Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access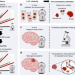 Non-invasive assessment of normal and impaired iron homeostasis in the brain
Non-invasive assessment of normal and impaired iron homeostasis in the brain
Assessment of different iron compounds in the living brain remains an open challenge. Here, the authors present a magnetic resonance imaging method which is sensitive to the iron homeostasis in the brain, and increases the detection of tumor tissue.
- Shir Filo
- , Rona Shaharabani
- & Aviv A. Mezer
-
Article
| Open Access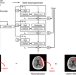 Emergency triage of brain computed tomography via anomaly detection with a deep generative model
Emergency triage of brain computed tomography via anomaly detection with a deep generative model
Triage is essential for the early diagnosis and reporting of emergency patients in the emergency department. Here, the authors develop an anomaly detection algorithm with a deep generative model that reprioritizes radiology worklists and provides lesion attention maps for brain CT images with critical findings.
- Seungjun Lee
- , Boryeong Jeong
- & Namkug Kim
-
Article
| Open Access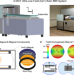 A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner
A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner
A low cost MRI scanner may have the potential to meet clinical needs at point of care or in low and middle income countries. Here the authors describe a low cost 0.055 Tesla MRI scanner that operates using a standard AC power outlet, and demonstrate its preliminary feasibility in diagnosing brain tumor and stroke.
- Yilong Liu
- , Alex T. L. Leong
- & Ed X. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Imaging the mouse brain using glass cranial windows has limitations in terms of flexibility and long-term imaging. Here the authors engineer transparent polymer skulls that can fit various skull morphologies and can be implanted for over 300 days, enabling simultaneous high resolution brain imaging and electrophysiology across large cortical areas.
- Leila Ghanbari
- , Russell E. Carter
- & Suhasa B. Kodandaramaiah
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying cerebral contributions to pain beyond nociception
Quantifying cerebral contributions to pain beyond nociception
Pain is affected by cerebral processes in addition to afferent nociceptive input. Here the authors develop an fMRI-based signature that predicts pain independent of the intensity of nociceptive signals and mediates the pain-modulating effects of several cognitive interventions.
- Choong-Wan Woo
- , Liane Schmidt
- & Tor D. Wager
-
Article
| Open Access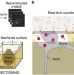 High-throughput dual-colour precision imaging for brain-wide connectome with cytoarchitectonic landmarks at the cellular level
High-throughput dual-colour precision imaging for brain-wide connectome with cytoarchitectonic landmarks at the cellular level
High-throughput imaging methods for brain-wide connectome mapping with precise location reference have been lacking. Here authors report a method that allows simultaneous acquisition of fluorescently labelled neurons and cytoarchitectural landmarks in the same mouse brain at the single-cell resolution.
- Hui Gong
- , Dongli Xu
- & Qingming Luo
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput automated home-cage mesoscopic functional imaging of mouse cortex
High-throughput automated home-cage mesoscopic functional imaging of mouse cortex
Functional imaging in awake head-fixed mice is a widely used technique to study neural responses. Here the authors report on an open source, fully automated unsupervised system for training mice to self initiate head fixation to enable stable mesoscopic functional imaging of cortical functional connectivity.
- Timothy H. Murphy
- , Jamie D. Boyd
- & Jeff M. LeDue
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-central nervous system functional imaging in larval Drosophila
Whole-central nervous system functional imaging in larval Drosophila
To understand how neuronal networks function, it is important to measure neuronal network activity at the systems level. Here Lemon et al. develop a framework that combines a high-speed multi-view light-sheet microscope, a whole-CNS imaging assay and computational tools to demonstrate simultaneous functional imaging across the entire isolated Drosophilalarval CNS.
- William C. Lemon
- , Stefan R. Pulver
- & Philipp J. Keller
-
Article
| Open Access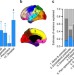 Large-scale genomics unveil polygenic architecture of human cortical surface area
Large-scale genomics unveil polygenic architecture of human cortical surface area
How genetic variation contributes to brain morphology is still poorly understood. Here Chenet al. combine brain imaging with single-nucleotide polymorphism data to discover that a substantial degree of cortical variation is derived from underlying genetic differences.
- Chi-Hua Chen
- , Qian Peng
- & Anders M. Dale
-
Article |
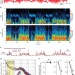 Mesoscale infraslow spontaneous membrane potential fluctuations recapitulate high-frequency activity cortical motifs
Mesoscale infraslow spontaneous membrane potential fluctuations recapitulate high-frequency activity cortical motifs
The brain exists in a state of constant activity but little is known about very low frequency forms of activity. Here, the authors use high-speed, wide-field, voltage-sensitive dye imaging to investigate the presence and functional structure of infraslow spontaneous activity in anaesthetized and awake mouse cortex.
- Allen W. Chan
- , Majid H. Mohajerani
- & Timothy H. Murphy
-
Article
| Open Access Direct wavefront sensing for high-resolution in vivo imaging in scattering tissue
Direct wavefront sensing for high-resolution in vivo imaging in scattering tissue
Direct wavefront sensing with laser ‘guide stars’ is used in astronomy and microscopy to correct for optical aberrations. Wang et al.use near-infrared guide stars to extend this approach to the highly scattering mouse brain, allowing high-resolution fluorescence imaging at 700μm depth.
- Kai Wang
- , Wenzhi Sun
- & Na Ji
-
Article |
 A long Stokes shift red fluorescent Ca2+ indicator protein for two-photon and ratiometric imaging
A long Stokes shift red fluorescent Ca2+ indicator protein for two-photon and ratiometric imaging
Current calcium-sensitive probes based on red fluorescent proteins are unsuitable for two-photon excitation at the near-infrared wavelengths commonly used for green fluorescent probes. Wu et al. use a structure-guided approach to engineer a red fluorescent probe with optimal two-photon excitation at these wavelengths.
- Jiahui Wu
- , Ahmed S. Abdelfattah
- & Robert E. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-based carbon-layered electrode array technology for neural imaging and optogenetic applications
Graphene-based carbon-layered electrode array technology for neural imaging and optogenetic applications
Monitoring neuronal activity in the rodent in vivobrain is commonly done using micro-electrode arrays but these devices are not normally compatible with optical technologies. Here the authors design a transparent and flexible electrode array based on graphene that allows them to combine electrophysiological recordings with optogenetic and imaging experiments.
- Dong-Wook Park
- , Amelia A. Schendel
- & Justin C. Williams
-
Article |
 Transparent and flexible low noise graphene electrodes for simultaneous electrophysiology and neuroimaging
Transparent and flexible low noise graphene electrodes for simultaneous electrophysiology and neuroimaging
Monitoring neuronal activity of large populations of neurons at high-temporal and spatial resolution is important to understand neurophysiology but requires improved tools and methods. Here the authors develop a transparent and flexible electrode based on graphene that allows them to combine electrophysiological recordings with calcium imaging.
- Duygu Kuzum
- , Hajime Takano
- & Brian Litt
-
Article
| Open Access Functional ultrasound imaging of intrinsic connectivity in the living rat brain with high spatiotemporal resolution
Functional ultrasound imaging of intrinsic connectivity in the living rat brain with high spatiotemporal resolution
Functional connectivity of brain networks is poorly understood, in part, due to limited imaging approaches. Here, the authors use ultrasound imaging to study functional connectivity in the adult rat brain in vivo, allowing for the identification of highly contrasted intrinsic connectivity patterns.
- Bruno-Félix Osmanski
- , Sophie Pezet
- & Mickael Tanter
-
Article
| Open Access Energy landscape and dynamics of brain activity during human bistable perception
Energy landscape and dynamics of brain activity during human bistable perception
Bistable visual perception requires changes in brain activity between different cortical areas. Here, Watanabe et al.demonstrate dynamic patterns of brain activity during bistable visual perception, which link behavioural variability and anatomical individual differences in focal brain regions.
- Takamitsu Watanabe
- , Naoki Masuda
- & Geraint Rees
-
Article
| Open Access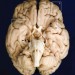 Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Studies on Patient H.M. showed that bilateral resection of the hippocampus results in impaired consolidation of long-term memory. Annese et al.create a digital map of Henry Molaison’s brain and find that a significant portion of the posterior hippocampus is actually histologically intact.
- Jacopo Annese
- , Natalie M. Schenker-Ahmed
- & Suzanne Corkin

 A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention