Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A nanopore machine promotes the vectorial transport of DNA across membranes
A nanopore machine promotes the vectorial transport of DNA across membranes
Transport of DNA molecules across lipid membranes requires protein conduits such as the nuclear pore complex. Franceschiniet al.engineer an artificial sequence-selective DNA transporter by attaching gating oligonucleotides to a bacterial nanopore.
- Lorenzo Franceschini
- , Misha Soskine
- & Giovanni Maglia
-
Article |
 High-resolution three-dimensional mapping of mRNA export through the nuclear pore
High-resolution three-dimensional mapping of mRNA export through the nuclear pore
Messenger RNAs and their associated proteins are transported from the nucleus through highly selective nuclear pore complexes. Using ultrahigh resolution single-molecule imaging, the authors visualise the path taken by each messenger RNA as it negotiates the pore’s selectivity filter.
- Jiong Ma
- , Zhen Liu
- & Weidong Yang
-
Article |
 Ca2+-dependent phospholipid scrambling by a reconstituted TMEM16 ion channel
Ca2+-dependent phospholipid scrambling by a reconstituted TMEM16 ion channel
TMEM16-channel family members have been shown to be involved in Ca2+-dependent lipid scrambling, but whether they have intrinsic scramblase activity remains controversial. Malvezzi et al. identify a TMEM16 family member in Aspergillus in which a single Ca2+-binding site regulates intrinsic channel and scramblase activities.
- Mattia Malvezzi
- , Madhavan Chalat
- & Alessio Accardi
-
Article |
 Srs2 prevents Rad51 filament formation by repetitive motion on DNA
Srs2 prevents Rad51 filament formation by repetitive motion on DNA
Srs2 is a DNA helicase and single-stranded DNA translocase that prevents homologous recombination by dismantling Rad51 filaments. Qiu et al.use single-molecule techniques to describe Rad51 filament formation and show that Srs2 displays repetitive activity on single-stranded DNA, which prevents re-formation of Rad51 filaments after dismantling.
- Yupeng Qiu
- , Edwin Antony
- & Sua Myong
-
Article |
 The unusual dynamics of parasite actin result from isodesmic polymerization
The unusual dynamics of parasite actin result from isodesmic polymerization
Actin normally polymerizes into filaments in a cooperative manner, with nucleation and elongation phases. Skillman et al. show that actin from the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondiipolymerizes in an isodesmic manner, without any evidence of nucleation, resulting in filaments that are very short and unstable.
- Kristen M. Skillman
- , Christopher I. Ma
- & L. David Sibley
-
Article |
 Synthetic polyamines promote rapid lamellipodial growth by regulating actin dynamics
Synthetic polyamines promote rapid lamellipodial growth by regulating actin dynamics
While small molecules that destabilize actin filaments are readily available, artificially stimulating actin polymerization in cells typically involves genetic manipulation. Here, the authors design cell-permeable branched polyamines that promote lamellipodium formation by stimulating actin polymerization.
- Iliana Nedeva
- , Girish Koripelly
- & Daniel Riveline
-
Article |
 Turbulence drives microscale patches of motile phytoplankton
Turbulence drives microscale patches of motile phytoplankton
Patchiness in the distribution of phytoplankton promotes many of the ecological interactions that underpin the marine food web. This study shows that turbulence, ubiquitous in the ocean, counter-intuitively ‘unmixes’ a population of motile phytoplankton, generating intense, small-scale patchiness in its distribution.
- William M. Durham
- , Eric Climent
- & Roman Stocker
-
Article |
 Selectivity mechanism of the mechanosensitive channel MscS revealed by probing channel subconducting states
Selectivity mechanism of the mechanosensitive channel MscS revealed by probing channel subconducting states
The E. colimechanosensitive channel MscS responds to hypoosmotic swelling by opening a weakly anion-selective pore. Here, the authors report that the structural determinants of this selectivity are located not in the pore, but in the large water-filled cytoplasmic domain.
- C. D. Cox
- , T. Nomura
- & B. Martinac
-
Article |
 Far-red light photoactivatable near-infrared fluorescent proteins engineered from a bacterial phytochrome
Far-red light photoactivatable near-infrared fluorescent proteins engineered from a bacterial phytochrome
Near-infrared fluorescent proteins have applications in deep-tissue and whole-body imaging. Here, the authors report photoactivatable near-infrared proteins engineered from bacteria, with substantial contrast enhancement, which may be advantageous for in vivoimaging in high autofluorescence conditions.
- Kiryl D. Piatkevich
- , Fedor V. Subach
- & Vladislav V. Verkhusha
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational landscapes of DNA polymerase I and mutator derivatives establish fidelity checkpoints for nucleotide insertion
Conformational landscapes of DNA polymerase I and mutator derivatives establish fidelity checkpoints for nucleotide insertion
The fidelity of DNA polymerases depends on conformational changes that promote the rejection of incorrect nucleotides. Here, by using an intramolecular single-molecule FRET assay, the authors establish and characterize the partially closed conformation as a crucial fidelity checkpoint.
- Johannes Hohlbein
- , Louise Aigrain
- & Achillefs N. Kapanidis
-
Article
| Open Access The thermodynamic patterns of eukaryotic genes suggest a mechanism for intron–exon recognition
The thermodynamic patterns of eukaryotic genes suggest a mechanism for intron–exon recognition
The thermodynamics of unwinding polynucleotide duplexes can be determined from energy changes for DNA and mRNA interactions. Here the authors show that the ratio between mRNA/DNA and DNA/DNA duplex stability upstream of the 3′- spice sites is a characteristic that can contribute to intron–exon recognition.
- Marina N. Nedelcheva-Veleva
- , Mihail Sarov
- & Stoyno S. Stoynov
-
Article |
 Stimulated emission depletion-based raster image correlation spectroscopy reveals biomolecular dynamics in live cells
Stimulated emission depletion-based raster image correlation spectroscopy reveals biomolecular dynamics in live cells
RICS is a fluorescence imaging technique used to reveal fast molecular dynamics inside living cells and tissues. Hedde et al.combine RICS with super-resolution STED microscopy (STED-RICS) to achieve an enhanced multiplexing capability and to extend the range of usable fluorophore concentrations.
- Per Niklas Hedde
- , René M. Dörlich
- & G. Ulrich Nienhaus
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics and stoichiometry of a regulated enhancer-binding protein in live Escherichia coli cells
Dynamics and stoichiometry of a regulated enhancer-binding protein in live Escherichia coli cells
Cellular adaptive responses require temporal and spatial control of key regulatory protein complexes. Mehta et al. describe the dynamic interaction of a transcriptional activator mediating membrane stress response in E. coliwith its negative regulator, the cell membrane and the transcription machinery.
- Parul Mehta
- , Goran Jovanovic
- & Martin Buck
-
Article
| Open Access Cyclic electron flow is redox-controlled but independent of state transition
Cyclic electron flow is redox-controlled but independent of state transition
The switch from linear to cyclic electron flow has long been thought to rely on the migration of antenna proteins from Photosystem II to Photosystem I. Takahashi et al. report that this is not the case and that cyclic electron flow is tuned by the intrachloroplastic redox power.
- Hiroko Takahashi
- , Sophie Clowez
- & Fabrice Rappaport
-
Article |
 Dynamics of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine during mouse spermatogenesis
Dynamics of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine during mouse spermatogenesis
Changes in DNA methylation during mammalian spermatogenesis are poorly understood. The authors show that the content of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, a stable intermediate of DNA demethylation, changes dynamically during mouse spermatogenesis and is associated with functional genomic regions and transcription.
- Haiyun Gan
- , Lu Wen
- & Fuchou Tang
-
Article |
 Mechanistic and environmental control of the prevalence and lifetime of amyloid oligomers
Mechanistic and environmental control of the prevalence and lifetime of amyloid oligomers
Amyloid fibrils are implicated in a number of diseases but the origin of their length distributions is poorly understood. Here, evidence is presented to support a structural transition at a critical mass concentration, above which fragmentation of fibrils is suppressed.
- Ryan J. Morris
- , Kym Eden
- & Cait E. MacPhee
-
Article
| Open Access The pore of voltage-gated potassium ion channels is strained when closed
The pore of voltage-gated potassium ion channels is strained when closed
Voltage-gated potassium channels open and close in response to changes in transmembrane potential, but their opening mechanism is poorly understood. Here, free energy molecular dynamics simulations show that strain accumulates as the pore closes, which subsequently drives opening.
- Philip W. Fowler
- & Mark S. P. Sansom
-
Article |
 Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis linked to gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated PIEZO1 ion channels
Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis linked to gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated PIEZO1 ion channels
Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis is a genetic condition in which the permeability of red blood cells to cations in increased. Albuisson and colleagues find that mutations in the mechanically-activated PIEZO1 ion channel are the major cause of the disease and result in more slowly inactivating currents.
- Juliette Albuisson
- , Swetha E Murthy
- & Ardem Patapoutian
-
Article |
 Formin mDia1 senses and generates mechanical forces on actin filaments
Formin mDia1 senses and generates mechanical forces on actin filaments
Formins are a family of protein complexes that accelerate actin filament nucleation and elongation. Jegou et al.show that the formin mDia1 can generate mechanical tension in actin filaments, while conversely, pulling forces applied by viscous drag increase formin elongation activity.
- Antoine Jégou
- , Marie-France Carlier
- & Guillaume Romet-Lemonne
-
Article |
 Transcription factor binding kinetics constrain noise suppression via negative feedback
Transcription factor binding kinetics constrain noise suppression via negative feedback
Live cell imaging have recently revealed that transcription factors spend up to 4 min to find and bind their chromosomal binding site. Grönlund et al. show that this slow search process leads to tradeoffs between strength and speed of negative autoregulation for effective noise suppression.
- Andreas Grönlund
- , Per Lötstedt
- & Johan Elf
-
Article
| Open Access ALKBH4-dependent demethylation of actin regulates actomyosin dynamics
ALKBH4-dependent demethylation of actin regulates actomyosin dynamics
The division of a single eukaryotic cell into two requires actomyosin-dependent contraction. Here the authors show that lysine methylation of actin inhibits contractility during cytokinesis by blocking its association with myosin, and this modification is reversed at the contractile ring by the demethylase ALKBH4.
- Ming-Ming Li
- , Anja Nilsen
- & Yun-Gui Yang
-
Article |
 Active cochlear amplification is dependent on supporting cell gap junctions
Active cochlear amplification is dependent on supporting cell gap junctions
Outer hair cell electromotility contributes to the cochlear amplifier during hearing. Here the authors find that targeted-deletion of the gap junction protein connexin 26 results in reduced electromotility of outer hair cells, reduced cochlear amplification and hearing loss in mice.
- Yan Zhu
- , Chun Liang
- & Hong-Bo Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid internal contraction boosts DNA friction
Rapid internal contraction boosts DNA friction
Single-molecule force spectroscopy provides useful quantitative information about the properties of macromolecules. Otto and colleagues non-invasively inspect the tension dynamics in a taut strand of DNA, thereby extending the use of single-molecule force spectroscopy to the study of macromolecular dynamics.
- Oliver Otto
- , Sebastian Sturm
- & Klaus Kroy
-
Article
| Open Access A novel mechanism for fine-tuning open-state stability in a voltage-gated potassium channel
A novel mechanism for fine-tuning open-state stability in a voltage-gated potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels cycle between closed and open states through poorly-defined transitions. Pless and colleagues incorporate artificial amino acids into Shaker potassium channels and find that that the negative electrostatic surface potential of Phe481, destabilizes the channel open state.
- Stephan A. Pless
- , Ana P. Niciforovic
- & Christopher A. Ahern
-
Article
| Open Access AtALMT9 is a malate-activated vacuolar chloride channel required for stomatal opening in Arabidopsis
AtALMT9 is a malate-activated vacuolar chloride channel required for stomatal opening in Arabidopsis
Aluminium-activated malate transporters are exclusive to plants, regulating the transport of ions across the membranes on which they are expressed. De Angeli and colleagues show that AtALMT9 acts as a vacuolar chloride channel that is activated by cytosolic malate, and that this regulates stomata aperture.
- Alexis De Angeli
- , Jingbo Zhang
- & Enrico Martinoia
-
Article
| Open Access Auto-production of biosurfactants reverses the coffee ring effect in a bacterial system
Auto-production of biosurfactants reverses the coffee ring effect in a bacterial system
The coffee ring effect is commonly observed in drying droplets containing suspended matter leading to a deposition at the droplet edge. Sempels et al. show that self-generated biosurfactants in living bacterial systems reverse the coffee ring effect and result in a homogeneous deposition.
- Wouter Sempels
- , Raf De Dier
- & Jan Vermant
-
Article
| Open Access The four-transmembrane protein IP39 of Euglena forms strands by a trimeric unit repeat
The four-transmembrane protein IP39 of Euglena forms strands by a trimeric unit repeat
IP39 is an abundant protozoan protein known to form highly-ordered striations in Euglena gracilis’ plasma membrane. Here, Suzuki et al. determine its three-dimensional structure by electron crystallography revealing that IP39 polymerises to form trimeric longitudinal units arranged in a molecular strand of antiparallel double-rows.
- Hiroshi Suzuki
- , Yasuyuki Ito
- & Sachiko Tsukita
-
Article |
 The function of fin rays as proprioceptive sensors in fish
The function of fin rays as proprioceptive sensors in fish
Electrophysiological studies in some fish species suggest that proprioception is needed for fin movement. Here the authors test mechanosensory abilities of afferent nerves in pectoral fin rays, and find that the activity of fin ray nerve fibres reflects the amplitude and velocity of fin ray bending.
- Richard Williams IV
- , Nicole Neubarth
- & Melina E. Hale
-
Article |
 Structural basis for potentiation by alcohols and anaesthetics in a ligand-gated ion channel
Structural basis for potentiation by alcohols and anaesthetics in a ligand-gated ion channel
Alcohols and anaesthetics exert their effects by potentiating ligand-gated ion channels. Here, the authors determine crystal structures of a bacterial ligand-gated ion channel in the presence of alcohols and anaesthetics, and describe a structural mechanism for stabilization of the open form of the channel.
- Ludovic Sauguet
- , Rebecca J. Howard
- & Marc Delarue
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanics of mineralized collagen fibrils in bone
Molecular mechanics of mineralized collagen fibrils in bone
Bone is a natural composite of collagen and hydroxyapatite but, surprising, little is known about its characteristics at the molecular scale. Nair et al. conduct molecular-scale simulations of mineralized collagen networks to better understand how bone achieves superior mechanical properties to its constituents.
- Arun K. Nair
- , Alfonso Gautieri
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical unzipping and rezipping of a single SNARE complex reveals hysteresis as a force-generating mechanism
Mechanical unzipping and rezipping of a single SNARE complex reveals hysteresis as a force-generating mechanism
Interactions between (SNARE) proteins on vesicle and target membranes provide the force necessary to drive membrane fusion. By applying piconewton forces to single SNARE complexes, the authors identify a partially assembled intermediate state that reveals how force is generated in a consistent direction.
- Duyoung Min
- , Kipom Kim
- & Tae-Young Yoon
-
Article |
 Dynamic switching of calmodulin interactions underlies Ca2+ regulation of CaV1.3 channels
Dynamic switching of calmodulin interactions underlies Ca2+ regulation of CaV1.3 channels
Calmodulin regulation of Ca2+ channels is an important Ca2+-feedback system. The structural underpinnings of this modulation are unclear, but this study reports the molecular states underlying channel regulation.
- Manu Ben Johny
- , Philemon S. Yang
- & David T. Yue
-
Article |
 Energetics of activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome
Energetics of activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome
Ribosomal protein synthesis is driven by the hydrolysis of GTP. Wallin and colleagues employ molecular dynamics and computer simulations to show that a universally conserved histidine promotes GTP hydrolysis in its protonated form, and is driven into the active conformation by interactions with the ribosome.
- Göran Wallin
- , Shina C. L. Kamerlin
- & Johan Åqvist
-
Article |
 A light-driven sodium ion pump in marine bacteria
A light-driven sodium ion pump in marine bacteria
Light-driven proton-pumping rhodopsins are widely distributed in microorganisms and convert sunlight energy into proton gradients. Inoue et al. report the discovery of a light-driven sodium ion pump from marine bacteria.
- Keiichi Inoue
- , Hikaru Ono
- & Hideki Kandori
-
Article |
 Evidence for a material gradient in the adhesive tarsal setae of the ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata
Evidence for a material gradient in the adhesive tarsal setae of the ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata
Many insects cling to surfaces by means of specific bristles on the tips of their legs. Peisker et al. show that in the beetle Coccinella septempunctatathe composition and stiffness of these bristles vary dramatically along their length, likely allowing for a better grip to uneven surfaces.
- Henrik Peisker
- , Jan Michels
- & Stanislav N. Gorb
-
Article |
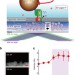 Biased Brownian stepping rotation of FoF1-ATP synthase driven by proton motive force
Biased Brownian stepping rotation of FoF1-ATP synthase driven by proton motive force
The visualization of ion-motive-force driven conformational dynamics of membrane proteins is hampered by technical difficulties. Here, the authors develop an experimental platform to visualize the rotary dynamics of ATP synthase driven by proton-motive-force.
- Rikiya Watanabe
- , Kazuhito V. Tabata
- & Hiroyuki Noji
-
Article |
 Probing transcription factor diffusion dynamics in the living mammalian embryo with photoactivatable fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Probing transcription factor diffusion dynamics in the living mammalian embryo with photoactivatable fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Transcription factor diffusion along DNA regulates many fundamental cellular and developmental processes. Kaur et al. combine photoactivation and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy to investigate transcription factor diffusion in mouse embryos and show that diffusion kinetics change during cell differentiation.
- Gurpreet Kaur
- , Mauro W. Costa
- & Nicolas Plachta
-
Article |
 CAND1 controls in vivo dynamics of the cullin 1-RING ubiquitin ligase repertoire
CAND1 controls in vivo dynamics of the cullin 1-RING ubiquitin ligase repertoire
Cullin 1-RING ubiquitin ligase complexes interact with a wide variety of substrates by recruiting different substrate receptor subunits. Here the authors demonstrate that CAND1 promotes rapid exchange of substrate receptors, thus ensuring comprehensive sampling of the entire repertoire.
- Shuangding Wu
- , Wenhong Zhu
- & Dieter A. Wolf
-
Article |
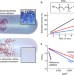 Impact of macromolecular crowding on DNA replication
Impact of macromolecular crowding on DNA replication
Macromolecular crowding significantly affects interactions between macromolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA. Akabayov and colleagues use a SAXS reconstitution assay to show that the effect of macromolecular crowding on T7 DNA replication causes structural changes of the replisome.
- Barak Akabayov
- , Sabine R. Akabayov
- & Charles C. Richardson
-
Article |
 Human haemodynamic frequency harmonics regulate the inflammatory phenotype of vascular endothelial cells
Human haemodynamic frequency harmonics regulate the inflammatory phenotype of vascular endothelial cells
Natural variations in blood flow haemodynamics are associated with localized inflammation and atherosclerosis. Here the authors show that individual harmonics present within this complex signal have distinct impacts on the inflammatory phenotype in endothelial cells.
- Ryan E. Feaver
- , Bradley D. Gelfand
- & Brett R. Blackman
-
Article |
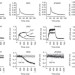 Enhanced dihydropyridine receptor calcium channel activity restores muscle strength in JP45/CASQ1 double knockout mice
Enhanced dihydropyridine receptor calcium channel activity restores muscle strength in JP45/CASQ1 double knockout mice
Calcium influx through the Cav1.1 channel initiates skeletal muscle contractions. Zorzato and colleagues report a role for the proteins JP45 and calsequestrin in strengthening skeletal muscle contraction by modulating Cav1.1 channel activity.
- Barbara Mosca
- , Osvaldo Delbono
- & Francesco Zorzato
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time single-molecule co-immunoprecipitation analyses reveal cancer-specific Ras signalling dynamics
Real-time single-molecule co-immunoprecipitation analyses reveal cancer-specific Ras signalling dynamics
Co-immunoprecipitation provides static and qualitative information about protein–protein interactions. Lee et al.create real-time movies of single protein–protein interactions during co-immunoprecipitation, and use them to assess the dynamics of mutant Ras proteins derived from tumours.
- Hong-Won Lee
- , Taeyoon Kyung
- & Tae-Young Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Disease mutations in the ryanodine receptor N-terminal region couple to a mobile intersubunit interface
Disease mutations in the ryanodine receptor N-terminal region couple to a mobile intersubunit interface
Ryanodine receptors are calcium-release channels located in the membrane of the sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum. Kimlicka et al.compare pseudo-atomic models of the N-terminal area in the open and closed states and characterize the mutations in the N-terminal that disrupt channel opening.
- Lynn Kimlicka
- , Kelvin Lau
- & Filip Van Petegem
-
Article |
 Mechanism of tetracycline resistance by ribosomal protection protein Tet(O)
Mechanism of tetracycline resistance by ribosomal protection protein Tet(O)
The bacterial tetracycline resistance protein Tet(O) binds to the ribosome, preventing tetracycline from inhibiting translation. Using cryo-electron microscopic reconstruction, the authors present an atomic model of Tet(O) bound to the 70S ribosome, and reveal how Tet(O) promotes antibiotic resistance.
- Wen Li
- , Gemma C. Atkinson
- & Joachim Frank
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between myosin IIA-mediated contractility and actin network integrity orchestrates podosome composition and oscillations
Interplay between myosin IIA-mediated contractility and actin network integrity orchestrates podosome composition and oscillations
Dendritic cells use protrusive structures called podosomes to probe the extracellular environment. Here the authors reveal how interplay between actin-mediated core growth and myosin-mediated tension regulates podosome protrusion.
- K. van den Dries
- , M.B.M Meddens
- & A. Cambi
-
Article |
 Non-uniform membrane diffusion enables steady-state cell polarization via vesicular trafficking
Non-uniform membrane diffusion enables steady-state cell polarization via vesicular trafficking
The mechanism by which proteins become polarized to a specific cortical site in budding yeast cells has been a topic of recent debate. Slaughter et al.show that differing diffusion rates of Cdc42 within plasma membrane environments sustain the polarized state.
- Brian D. Slaughter
- , Jay R. Unruh
- & Rong Li
-
Article |
 Evolution of the protein stoichiometry in the L12 stalk of bacterial and organellar ribosomes
Evolution of the protein stoichiometry in the L12 stalk of bacterial and organellar ribosomes
The ribosomal stalk L12 is the only multi-copy protein in the ribosome and is essential for translation. Here Davydov et al.use a bioinformatics and mass spectrometry approach to study the evolution of L12 in bacterial ribosomes and predict its stoichiometry in a wide range of species.
- Iakov I. Davydov
- , Ingo Wohlgemuth
- & Marina V. Rodnina
-
Article
| Open Access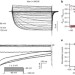 Multiple pore conformations driven by asynchronous movements of voltage sensors in a eukaryotic sodium channel
Multiple pore conformations driven by asynchronous movements of voltage sensors in a eukaryotic sodium channel
In outwardly rectifying potassium channels, depolarization initiates conformational changes in voltage-sensing domains. Goldschen-Ohmet al. find that movement of three specific domains correlates with conductance levels, and rearrangements of a fourth domain results in preinactivation subconductance states.
- Marcel P. Goldschen-Ohm
- , Deborah L. Capes
- & Baron Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into protein-only RNase P complexed with tRNA
Structural insights into protein-only RNase P complexed with tRNA
RNase P is a key enzyme implicated in transfer RNA maturation that removes the 5′-leader sequences from transfer RNA precursors. In this study, a biophysical characterization of a novel protein-only variant of RNase P, known as PRORP (PROteinaceous RNase P), reveals that transfer RNA recognition by PRORP is similar to that by ribonucleoprotein RNase P.
- Anthony Gobert
- , Franziska Pinker
- & Philippe Giegé

 Role of the C-terminal domain in the structure and function of tetrameric sodium channels
Role of the C-terminal domain in the structure and function of tetrameric sodium channels