Featured
-
-
Article |
 Mutual adaptation of a membrane protein and its lipid bilayer during conformational changes
Mutual adaptation of a membrane protein and its lipid bilayer during conformational changes
The detailed interactions of membrane proteins with their lipid environment are poorly understood. Sonntaget al. use low-resolution X-ray crystallographic data and molecular dynamics simulations to study the manner in which the sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca2+–ATPase adapts to different membrane environments.
- Yonathan Sonntag
- , Maria Musgaard
- & Lea Thøgersen
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional enzyme diffusion in laterally confined DNA monolayers
Two-dimensional enzyme diffusion in laterally confined DNA monolayers
Little is known about the effects of molecular crowding and confinement on biomolecule function. Castronovoet al. investigate the reactions of restriction enzymes with DNA confined in bushy matrices and find that the enzymes enter at the side of the matrix before diffusing two-dimensionally.
- Matteo Castronovo
- , Agnese Lucesoli
- & Giacinto Scoles
-
Article |
 Ligand-specific deactivation time course of GluN1/GluN2D NMDA receptors
Ligand-specific deactivation time course of GluN1/GluN2D NMDA receptors
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediate excitatory synaptic transmission, and those containing GluN2D subunits have an unusually long deactivation time. Vance et al. show that the conformational variability of the ligand-binding domain and the structure of the activating ligand influence deactivation time.
- Katie M. Vance
- , Noriko Simorowski
- & Hiro Furukawa
-
Article |
 Frequency-dependent recruitment of V2a interneurons during fictive locomotion in the mouse spinal cord
Frequency-dependent recruitment of V2a interneurons during fictive locomotion in the mouse spinal cord
The spinal V2a interneurons control left–right limb alternation during mouse locomotion, but only at high frequencies. In this study, the authors show that only half of these neurons are active during locomotion, and that they receive increasing synaptic drive to increase their activity as locomotion accelerates.
- Guisheng Zhong
- , Kamal Sharma
- & Ronald M. Harris-Warrick
-
Article
| Open Access Annexin-A5 assembled into two-dimensional arrays promotes cell membrane repair
Annexin-A5 assembled into two-dimensional arrays promotes cell membrane repair
Eukaryotic cell plasma membranes possess a mechanism to repair tears caused by stimuli such as mechanical stress. The authors demonstrate that annexin-A5, when assembled into two-dimensional arrays in the presence of calcium, is required for membrane repair.
- Anthony Bouter
- , Céline Gounou
- & Alain R. Brisson
-
Article
| Open Access The deubiquitinating enzyme USP17 is essential for GTPase subcellular localization and cell motility
The deubiquitinating enzyme USP17 is essential for GTPase subcellular localization and cell motility
Deubiquitinating enzymes are involved in multiple cellular processes, including cell viability. The authors reveal a role for the deubiquitinating enzyme, USP17, in the migration of cells in response to chemokines and show that USP17 is required for the relocalization of GTPases involved in cell motility.
- Michelle de la Vega
- , Alyson A. Kelvin
- & James A. Johnston
-
Article |
 Adhesive water networks facilitate binding of protein interfaces
Adhesive water networks facilitate binding of protein interfaces
The formation of hydrophilic protein–protein interactions cannot be explained by charge–charge interactions. Here, molecular simulations reveal that water forms an adhesive hydrogen-bonded network between proteins, stabilizing intermediate states before the bound complex forms.
- Mazen Ahmad
- , Wei Gu
- & Volkhard Helms
-
Article |
 A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
Single-molecule force spectroscopy is used to study single molecule interactions, but probing short-lived events is difficult. Here, a nanomechanical interface is developed, which allows the study of microsecond timescale interactions.
- Mingdong Dong
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access Lipid-dependent gating of a voltage-gated potassium channel
Lipid-dependent gating of a voltage-gated potassium channel
Lipid phosphodiesters affect the conformation of certain potassium channels, but the details of the lipid-channel interactions are unclear. Here, the KvAP channel is found to switch from an active to a resting state when the channels are transferred from a phospholipid membrane to a bilayer lacking phosphodiesters.
- Hui Zheng
- , Weiran Liu
- & Qiu-Xing Jiang
-
Article |
 A modern ionotropic glutamate receptor with a K+ selectivity signature sequence
A modern ionotropic glutamate receptor with a K+ selectivity signature sequence
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian nervous system. Here, a glutamate receptor is reported that has properties intermediate to those of bacterial and eukaryotic glutamate-gated ion channels, suggesting a link in the evolution of ionotropic glutamate receptors.
- H. Janovjak
- , G. Sandoz
- & E. Y. Isacoff
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis for selective binding of non-methylated CpG islands by the CFP1 CXXC domain
The structural basis for selective binding of non-methylated CpG islands by the CFP1 CXXC domain
CXXC domain proteins bind to CpG DNA sequences and influence chromatin modification. Xuet al.report crystal structures of the CXXC protein CFP1, a component of the SETD1 histone H3K4 methyl transferase complex, and study the molecular mechanisms of DNA-binding specificity.
- Chao Xu
- , Chuanbing Bian
- & Jinrong Min
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving stepping rotation in Thermus thermophilus H+-ATPase/synthase with an essentially drag-free probe
Resolving stepping rotation in Thermus thermophilus H+-ATPase/synthase with an essentially drag-free probe
Rotary ATPases FoF1 and VoV1 couple ATP hydrolysis with proton flow. Furuike et al. observe ATP-driven rotation in V1 and VoV1, at submillisecond resolution, and find that rate-limiting reactions in V1 all occur at the same angle, and stator–rotor interactions in Vointroduce additional checkpoints.
- Shou Furuike
- , Masahiro Nakano
- & Ken Yokoyama
-
Article |
 Measurement of cochlear power gain in the sensitive gerbil ear
Measurement of cochlear power gain in the sensitive gerbil ear
The cochlear amplifier in the inner ear is thought to mediate sensitivity to soft sounds, but this power gain has not been measured directly. Renet aluse an interferometer to measure the volume displacement and velocity of the cochlear partition and demonstrate experimentally that the cochlea amplifies soft sounds.
- Tianying Ren
- , Wenxuan He
- & Peter G. Gillespie
-
Article |
 An adaptive explanation for the horse-like shape of seahorses
An adaptive explanation for the horse-like shape of seahorses
Seahorses evolved from pipefish, which have a remarkably different body shape. Here, by examining seahorse feeding behaviour and using a mathematical model, Van Wassenberghet al. demonstrate that the head, neck and trunk posture of the seahorse allows for the effective capture of their prey.
- Sam Van Wassenbergh
- , Gert Roos
- & Lara Ferry
-
Article |
 A novel gene required for male fertility and functional CATSPER channel formation in spermatozoa
A novel gene required for male fertility and functional CATSPER channel formation in spermatozoa
The CATSPER heteromeric ion channel complex is required for male fertility and six protein components of the complex have been identified. In this study, the authors identify a seventh gene, CATSPERδ, which is necessary for functional CatSper channels and hyperactivated sperm motility.
- Jean-Ju Chung
- , Betsy Navarro
- & David E. Clapham
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational rearrangement of gastric H+,K+-ATPase induced by an acid suppressant
Conformational rearrangement of gastric H+,K+-ATPase induced by an acid suppressant
The gastric proton pump, H+,K+-ATPase, contributes to stomach acidification and is a target of acid suppressants. Here, the three-dimensional structure of the pump is determined using electron crystallography, providing the first structural information about the binding of a new class of acid suppressants.
- Kazuhiro Abe
- , Kazutoshi Tani
- & Yoshinori Fujiyoshi
-
Article
| Open Access Discrete plasticity in sub-10-nm-sized gold crystals
Discrete plasticity in sub-10-nm-sized gold crystals
Deformations in nanocrystals smaller than 10 nm are not well understood. The authors perform compression high-resolution transmission electron microscopy studies of gold nanoparticles, and determine that the nanoparticles deform through the emission of partial dislocations from free surfaces.
- He Zheng
- , Ajing Cao
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article |
 Cyclic hardening in bundled actin networks
Cyclic hardening in bundled actin networks
Materials such as rubber tend to soften when cyclically deformed. Here, however, the authors find that bundled actin networks can show cyclic hardening and retain a memory of the maximum strain they have been subjected to.
- K. M. Schmoller
- , P. Fernández
- & A. R. Bausch
-
Article
| Open Access Substrate docking to γ-secretase allows access of γ-secretase modulators to an allosteric site
Substrate docking to γ-secretase allows access of γ-secretase modulators to an allosteric site
γ-Secretase modulators have promise in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but their molecular target is uncertain. Here, fluorescence resonance energy transfer is used to determine that the γ-secretase allosteric site is within the γ-secretase complex and that substrate docking is required for modulators to access the site.
- Kengo Uemura
- , Katherine C. Farner
- & Oksana Berezovska
-
Article |
 Mechanism of signal transduction of the LOV2-Jα photosensor from Avena sativa
Mechanism of signal transduction of the LOV2-Jα photosensor from Avena sativa
Fusion proteins containing blue-light-activated domains have been used as molecular switches to investigate cell signalling, but molecular understanding of the transduction pathway is lacking. Here, MD simulations are used to elucidate the transduction mechanism in a light oxygen voltage2-Ja photosensor.
- Emanuel Peter
- , Bernhard Dick
- & Stephan A. Baeurle
-
Article |
 Overlap between folding and functional energy landscapes for adenylate kinase conformational change
Overlap between folding and functional energy landscapes for adenylate kinase conformational change
Enzyme function is often dependent on fluctuations between inactive and active states. Olsson and Wolf-Watz show that switching between the inactive and active states of adenylate kinase is associated with partial unfolding/refolding of the enzyme.
- Ulrika Olsson
- & Magnus Wolf-Watz
-
Article
| Open Access Drug export and allosteric coupling in a multidrug transporter revealed by molecular simulations
Drug export and allosteric coupling in a multidrug transporter revealed by molecular simulations
The drug transporter AcrB is a component of the tripartite efflux system AcrB–AcrA–TolC, which is important in multidrug-resistantEscherichia coli. Takada and co-workers used molecular simulations to further reveal the mechanism of drug export.
- Xin-Qiu Yao
- , Hiroo Kenzaki
- & Shoji Takada
-
Article
| Open Access Tectorial membrane travelling waves underlie abnormal hearing in Tectb mutant mice
Tectorial membrane travelling waves underlie abnormal hearing in Tectb mutant mice
Mutation of theTectbgene reduces auditory sensitivity but increases frequency selectivity. Here the authors show that Tectb mutation reduces both the spatial and temporal propagation of travelling waves along the tectorial membrane, explaining the unexpected auditory abnormalities in this mutant.
- Roozbeh Ghaffari
- , Alexander J. Aranyosi
- & Dennis M. Freeman
-
Article |
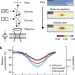 Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis
Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis
Protein interactions in biological environments are expected to differ from the situationin vitro. In this study, a thermophoresis-based technique is described that allows the analysis of protein and small-molecule interactions in biological liquids; the work may allow more efficient drug development.
- Christoph J. Wienken
- , Philipp Baaske
- & Stefan Duhr
-
Article
| Open Access Structural bases for the interaction of frataxin with the central components of iron–sulphur cluster assembly
Structural bases for the interaction of frataxin with the central components of iron–sulphur cluster assembly
Frataxin is an essential protein that has been linked to iron–sulphur cluster assembly, and reduced levels are associated with Friedrich's ataxia. In this study, a combination of techniques is used to probe the interactions of the bacterial frataxin orthologue CyaY with the iron–sulphur cluster assembly machinery.
- Filippo Prischi
- , Petr V. Konarev
- & Annalisa Pastore
-
Article |
 A single-vesicle content mixing assay for SNARE-mediated membrane fusion
A single-vesicle content mixing assay for SNARE-mediated membrane fusion
SNARE protein-mediated vesicle fusion is usually monitored by indirect lipid mixing. Diaoet al. have developed a FRET-based single-vesicle content mixing assay, which elucidates fusion pore formation, and shows that the yeast SNARE complex mediates pore expansion in the absence of accessory proteins.
- Jiajie Diao
- , Zengliu Su
- & Taekjip Ha
-
Article
| Open Access Pore-opening mechanism in trimeric P2X receptor channels
Pore-opening mechanism in trimeric P2X receptor channels
A recent X-ray structure revealed the closed state of a P2X receptor ion channel. Here, Li and colleagues probe the structural rearrangements that take place during channel opening by measuring the effects of covalent modification of engineered cysteines.
- Mufeng Li
- , Toshimitsu Kawate
- & Kenton J. Swartz
-
Article |
 PI(3,5)P2 controls membrane trafficking by direct activation of mucolipin Ca2+ release channels in the endolysosome
PI(3,5)P2 controls membrane trafficking by direct activation of mucolipin Ca2+ release channels in the endolysosome
Phosphoinositides activate intracellular ion channels to release Ca2+ from membrane-bound stores. This study demonstrates that Ca2+-permeable mucolipin TRP channels, TRPMLs, are activated by the phospholipid PI(3,5)P2in murine endolysosomes and yeast vacuoles.
- Xian-ping Dong
- , Dongbiao Shen
- & Haoxing Xu
-
Article |
 Peptidoglycan architecture can specify division planes in Staphylococcus aureus
Peptidoglycan architecture can specify division planes in Staphylococcus aureus
To ensure correct cell division Staphylococci must remember which plane they previously divided along, but the mechanism by which this is achieved is unclear. In this article, using atomic force microscopy, peptidoglycan ribs are reported to mark previous planes of division.
- Robert D. Turner
- , Emma C. Ratcliffe
- & Simon J. Foster
-
Article
| Open Access A doublecortin containing microtubule-associated protein is implicated in mechanotransduction in Drosophila sensory cilia
A doublecortin containing microtubule-associated protein is implicated in mechanotransduction in Drosophila sensory cilia
Mechanoreceptors are important for detecting external stimuli. In this study a putative receptor identified inDrosophilais shown to be potentially important for hearing and the amplification of mechanotransduction.
- S. Bechstedt
- , J.T. Albert
- & J. Howard

 Engineering biosynthetic excitable tissues from unexcitable cells for electrophysiological and cell therapy studies
Engineering biosynthetic excitable tissues from unexcitable cells for electrophysiological and cell therapy studies