Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access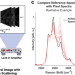 Multi-molecular hyperspectral PRM-SRS microscopy
Multi-molecular hyperspectral PRM-SRS microscopy
Spatial imaging methods in lipid research can disrupt tissue integrity and can have limited spatial and spectral resolution. Here, the authors present an SRS-based hyperspectral imaging platform to visualise lipids and lipoproteins in a variety of tissues and animal species.
- Wenxu Zhang
- , Yajuan Li
- & Lingyan Shi
-
Article
| Open Access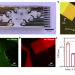 A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
Interfacing living systems with electronics for biosensing and biocomputing applications is challenging. Here, Gao et al. present hybrid transistors with electroactive bacteria capable of extracellular electron transfer, enabling transduction of biological computations to electrical readouts.
- Yang Gao
- , Yuchen Zhou
- & Benjamin K. Keitz
-
Article
| Open Access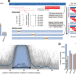 Efficient encoding of large antigenic spaces by epitope prioritization with Dolphyn
Efficient encoding of large antigenic spaces by epitope prioritization with Dolphyn
Profiling antibody responses to vast antigenic spaces has been challenging using programmable phage display (PhIP-Seq). Here, authors develop a methodology for compressing large proteomic spaces and have discovered human antibodies targeting gut bacteria-infecting phages.
- Anna-Maria Liebhoff
- , Thiagarajan Venkataraman
- & H. Benjamin Larman
-
Article
| Open Access Structural optimization of siRNA conjugates for albumin binding achieves effective MCL1-directed cancer therapy
Structural optimization of siRNA conjugates for albumin binding achieves effective MCL1-directed cancer therapy
Limited tumor cell delivery is a major challenge for the efficacious delivery of siRNAs to silence traditionally undruggable oncogenes. Here the authors optimize siRNAs for in situ binding to albumin through C18 lipid modifications and show the application of the lead conjugate structure for targeting MCL1 in orthotopic breast tumors in mice.
- Ella N. Hoogenboezem
- , Shrusti S. Patel
- & Craig L. Duvall
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
The assembly of oligopeptide and polypeptide molecules can reconstruct various ordered advanced structures. Here the authors develop a “molecular velcro”-inspired amphiphilic supramolecular co-assembly strategy, which improves the mechanical strength and cartilaginous regeneration efficiency through conformation transition.
- Chengkun Zhao
- , Xing Li
- & Yong Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Domain-inlaid Nme2Cas9 adenine base editors with improved activity and targeting scope
Domain-inlaid Nme2Cas9 adenine base editors with improved activity and targeting scope
Nme2Cas9 has been well established as a genome editing platform. Here the authors engineer Nme2Cas9 to further increase the activity and targeting scope of compact Nme2Cas9 base editors and validate domain-inlaid Nme2-ABEs for single-AAV delivery in vivo.
- Nathan Bamidele
- , Han Zhang
- & Erik J. Sontheimer
-
Article
| Open Access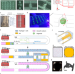 A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip
A microfluidic platform integrating functional vascularized organoids-on-chip
Vascularization remains a significant challenge in organoid technology. Here, the authors develop a microfluidic platform that enhances organoid growth, function and maturation, by establishing functional perfusable vascular networks.
- Clément Quintard
- , Emily Tubbs
- & Xavier Gidrol
-
Article
| Open Access A system for inducible mitochondria-specific protein degradation in vivo
A system for inducible mitochondria-specific protein degradation in vivo
Conditional degradation of proteins is instrumental to advance our knowledge of cell biology but has been lacking for organelles like mitochondria. Here, the authors develop a proteolysis system based on the mycoplasma Lon protease that functions selectively within mitochondria in yeast and human cells.
- Swastika Sanyal
- , Anna Kouznetsova
- & Camilla Björkegren
-
Article
| Open Access A genome and gene catalog of the aquatic microbiomes of the Tibetan Plateau
A genome and gene catalog of the aquatic microbiomes of the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau is the largest plateau in the world and hosts a variety of aquatic ecosystems. Here, the authors present a gene and genome catalogue of Tibetan Plateau aquatic microbiomes, greatly expanding known taxonomic and functional diversity for the region and giving insights into its microbial biogeography.
- Mingyue Cheng
- , Shuai Luo
- & Kang Ning
-
Comment
| Open Access Fudging the volcano-plot without dredging the data
Fudging the volcano-plot without dredging the data
Selecting omic biomarkers using both their effect size and their differential status significance (i.e., selecting the “volcano-plot outer spray”) has long been equally biologically relevant and statistically troublesome. However, recent proposals are paving the way to resolving this dilemma.
- Thomas Burger
-
Article
| Open Access Compact zinc finger architecture utilizing toxin-derived cytidine deaminases for highly efficient base editing in human cells
Compact zinc finger architecture utilizing toxin-derived cytidine deaminases for highly efficient base editing in human cells
The most recent class of base editors utilize DddAtox, a deaminase domain that can act upon double-stranded DNA. Here the authors target DddAtox fragments and a FokI-based nickase to the human CIITA gene by fusing these domains to arrays of engineered zinc fingers; they also identify a variety of DddAtox orthologues.
- Friedrich Fauser
- , Bhakti N. Kadam
- & Jeffrey C. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access TFvelo: gene regulation inspired RNA velocity estimation
TFvelo: gene regulation inspired RNA velocity estimation
Most RNA velocity models extract dynamics from the phase delay between unspliced and spliced mRNA for each gene. Here, authors propose TFvelo, broadening RNA velocity beyond splicing information to include gene regulation. TFvelo accurately models genes dynamics and infers cell pseudo-time from RNA abundance data.
- Jiachen Li
- , Xiaoyong Pan
- & Hong-Bin Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Biporous silica nanostructure-induced nanovortex in microfluidics for nucleic acid enrichment, isolation, and PCR-free detection
Biporous silica nanostructure-induced nanovortex in microfluidics for nucleic acid enrichment, isolation, and PCR-free detection
Efficient enrichment and isolation of pathogens are crucial for accurate and sensitive disease identification. Here, the authors present a chip equipped with biporous nanofilms that induces a nanovetex in a microfluidic channel for nucleic acid enrichment, isolation, and detection.
- Eunyoung Jeon
- , Bonhan Koo
- & Joonseok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Injectable pro-regenerative biomaterials are vital for developing minimally invasive regenerative treatment, but impeded by brittleness and lack of biological functions. Here the authors address these issues by engineering injectable functionalized composites that facilitate the sequential release of IL-4 and IGF-1 to regulate macrophages and stem cell behavior for enhanced in situ regeneration.
- Yi Li
- , Siyang Liu
- & Meifeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling early pathophysiological phenotypes of diabetic retinopathy in a human inner blood-retinal barrier-on-a-chip
Modeling early pathophysiological phenotypes of diabetic retinopathy in a human inner blood-retinal barrier-on-a-chip
Here the authors develop perfusable inner blood-retinal barrier-specific microvascular networks with human primary retinal microvascular cells. They show that chronic diabetic stimulation leads to the generation of early hallmarks of diabetic retinopathy, including pericyte and capillary dropout, ghost vessels, and inflammation.
- Thomas L. Maurissen
- , Alena J. Spielmann
- & Héloïse Ragelle
-
Article
| Open Access Operando investigation of the synergistic effect of electric field treatment and copper for bacteria inactivation
Operando investigation of the synergistic effect of electric field treatment and copper for bacteria inactivation
The overuse of chemicals in our disinfection processes has warranted the development of alternatives. Here, authors use a lab-on-a-chip device to study and observe the synergistic effects of electric field treatment and copper for inactivation of bacteria with promising applications in many fields.
- Mourin Jarin
- , Ting Wang
- & Xing Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Broad protection against clade 1 sarbecoviruses after a single immunization with cocktail spike-protein-nanoparticle vaccine
Broad protection against clade 1 sarbecoviruses after a single immunization with cocktail spike-protein-nanoparticle vaccine
Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 and emergence of other sarbecoviruses are of potential concern. Here, the authors designed a trivalent spike-protein-nanoparticle vaccine that elicits neutralizing antibodies and protects female hamsters against challenges with SARS-CoV-2-like and SARS-CoV-1-like coronaviruses.
- Peter J. Halfmann
- , Kathryn Loeffler
- & Ravi S. Kane
-
Article
| Open Access A 3D printable tissue adhesive
A 3D printable tissue adhesive
Tissue adhesives have received significant interest for their clinical utility but are typically incompatible with advanced manufacturing methods. Here, the authors introduce a 3D printable tissue adhesive for the fabrication of patches and devices for diverse biomedical applications.
- Sarah J. Wu
- , Jingjing Wu
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A method to estimate the contribution of rare coding variants to complex trait heritability
A method to estimate the contribution of rare coding variants to complex trait heritability
The contribution of rare variants to complex traits has not been well studied. Here, the authors present RARity, a method to assess rare variant heritability without assuming a particular genetic architecture and enabling both gene-level and exome-wide heritability estimation of continuous traits.
- Nazia Pathan
- , Wei Q. Deng
- & Guillaume Paré
-
Article
| Open Access Natural diversity screening, assay development, and characterization of nylon-6 enzymatic depolymerization
Natural diversity screening, assay development, and characterization of nylon-6 enzymatic depolymerization
Polyamides (PAs) or nylons are types of plastics with wide applications, but due to their accumulation in the environment, strategies for their deconstruction are of interest. Here, the authors screen 40 potential nylon-hydrolyzing enzymes (nylonases) using a mass spectrometry-based approach and identify a thermostabilized N-terminal nucleophile hydrolase as the most promising for further development, as well as crucial targets for progressing PA6 enzymatic depolymerization.
- Elizabeth L. Bell
- , Gloria Rosetto
- & Gregg T. Beckham
-
Article
| Open Access Micrometer-thick and porous nanocomposite coating for electrochemical sensors with exceptional antifouling and electroconducting properties
Micrometer-thick and porous nanocomposite coating for electrochemical sensors with exceptional antifouling and electroconducting properties
It is vital but challenging to develop coating technologies for addressing reliability and durability issues of electrochemical sensors when exposed to diverse and complex biological environments. Here, the authors report a micrometer-thick, porous and robust nanocomposite coating that enables highly sensitive and stable electrochemical sensors.
- Jeong-Chan Lee
- , Su Yeong Kim
- & Donald E. Ingber
-
Article
| Open Access Combinatorial optimization of gene expression through recombinase-mediated promoter and terminator shuffling in yeast
Combinatorial optimization of gene expression through recombinase-mediated promoter and terminator shuffling in yeast
Fine-tuning the expression of biosynthetic pathway genes is crucial to improve microbial production titres. Here, the authors present GEMbLeR, an optimization strategy to balance the expression of multiple genes simultaneously over a wide range.
- Charlotte Cautereels
- , Jolien Smets
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal LoxPsym sites allow multiplexed site-specific recombination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic hosts
Orthogonal LoxPsym sites allow multiplexed site-specific recombination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic hosts
Site-specific recombinases such as the Cre-LoxP system are routinely used for genome engineering in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Here the authors develop 63 symmetrical LoxP variants and test 1192 pairwise combinations to determine their cross-reactivity and specificity upon Cre activation.
- Charlotte Cautereels
- , Jolien Smets
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing back primed resistance in cancer via sister cells
Tracing back primed resistance in cancer via sister cells
Transcriptional cell states can drive treatment resistance in cancer. Here, the authors develop ReSisTrace to predict cell states that are primed to resist ovarian cancer treatment and validate their findings using small molecule inhibitors.
- Jun Dai
- , Shuyu Zheng
- & Anna Vähärautio
-
Article
| Open Access Antiviral fibrils of self-assembled peptides with tunable compositions
Antiviral fibrils of self-assembled peptides with tunable compositions
In this work, the authors report the use of a computationally and rationally designed self-assembling peptide that has robust antiviral capability with demonstrated specificity in binding to SARS-CoV-2 and inhibition of viral entry into human cells.
- Joseph Dodd-o
- , Abhishek Roy
- & Vivek Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access MAIVeSS: streamlined selection of antigenically matched, high-yield viruses for seasonal influenza vaccine production
MAIVeSS: streamlined selection of antigenically matched, high-yield viruses for seasonal influenza vaccine production
Vaccines combat global influenza threats, relying on timely selection of optimal seed viruses. Here, authors introduce MAIVeSS, a machine learning assisted framework to streamline vaccine seed virus selection using genomic sequence, expediting seasonal flu vaccine production and supply.
- Cheng Gao
- , Feng Wen
- & Xiu-Feng Wan
-
Article
| Open Access AAV-delivered muscone-induced transgene system for treating chronic diseases in mice via inhalation
AAV-delivered muscone-induced transgene system for treating chronic diseases in mice via inhalation
Long-term control of therapeutic transgene expression is needed. Here the authors report a muscone-induced transgene system packaged into AAVs based on a G protein-coupled murine olfactory receptor and a synthetic cAMP-responsive promoter: they show dose- and exposure-time-dependent gene expression control in mice.
- Xin Wu
- , Yuanhuan Yu
- & Haifeng Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of chemosensory tissues and cells across ecologically diverse Drosophilids
Evolution of chemosensory tissues and cells across ecologically diverse Drosophilids
Chemosensory tissues are remarkably variable between species but the cause of this diversity is unclear. Here, the authors conduct transcriptomic analyses of chemosensory tissues from diverse Drosophila species, revealing evidence of stabilizing selection and recent species- and sex-specific changes.
- Gwénaëlle Bontonou
- , Bastien Saint-Leandre
- & J. Roman Arguello
-
Article
| Open Access Orchestrating chromosome conformation capture analysis with Bioconductor
Orchestrating chromosome conformation capture analysis with Bioconductor
The Bioconductor project aims to develop R packages for analysis of genomic datasets. Here the authors show the HiCExperiment package suite and its companion online book (https://bioconductor.org/books/OHCA/) which present data structures, computational methods and visualization tools available in Bioconductor to investigate chromatin conformation capture (3C) data in R.
- Jacques Serizay
- , Cyril Matthey-Doret
- & Romain Koszul
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering stringent genetic biocontainment of yeast with a protein stability switch
Engineering stringent genetic biocontainment of yeast with a protein stability switch
Comprehensive safety measures are lacking to employ engineered microorganisms in open-environment applications. Here the authors introduce a genetically encoded biocontainment system for engineered microorganisms based on conditional protein stability.
- Stefan A. Hoffmann
- & Yizhi Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Descriptive data in biomedical research are expanding rapidly, but functional validation methods lag behind. Here, authors present Logical Synthetic cis-regulatory DNA, a framework to design reporters that mark cellular states and pathways, showcasing its applicability to complex phenotypic states.
- Carlos Company
- , Matthias Jürgen Schmitt
- & Gaetano Gargiulo
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically resilient hybrid aerogels containing fibers of dual-scale sizes and knotty networks for tissue regeneration
Mechanically resilient hybrid aerogels containing fibers of dual-scale sizes and knotty networks for tissue regeneration
Aerogels are suitable for soft tissue engineering, but often come with brittleness. Here the authors develop a hybrid aerogel with micro- and nanofiber networks that optimizes tensile moduli and fracture energies and show that these materials are super-elastic, fostering rapid tissue ingrowth and allowing minimally invasive procedures.
- S. M. Shatil Shahriar
- , Alec D. McCarthy
- & Jingwei Xie
-
Article
| Open Access The impacts of active and self-supervised learning on efficient annotation of single-cell expression data
The impacts of active and self-supervised learning on efficient annotation of single-cell expression data
Cell type annotation for single-cell data is challenging. Here, authors explore active and self-supervised learning and introduce adaptive reweighting as a tailored heuristic, demonstrating competitive performance and showing that incorporating prior knowledge enhances cell type annotation accuracy.
- Michael J. Geuenich
- , Dae-won Gong
- & Kieran R. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Micropillar arrays, wide window acquisition and AI-based data analysis improve comprehensiveness in multiple proteomic applications
Micropillar arrays, wide window acquisition and AI-based data analysis improve comprehensiveness in multiple proteomic applications
Obtaining a comprehensive proteomic profile for complex samples is still an elusive task. Here, the authors present an LC-MS/MS workflow including micropillar arrays, wide isolation windows and AI-based data analysis to boost proteomic coverage and throughput for multiple proteomic samples.
- Manuel Matzinger
- , Anna Schmücker
- & Rupert L. Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Systems engineering of Escherichia coli for high-level glutarate production from glucose
Systems engineering of Escherichia coli for high-level glutarate production from glucose
Glutarate is a platform chemical widely used in the production of polyesters and polyamindes. Here, the authors design the shortest and thermodynamically favorable pathway, and increase glutarate production from glucose through systematic engineering of E. coli.
- Zhilan Zhang
- , Ruyin Chu
- & Cong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning oxidant and antioxidant activities of ceria by anchoring copper single-site for antibacterial application
Tuning oxidant and antioxidant activities of ceria by anchoring copper single-site for antibacterial application
Nanozymes used for antibacterial therapy conventionally have complex catalytic activities that cause multiple pathways in parallel and unwanted outcome. Here, the authors report a Cu-CeO2 single site nanozyme in which Cu single site modification can enhance the peroxidase-like activity and inhibit the hydroxyl radical antioxidant capacity of CeO2 to optimise the antibacterial effects.
- Peng Jiang
- , Ludan Zhang
- & Yuguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A sequence-aware merger of genomic structural variations at population scale
A sequence-aware merger of genomic structural variations at population scale
Existing tools for structural variations (SVs) calling and merging often lead to fragmented SVs and the potential of introducing unnecessary errors. Here, the authors report the PanPop pipeline to address these issues by implementing sequence-aware SV merging algorithm to efficiently merge SVs of various types.
- Zeyu Zheng
- , Mingjia Zhu
- & Yongzhi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-CRISPR Anopheles mosquitoes inhibit gene drive spread under challenging behavioural conditions in large cages
Anti-CRISPR Anopheles mosquitoes inhibit gene drive spread under challenging behavioural conditions in large cages
CRISPR-based gene drives have the potential to spread within populations and are considered as promising vector control tools. Here the authors show an anti-drive mosquito strain that prevents the spread and collapse of a population suppression gene drive in laboratory Anopheles mosquito large cage trials in complex ecological and behavioral conditions.
- Rocco D’Amato
- , Chrysanthi Taxiarchi
- & Ruth Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed screening reveals how cancer-specific alternative polyadenylation shapes tumor growth in vivo
Multiplexed screening reveals how cancer-specific alternative polyadenylation shapes tumor growth in vivo
Dysregulation of alternative polyadenylation (APA) is associated with poor prognosis in cancer but its functional role is less clear. Here, the authors develop a CRISPR-Cas9- based screen to determine the effects of different APA events on melanoma growth in mouse models.
- Austin M. Gabel
- , Andrea E. Belleville
- & Robert K. Bradley
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial protoplast-derived nanovesicles carrying CRISPR-Cas9 tools re-educate tumor-associated macrophages for enhanced cancer immunotherapy
Bacterial protoplast-derived nanovesicles carrying CRISPR-Cas9 tools re-educate tumor-associated macrophages for enhanced cancer immunotherapy
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing systems have great potential in cancer therapy. Here the authors report a gene-editing delivery system using functionalized nanovesicles derived from E. coli protoplasts to encapsulate Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoprotein for the selective targeting of Pik3cg in tumor associated macrophages.
- Mingming Zhao
- , Xiaohui Cheng
- & Junfeng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access DeepFocus: fast focus and astigmatism correction for electron microscopy
DeepFocus: fast focus and astigmatism correction for electron microscopy
High-throughput electron microscopy demands minimal human intervention and high image quality. Here, authors introduce DeepFocus, a data-driven method for aberration correction in electron microscopy, robust for low SNR images, fast and easily adaptable to microscopes and samples. Peer Review Information: Nature Communications thanks Yang Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
- P. J. Schubert
- , R. Saxena
- & J. Kornfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Two way workable microchanneled hydrogel suture to diagnose, treat and monitor the infarcted heart
Myocardial infarction can lead to malignant arrhythmia and myocardial remodeling. Here, the authors report a microchanneled hydrogel suture for two-way signal communication, pumping drugs on demand, and cardiac repair.
- Fangchao Xue
- , Shanlan Zhao
- & Wen Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us
Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us
Using All of Us pilot data, the authors compared short- and long-read performance across medically relevant genes and showcased the utility of long reads to improve variant detection and phasing in easy and hard to resolve medically relevant genes.
- M. Mahmoud
- , Y. Huang
- & F. J. Sedlazeck
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear and cytoplasmic specific RNA binding proteome enrichment and its changes upon ferroptosis induction
Nuclear and cytoplasmic specific RNA binding proteome enrichment and its changes upon ferroptosis induction
The reported assay shows a subcellular-specific RNA labeling method for efficient enrichment and deep profiling of nuclear and cytoplasmic RBPs, the authors apply this to investigate changes of subcellular-specific RBP-RNA interactions in ferroptosis.
- Haofan Sun
- , Bin Fu
- & Weijie Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data
Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data
Batch effects hinder multi-sample single-cell data analyses. Here, authors present STACAS, a scalable single-cell RNA-seq data integration tool that uses prior cell type knowledge to preserve biological variability, demonstrating robustness to noisy input cell type labels.
- Massimo Andreatta
- , Léonard Hérault
- & Santiago J. Carmona
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic carbon–carbon bond cleavage in lignin via manganese–zirconium-mediated autoxidation
Catalytic carbon–carbon bond cleavage in lignin via manganese–zirconium-mediated autoxidation
Efforts to produce aromatic monomers through catalytic lignin depolymerization were focused on aryl–ether bond cleavage, while the carbon–carbon bonds of a large fraction of aromatic monomers in lignin are difficult to cleave. Here, the authors report a catalytic autoxidation method using manganese and zirconium salts as catalysts to cleave the C–C bonds in lignin-derived dimers and oligomers from pine and poplar.
- Chad T. Palumbo
- , Nina X. Gu
- & Gregg T. Beckham
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a transposon-associated TnpB-ωRNA system for efficient gene editing and phenotypic correction of a tyrosinaemia mouse model
Engineering a transposon-associated TnpB-ωRNA system for efficient gene editing and phenotypic correction of a tyrosinaemia mouse model
Miniature gene editing tools are highly desired for efficient in vivo delivery and disease treatment. Here, the authors reported engineering hypercompact TnpB-ωRNA for robust gene editing with minimal off-target effect in cultured cells and use it to rescue fatal genetic liver disease in a tyrosinaemia mouse model.
- Zhifang Li
- , Ruochen Guo
- & Chunlong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ-sprayed therapeutic hydrogel for oxygen-actuated Janus regulation of postsurgical tumor recurrence/metastasis and wound healing
In-situ-sprayed therapeutic hydrogel for oxygen-actuated Janus regulation of postsurgical tumor recurrence/metastasis and wound healing
Surgery is a primary therapeutic modality for treating melanoma, but it is challenging to tackle tumor recurrence/metastasis and postsurgical wounds. Here the authors report a sprayable hydrogel capable of long-lasting and controllable oxygen supply for preventing tumor recurrence/metastasis and simultaneously promoting wound healing during the postsurgical treatment of melanoma.
- Shuiling Chen
- , Yang Luo
- & Shaobing Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically-defined and scalable culture system for intestinal stem cells derived from human intestinal organoids
Chemically-defined and scalable culture system for intestinal stem cells derived from human intestinal organoids
Challenges in reproducibility and large-scale expansion limit the current applicability of human intestinal organoids. Here, the authors present a feeder-free, chemically-defined culture method for enrichment of intestinal stem cells isolated from 3D human intestinal organoids.
- Ohman Kwon
- , Hana Lee
- & Mi-Young Son
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 Orthogonal inducible control of Cas13 circuits enables programmable RNA regulation in mammalian cells
Orthogonal inducible control of Cas13 circuits enables programmable RNA regulation in mammalian cells