust DNA rewinding critical for stalled DNA replication fork rescue
RecG and UvsW catalyse robust DNA rewinding critical for stalled DNA replication fork rescue
The helicases UvsW and RecG have both unwinding and rewinding activities and are involved in the rescue of stalled DNA replication forks. Here Manosas et al. use single-molecule techniques to characterize the rewinding activities of the two helicases, concluding that rewinding is actively catalysed.
- Maria Manosas
- , Senthil K. Perumal
- & Vincent Croquette
-
Article |
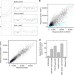 An acetylome peptide microarray reveals specificities and deacetylation substrates for all human sirtuin isoforms
An acetylome peptide microarray reveals specificities and deacetylation substrates for all human sirtuin isoforms
Protein deacetylases of the sirtuin family have important roles in aging and metabolism. Using peptide microarrays displaying physiological lysine acetylation sites, the authors map the substrate preferences of all seven human sirtuin isoforms, revealing enzyme specificities and identifying new sirtuin substrates.
- David Rauh
- , Frank Fischer
- & Clemens Steegborn
-
Article |
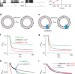 Ca2+-dependent phospholipid scrambling by a reconstituted TMEM16 ion channel
Ca2+-dependent phospholipid scrambling by a reconstituted TMEM16 ion channel
TMEM16-channel family members have been shown to be involved in Ca2+-dependent lipid scrambling, but whether they have intrinsic scramblase activity remains controversial. Malvezzi et al. identify a TMEM16 family member in Aspergillus in which a single Ca2+-binding site regulates intrinsic channel and scramblase activities.
- Mattia Malvezzi
- , Madhavan Chalat
- & Alessio Accardi
-
Article |
 Dynamic optimization identifies optimal programmes for pathway regulation in prokaryotes
Dynamic optimization identifies optimal programmes for pathway regulation in prokaryotes
The ability to induce metabolic pathways in response to a changing environment is an important component of bacterial fitness. Bartl et al. identify optimal programmes for metabolic pathway activation depending on protein synthesis capacity constraints, and demonstrate their impact on operonic organization.
- Martin Bartl
- , Martin Kötzing
- & Christoph Kaleta
-
Article
| Open Access p53 increases MHC class I expression by upregulating the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1
p53 increases MHC class I expression by upregulating the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1
The protein p53 is an important tumour suppressor. Here Wanget al.show that p53 can induce expression of MHC class I on the cell surface by promoting expression of the aminopeptidase ERAP1, and that this mechanism operates in cancer cells as well as those infected with influenza virus.
- Bei Wang
- , Dandan Niu
- & Ee Chee Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Complement anaphylatoxin C3a is a potent inducer of embryonic chick retina regeneration
Complement anaphylatoxin C3a is a potent inducer of embryonic chick retina regeneration
Components of the complement system have been shown to promote liver regeneration. Haynes et al. demonstrate that the complement fragment C3a can induce regeneration of the embryonic chick retina from stem and progenitor cells of the ciliary margin via activation of STAT3 and other downstream signalling pathways.
- Tracy Haynes
- , Agustin Luz-Madrigal
- & Katia Del Rio-Tsonis
-
Article |
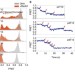 Srs2 prevents Rad51 filament formation by repetitive motion on DNA
Srs2 prevents Rad51 filament formation by repetitive motion on DNA
Srs2 is a DNA helicase and single-stranded DNA translocase that prevents homologous recombination by dismantling Rad51 filaments. Qiu et al.use single-molecule techniques to describe Rad51 filament formation and show that Srs2 displays repetitive activity on single-stranded DNA, which prevents re-formation of Rad51 filaments after dismantling.
- Yupeng Qiu
- , Edwin Antony
- & Sua Myong
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of poly(ADP-ribose) bound to PARG reveals inherent balance between exo- and endo-glycohydrolase activities
Visualization of poly(ADP-ribose) bound to PARG reveals inherent balance between exo- and endo-glycohydrolase activities
Poly-ADP-ribosylation is a post-translational modification that is countered by poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolases (PARGs). In this study, the authors present the crystal structure of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARGs) in complex with a poly(ADP-ribose) substrate, and reveal that poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARGs) enzymes act predominantly as exo- rather than as endo-glycohydrolases.
- Eva Barkauskaite
- , Amy Brassington
- & David Leys
-
Article
| Open Access Endonuclease V cleaves at inosines in RNA
Endonuclease V cleaves at inosines in RNA
Bacterial endonuclease V enzymes are characterized as DNA repair proteins. Here the authors show that human endonuclease V is an inosine-specific ribonuclease, indicating a role for this enzyme in normal RNA metabolism rather than DNA repair.
- Erik Sebastian Vik
- , Meh Sameen Nawaz
- & Ingrun Alseth
-
Article
| Open Access Human endonuclease V is a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA
Human endonuclease V is a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA
In Escherichia coli, the highly conserved enzyme endonuclease V has a role in DNA repair. Here the authors show that human endonuclease V is an inosine 3' endoribonuclease and that Tudor Staphylococcal nuclease enhances this activity, suggesting a role for human endonuclease V in RNA metabolism.
- Yoko Morita
- , Toshihiro Shibutani
- & Isao Kuraoka
-
Article |
 PPARγ-induced PARylation promotes local DNA demethylation by production of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
PPARγ-induced PARylation promotes local DNA demethylation by production of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
Tet proteins control DNA demethylation, but how the DNA target regions are determined is unclear. Here the authors report that during adipocyte differentiation, PPARγ binds to the PPAR-response element and recruits Tet proteins, thereby inducing local DNA demethylation.
- Katsunori Fujiki
- , Akihiro Shinoda
- & Masayuki Murata
-
Article |
 Alzheimer’s disease mutations in APP but not γ-secretase modulators affect epsilon-cleavage-dependent AICD production
Alzheimer’s disease mutations in APP but not γ-secretase modulators affect epsilon-cleavage-dependent AICD production
Clinical trials of γ-secretase inhibitors to treat Alzheimer’s disease show that side effects occur from their non-selective action. Dimitrov et al.show that improved second generation γ-secretase modulators spare cleavage sites of substrate proteins that are implicated in the side effects.
- Mitko Dimitrov
- , Jean-René Alattia
- & Patrick C. Fraering
-
Article |
 Tertiary structural elements determine the extent and specificity of messenger RNA editing
Tertiary structural elements determine the extent and specificity of messenger RNA editing
A central, imperfect duplex RNA secondary structure is generally required for site-specific adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing by ADAR enzymes. Rieder et al. show in Drosophila that conserved and complex long-range RNA tertiary structures form in vivoand can also regulate specific RNA-editing events by ADAR enzymes.
- Leila E. Rieder
- , Cynthia J. Staber
- & Robert A. Reenan
-
Article |
 Involvement of Bag6 and the TRC pathway in proteasome assembly
Involvement of Bag6 and the TRC pathway in proteasome assembly
The 26S proteasome comprises over 33 different subunits that must be correctly assembled by dedicated chaperones for efficient protein degradation. Here the authors find that general chaperone proteins are also vital for proper proteasome assembly.
- Takashi Akahane
- , Kazutaka Sahara
- & Shigeo Murata
-
Article |
 Reductive glutamine metabolism is a function of the α-ketoglutarate to citrate ratio in cells
Reductive glutamine metabolism is a function of the α-ketoglutarate to citrate ratio in cells
Reductive glutamine metabolism supports cell proliferation under stress conditions such as hypoxia. Here Fendtet al.report that the ratio between the two metabolites α-ketoglutarate and citrate determines whether glutamine is metabolized oxidatively or reductively.
- Sarah-Maria Fendt
- , Eric L. Bell
- & Gregory Stephanopoulos
-
Article |
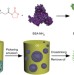 Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Proteins are ideal building blocks for self-assembly of artificial cell-like architectures, but their realization is rare. Huang et al.report an interfacial assembly of protein–polymer conjugates, which exhibit cellular properties such as encapsulating guest molecules and switching enzyme activity.
- Xin Huang
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
 Measurement of acetylation turnover at distinct lysines in human histones identifies long-lived acetylation sites
Measurement of acetylation turnover at distinct lysines in human histones identifies long-lived acetylation sites
Dynamic changes in histone acetylation are associated with regulation of gene expression. Zheng and colleagues develop a metabolic labelling technique that facilitates the measurement of acetylation turnover rates, and identify a group of sites whose acetylation is remarkably stable.
- Yupeng Zheng
- , Paul M. Thomas
- & Neil L. Kelleher
-
Article
| Open Access Retinoic acid receptor alpha is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
Retinoic acid receptor alpha is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
Many patients with breast cancer develop resistance to the drug tamoxifen and relapse. Here Johansson et al. identify the nuclear receptor retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) as a marker of tamoxifen resistance and show that RARA expression correlates negatively with relapse-free survival of patients.
- Henrik J. Johansson
- , Betzabe C. Sanchez
- & Janne Lehtiö
-
Article |
 Genome-scale proteome quantification by DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry
Genome-scale proteome quantification by DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry
The complexity and dynamic range of mammalian proteomes has stymied comprehensive protein quantification for the past twenty years. Zhou et al. develop DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry and use it to quantify a murine stem cell proteome to a depth equivalent to RNA-seq-based ribosome profiling.
- Feng Zhou
- , Yu Lu
- & Jarrod A. Marto
-
Article |
 DNA repair choice defines a common pathway for recruitment of chromatin regulators
DNA repair choice defines a common pathway for recruitment of chromatin regulators
Chromatin regulators facilitate repair of DNA double-strand breaks in chromosomal DNA. The authors show that the recruitment of such chromatin regulators to DNA lesions is controlled by the choice of DNA repair pathway.
- Gwendolyn Bennett
- , Manolis Papamichos-Chronakis
- & Craig L. Peterson
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical and genetic validation of thiamine utilization as an antimalarial drug target
Chemical and genetic validation of thiamine utilization as an antimalarial drug target
The malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum utilizes thiamine for the production of essential enzymatic cofactors. Chan et al. show that inhibition of thiamine utilization with oxythiamine inhibits proliferation of P. falciparumand reduces parasite growth in a mouse model of malaria infection.
- Xie Wah Audrey Chan
- , Carsten Wrenger
- & Kevin J. Saliba
-
Article
| Open Access The crystal structure of multidrug-resistance regulator RamR with multiple drugs
The crystal structure of multidrug-resistance regulator RamR with multiple drugs
RamR is an important multidrug-resistance factor, however, its structure and the molecules to which it responds are hitherto unknown. Here, the authors report the crystal structures of RamR complexed with multiple drugs, revealing significant flexibility in its substrate-recognition region.
- Suguru Yamasaki
- , Eiji Nikaido
- & Kunihiko Nishino
-
Article |
 Antagonism between binding site affinity and conformational dynamics tunes alternative cis-interactions within Shp2
Antagonism between binding site affinity and conformational dynamics tunes alternative cis-interactions within Shp2
Competition between inter- and intra-molecular interactions is a commonly observed property of modular signalling proteins. Here, the authors show that in the phosphatase Shp2, this balance is maintained by a trade-off between binding site affinities and conformational stability.
- Jie Sun
- , Shaoying Lu
- & Yingxiao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and function of Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase reveals aspects of RING and HECT ligases
Structure and function of Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase reveals aspects of RING and HECT ligases
The Parkinson’s disease-associated protein Parkin regulates the fate of damaged mitochondria by ubiquitinating mitochondrial substrates. Riley et al. present the crystal structure of the Parkin-R0RBR domain, providing new insight into the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme.
- B.E. Riley
- , J.C. Lougheed
- & J.A. Johnston
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular explanation for the recessive nature of parkin-linked Parkinson’s disease
A molecular explanation for the recessive nature of parkin-linked Parkinson’s disease
Mutations in the E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin are associated with juvenile Parkinson’s disease. Here the authors report the solution structure of the Parkin RING2 domain, revealing how disease-associated mutations affect its function and providing a molecular explanation for the recessive nature of the disease.
- Donald E. Spratt
- , R Julio Martinez-Torres
- & Gary S. Shaw
-
Article |
 Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice
Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) regulates energy metabolism in peripheral tissues. Here Planavila and colleagues show that FGF21 also acts directly on cardiomyocytes, thereby protecting mice against cardiac hypertrophy.
- A. Planavila
- , I. Redondo
- & F. Villarroya
-
Article |
 Identification and optimization of small-molecule agonists of the human relaxin hormone receptor RXFP1
Identification and optimization of small-molecule agonists of the human relaxin hormone receptor RXFP1
The peptide hormone relaxin has potential in the treatment of acute heart failure, but it must be intravenously injected and has a short half-life after administration. Now, small-molecule alternatives to relaxin are reported with similar efficacies to the natural hormone in functional assays.
- Jingbo Xiao
- , Zaohua Huang
- & Juan J. Marugan
-
Article
| Open Access Cyclic electron flow is redox-controlled but independent of state transition
Cyclic electron flow is redox-controlled but independent of state transition
The switch from linear to cyclic electron flow has long been thought to rely on the migration of antenna proteins from Photosystem II to Photosystem I. Takahashi et al. report that this is not the case and that cyclic electron flow is tuned by the intrachloroplastic redox power.
- Hiroko Takahashi
- , Sophie Clowez
- & Fabrice Rappaport
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative cross-linking and mass spectrometry of an intact F-type ATPase suggest a role for phosphorylation
Comparative cross-linking and mass spectrometry of an intact F-type ATPase suggest a role for phosphorylation
Rotary ATPases are membrane-embedded motors that produce or consume ATP and control pH within cells. Schmidt et al.use mass spectrometry to characterize the intact chloroplast ATPase from spinach and, using comparative cross-linking, show that phosphorylation affects stability and nucleotide occupancy.
- Carla Schmidt
- , Min Zhou
- & Carol V. Robinson
-
Article |
 An essential role for the N-terminal fragment of Toll-like receptor 9 in DNA sensing
An essential role for the N-terminal fragment of Toll-like receptor 9 in DNA sensing
Toll-like receptor 9 detects microbial DNA, and is activated by cleavage in the endolysosome. Onji et al. discover that following cleavage, the two parts of the protein remain associated, and this interaction is required for DNA sensing.
- Masahiro Onji
- , Atsuo Kanno
- & Kensuke Miyake
-
Article |
 NMR structure of human restriction factor APOBEC3A reveals substrate binding and enzyme specificity
NMR structure of human restriction factor APOBEC3A reveals substrate binding and enzyme specificity
The cytidine deaminase APOBEC3A has potent antiviral activity, degrading foreign DNA, and inhibiting viral replication, retrotransposition and reverse transcription. Byeon et al. present the solution structure of APOBEC3A, and reveal insights into its substrate specificity.
- In-Ja L. Byeon
- , Jinwoo Ahn
- & Angela M. Gronenborn
-
Article
| Open Access The pore of voltage-gated potassium ion channels is strained when closed
The pore of voltage-gated potassium ion channels is strained when closed
Voltage-gated potassium channels open and close in response to changes in transmembrane potential, but their opening mechanism is poorly understood. Here, free energy molecular dynamics simulations show that strain accumulates as the pore closes, which subsequently drives opening.
- Philip W. Fowler
- & Mark S. P. Sansom
-
Article |
 A mutation in the receptor Methoprene-tolerant alters juvenile hormone response in insects and crustaceans
A mutation in the receptor Methoprene-tolerant alters juvenile hormone response in insects and crustaceans
Juvenile hormone (JH) is a key regulator of development both in insects and the crustacea Daphnia pulex and D. magna. Here, Miyakawa et al.investigate the evolutionary significance of a single amino-acid variation between crustacea and insects in the JH receptor gene, Methoprene-tolerant.
- Hitoshi Miyakawa
- , Kenji Toyota
- & Taisen Iguchi
-
Article |
 Coordinated activation of the Rac-GAP β2-chimaerin by an atypical proline-rich domain and diacylglycerol
Coordinated activation of the Rac-GAP β2-chimaerin by an atypical proline-rich domain and diacylglycerol
Chimaerins are small GTPase-activating proteins that regulate Rac signalling in response to diacylglycerol. Here the authors discover that activation of β2-chimaerin requires an additional stimulus, in the form of an atypical interaction with the adaptor protein Nck.
- Alvaro Gutierrez-Uzquiza
- , Francheska Colon-Gonzalez
- & Marcelo G. Kazanietz
-
Article |
 Characterization of salt-adapted secreted lignocellulolytic enzymes from the mangrove fungus Pestalotiopsis sp.
Characterization of salt-adapted secreted lignocellulolytic enzymes from the mangrove fungus Pestalotiopsis sp.
Fungi associated with the roots of mangroves are thought to turn-over significant quantities of organic matter including lignocellulose. Arfi et al. investigate the lignocellolytic potential of a fungal species isolated from mangrove roots and the adaptation of its enzymatic repertoire to a high salinity environment.
- Yonathan Arfi
- , Didier Chevret
- & Eric Record
-
Article |
 Ultraviolet-B-mediated induction of protein–protein interactions in mammalian cells
Ultraviolet-B-mediated induction of protein–protein interactions in mammalian cells
Light-sensitive proteins are useful tools to control protein localization and gene expression, but are currently limited to excitation with red or blue light. Here Crefcoeur et al. present a novel optogenetic system to induce protein–protein interactions with ultraviolet-B light that does not require exogenous chromophores.
- Remco P. Crefcoeur
- , Ruohe Yin
- & Thanos D. Halazonetis
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid internal contraction boosts DNA friction
Rapid internal contraction boosts DNA friction
Single-molecule force spectroscopy provides useful quantitative information about the properties of macromolecules. Otto and colleagues non-invasively inspect the tension dynamics in a taut strand of DNA, thereby extending the use of single-molecule force spectroscopy to the study of macromolecular dynamics.
- Oliver Otto
- , Sebastian Sturm
- & Klaus Kroy
-
Article |
 G-quadruplex structures are stable and detectable in human genomic DNA
G-quadruplex structures are stable and detectable in human genomic DNA
Guanine-rich DNA can form four-stranded structures called G-quadruplexes, which are thought to influence DNA replication, transcription and repair; their stability and prevalence in the genome is in need of further elucidation. Here the authors employ an antibody-based approach to sensitively map G-quadruplexes in the genome.
- Enid Yi Ni Lam
- , Dario Beraldi
- & Shankar Balasubramanian
-
Article
| Open Access A novel mechanism for fine-tuning open-state stability in a voltage-gated potassium channel
A novel mechanism for fine-tuning open-state stability in a voltage-gated potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels cycle between closed and open states through poorly-defined transitions. Pless and colleagues incorporate artificial amino acids into Shaker potassium channels and find that that the negative electrostatic surface potential of Phe481, destabilizes the channel open state.
- Stephan A. Pless
- , Ana P. Niciforovic
- & Christopher A. Ahern
-
Article |
 Ribosomal protein S1 functions as a termination factor in RNA synthesis by Qβ phage replicase
Ribosomal protein S1 functions as a termination factor in RNA synthesis by Qβ phage replicase
Protein S1, a subunit of the Qß phage RNA-directed RNA polymerase, was thought to only initiate copying of the phage RNA plus strand. Here, the authors show that S1 stimulates replication of any cognate template by promoting release of the newly synthesized product strand.
- Nikita N. Vasilyev
- , Zarina S. Kutlubaeva
- & Alexander B. Chetverin
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand binding and aggregation of pathogenic SOD1
Ligand binding and aggregation of pathogenic SOD1
Mutations of the SOD1gene are implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Wright and colleagues find that SOD1 aggregation in cells is arrested by compounds that bind at the core of SOD1 aggregates, rather than at the dimer interface site.
- Gareth S.A. Wright
- , Svetlana V. Antonyuk
- & S Samar Hasnain
-
Article
| Open Access The four-transmembrane protein IP39 of Euglena forms strands by a trimeric unit repeat
The four-transmembrane protein IP39 of Euglena forms strands by a trimeric unit repeat
IP39 is an abundant protozoan protein known to form highly-ordered striations in Euglena gracilis’ plasma membrane. Here, Suzuki et al. determine its three-dimensional structure by electron crystallography revealing that IP39 polymerises to form trimeric longitudinal units arranged in a molecular strand of antiparallel double-rows.
- Hiroshi Suzuki
- , Yasuyuki Ito
- & Sachiko Tsukita
-
Article |
 Dynamin−SNARE interactions control trans-SNARE formation in intracellular membrane fusion
Dynamin−SNARE interactions control trans-SNARE formation in intracellular membrane fusion
Dynamin promotes membrane fission by constricting the neck of invaginating membranes; however, it was recently shown that dynamin also regulates membrane fusion. Here the authors show that this fusogenic activity is mediated by interaction with the Qa SNARE, thereby promoting trans-SNARE formation.
- Kannan Alpadi
- , Aditya Kulkarni
- & Christopher Peters
-
Article |
 Structural basis for potentiation by alcohols and anaesthetics in a ligand-gated ion channel
Structural basis for potentiation by alcohols and anaesthetics in a ligand-gated ion channel
Alcohols and anaesthetics exert their effects by potentiating ligand-gated ion channels. Here, the authors determine crystal structures of a bacterial ligand-gated ion channel in the presence of alcohols and anaesthetics, and describe a structural mechanism for stabilization of the open form of the channel.
- Ludovic Sauguet
- , Rebecca J. Howard
- & Marc Delarue
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of protein phosphatase 2A stable latency
Structural basis of protein phosphatase 2A stable latency
The protein α4 is essential for the formation, stability and activity of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) complexes. Here the authors solve the crystal structure of a truncated PP2A bound to α4 and show that α4 binds to a partially folded form of the protein, stabilizing the enzyme in an inactive state.
- Li Jiang
- , Vitali Stanevich
- & Yongna Xing
-
Article |
 Dynamic switching of calmodulin interactions underlies Ca2+ regulation of CaV1.3 channels
Dynamic switching of calmodulin interactions underlies Ca2+ regulation of CaV1.3 channels
Calmodulin regulation of Ca2+ channels is an important Ca2+-feedback system. The structural underpinnings of this modulation are unclear, but this study reports the molecular states underlying channel regulation.
- Manu Ben Johny
- , Philemon S. Yang
- & David T. Yue
-
Article |
 Energetics of activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome
Energetics of activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome
Ribosomal protein synthesis is driven by the hydrolysis of GTP. Wallin and colleagues employ molecular dynamics and computer simulations to show that a universally conserved histidine promotes GTP hydrolysis in its protonated form, and is driven into the active conformation by interactions with the ribosome.
- Göran Wallin
- , Shina C. L. Kamerlin
- & Johan Åqvist
-
Article
| Open Access Association between Gαi2 and ELMO1/Dock180 connects chemokine signalling with Rac activation and metastasis
Association between Gαi2 and ELMO1/Dock180 connects chemokine signalling with Rac activation and metastasis
Chemokines promote breast cancer metastasis by stimulating re-organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Li et al. identify the human engulfment and cell motility protein ELMO1 as an intermediary between chemokine-dependent Gαi2 signalling and small GTPase signalling mediated by Rac.
- Hongyan Li
- , Lei Yang
- & Ning Zhang
-
Article |
 A new protein complex promoting the assembly of Rad51 filaments
A new protein complex promoting the assembly of Rad51 filaments
RecA/Rad51 proteins catalyse the recognition and exchange between two homologous DNA strands during homologous recombination. Sasanuma et al. now demonstrate that Rad51 association with ssDNA is mediated by a complex consisting of Psy3, Csm2, Shu1 and Shu2 proteins.
- Hiroyuki Sasanuma
- , Maki S. Tawaramoto
- & Akira Shinohara
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biogeochemistry
- Bioinorganic chemistry
- Biophysical chemistry
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical modification
- Cytokines
- DNA
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Histocytochemistry
- Hormones
- Immunochemistry
- Ion channels
- Isoenzymes
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Neurochemistry
- Peptides
- Prions
- Proteases
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Structural biology

 Amyloid-β nanotubes are associated with prion protein-dependent synaptotoxicity
Amyloid-β nanotubes are associated with prion protein-dependent synaptotoxicity