Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Stable platinum nanoparticles on specific MgAl2O4 spinel facets at high temperatures in oxidizing atmospheres
Stable platinum nanoparticles on specific MgAl2O4 spinel facets at high temperatures in oxidizing atmospheres
Supported platinum nanoparticles are highly active catalysts, but often gradually degrade under standard reaction conditions. Here, a well-defined spinel material is used as a support, resulting in a catalyst capable of maintaining performance even after severe thermal aging in oxidizing atmospheres.
- Wei-Zhen Li
- , Libor Kovarik
- & Charles H. F. Peden
-
Article |
 Ordered macroporous platinum electrode and enhanced mass transfer in fuel cells using inverse opal structure
Ordered macroporous platinum electrode and enhanced mass transfer in fuel cells using inverse opal structure
Inverse opal structures are desirable for fuel cell electrodes, but application of such structures in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells is yet to be realised. Kimet al.report fabrication of a platinum catalyst layer with an inverse opal structure, and show improved fuel cell performance.
- Ok-Hee Kim
- , Yong-Hun Cho
- & Yung-Eun Sung
-
Article |
 Cadmium iodide-mediated allenylation of terminal alkynes with ketones
Cadmium iodide-mediated allenylation of terminal alkynes with ketones
The allenylation of terminal alkynes is a convenient route to allenes from simple starting materials, though previously limited to formaldehyde and aldehyde substrates. Here a method enabling the use of ketones is reported, giving easy access to trisubstituted allenes.
- Xinjun Tang
- , Can Zhu
- & Shengming Ma
-
Article |
 Double perovskites as a family of highly active catalysts for oxygen evolution in alkaline solution
Double perovskites as a family of highly active catalysts for oxygen evolution in alkaline solution
New catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in basic solution are important for energy storage applications. Here, the authors report the high activity and stability of double perovskites in this role, and their performance is attributed to the proximity of the oxygenp-band to the Fermi level.
- Alexis Grimaud
- , Kevin J. May
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
Article |
 Unidirectional suppression of hydrogen oxidation on oxidized platinum clusters
Unidirectional suppression of hydrogen oxidation on oxidized platinum clusters
Platinum is a widely studied catalyst for the reduction of protons to hydrogen in water splitting, but it also catalyses the competing hydrogen oxidation back-reaction, thus limiting efficiency. Here, the authors show that the back-reaction can be limited by tuning the platinum oxidation state.
- Yu Hang Li
- , Jun Xing
- & Hua Gui Yang
-
Article |
 Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Liquid water shows anomalous behaviour, which is expected to be related with critical phenomena below its melting temperature. Taschinet al.experimentally identify two intermolecular vibrational modes that provide evidence for the coexistence of high-density and low-density water forms.
- A. Taschin
- , P. Bartolini
- & R. Torre
-
Article |
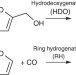 Directing reaction pathways by catalyst active-site selection using self-assembled monolayers
Directing reaction pathways by catalyst active-site selection using self-assembled monolayers
Control of active sites of heterogeneous catalysts can lead to enhanced product selectivity. Here, the authors use self-assembled alkanethiolate monolayers with varying surface densities to tune the selectivity of hydrogenation and hydrodeoxygenation of furfural on supported palladium catalysts.
- Simon H. Pang
- , Carolyn A. Schoenbaum
- & J. Will Medlin
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional vanadyl phosphate ultrathin nanosheets for high energy density and flexible pseudocapacitors
Two-dimensional vanadyl phosphate ultrathin nanosheets for high energy density and flexible pseudocapacitors
Graphene-like materials with pseudocapacitive characteristics are desirable for flexible solid-state pseudocapacitors. Here Wu et al. report such a graphene analogue, vanadyl phosphate ultrathin nanosheets, which exhibits excellent pseudocapacitive properties, leading to a high energy density.
- Changzheng Wu
- , Xiuli Lu
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
 Carbon precipitation from heavy hydrocarbon fluid in deep planetary interiors
Carbon precipitation from heavy hydrocarbon fluid in deep planetary interiors
Methane is a major constituent of planetary interiors, yet phase relations in the C–H system are poorly understood. This work documents the chemical reactivity of the C–H system over a wide range of temperatures and pressures, and sheds light on the chemical composition of Earth and icy giants.
- Sergey S. Lobanov
- , Pei-Nan Chen
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article |
 Diameter-dependent ion transport through the interior of isolated single-walled carbon nanotubes
Diameter-dependent ion transport through the interior of isolated single-walled carbon nanotubes
Calculations suggest that ion transport through nanochannels is significantly modified as the diameter approaches molecular dimensions. Choi et al.introduce a single-nanotube platform to demonstrate this effect and find a maximum ion transport rate at a diameter of approximately 1.6 nm.
- Wonjoon Choi
- , Zachary W. Ulissi
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Macroscopic scattering of cracks initiated at single impurity atoms
Macroscopic scattering of cracks initiated at single impurity atoms
The mechanical properties of brittle materials are largely determined by how cracks propagate through them. Contrary to expectations, Kermodeet al.show that a crack propagating below a critical speed through a silicon crystal can be scattered by a single isolated boron impurity.
- J.R. Kermode
- , L. Ben-Bashat
- & A. De Vita
-
Article
| Open Access A protective layer approach to solvatochromic sensors
A protective layer approach to solvatochromic sensors
Colorimetric differentiation of solvents is difficult as many solvatochromic molecules exhibit broad overlaps in their absorption and emission bands. Here, the authors present a ‘turn-on’ type sensor in which the colorimetric sensor responds only when its protective layer is disrupted by a specific solvent.
- Jung Lee
- , Hyun Taek Chang
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A platform for designing hyperpolarized magnetic resonance chemical probes
A platform for designing hyperpolarized magnetic resonance chemical probes
Hyperpolarization of chemical nuclei is known to greatly increase sensitivity to characterization by magnetic resonance imaging. Here a new platform that allows for the design of a number of hyperpolarized probes for chemical sensing applications is demonstrated.
- Hiroshi Nonaka
- , Ryunosuke Hata
- & Shinsuke Sando
-
Article |
 DNA-directed self-assembly of shape-controlled hydrogels
DNA-directed self-assembly of shape-controlled hydrogels
The development of a series of orthogonal binding interactions to direct the controlled self-assembly of mesoscale objects is desirable. Here, the authors use DNA as a sequence-specific glue to assemble hydrogel cuboids into a diverse series of structures in the micro- to millimeter length scale.
- Hao Qi
- , Majid Ghodousi
- & Ali Khademhosseini
-
Article |
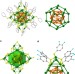 All-thiol-stabilized Ag44 and Au12Ag32 nanoparticles with single-crystal structures
All-thiol-stabilized Ag44 and Au12Ag32 nanoparticles with single-crystal structures
Noble metal nanoparticles are used for applications in optics, catalysis, sensing and others. Here the authors study the crystal structures of silver and gold-silver intermetallic nanoparticles stabilized by thiol ligand layers, helping to understand the relationship between their structure and properties.
- Huayan Yang
- , Yu Wang
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article |
 Twin-induced one-dimensional homojunctions yield high quantum efficiency for solar hydrogen generation
Twin-induced one-dimensional homojunctions yield high quantum efficiency for solar hydrogen generation
Efficient charge separation is of crucial importance for enhanced performance of photocatalysts. Here the authors demonstrate efficient charge separation by twin induced one-dimensional homojunctions, which have a high efficiency for solar hydrogen evolution without the need for additional dopants.
- Maochang Liu
- , Dengwei Jing
- & Liejin Guo
-
Article |
 A copper-phyllosilicate core-sheath nanoreactor for carbon–oxygen hydrogenolysis reactions
A copper-phyllosilicate core-sheath nanoreactor for carbon–oxygen hydrogenolysis reactions
Nanoscale copper catalysts are useful for the selective hydrogenation of carbon–oxygen bonds, although they may be deactivated under harsh conditions. Here the authors report the enhanced activity and stability of core-sheath copper-phyllosilicate nanoreactors due to electronic and morphological effects.
- Hairong Yue
- , Yujun Zhao
- & Jinlong Gong
-
Article |
 The first total synthesis of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A
The first total synthesis of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A
Pipecolidepsin A—commonly isolated from a marine sponge—is a promising anticancer agent but is challenging to synthesise in the lab. Here the authors describe the first total synthesis of this cyclodepsipeptide using a versatile strategy applicable to other similar compounds.
- Marta Pelay-Gimeno
- , Yésica García-Ramos
- & Fernando Albericio
-
Article
| Open Access Activation and splitting of carbon dioxide on the surface of an inorganic electride material
Activation and splitting of carbon dioxide on the surface of an inorganic electride material
Effective activation and spitting of carbon dioxide are important steps in its conversion to valuable chemicals. Here the authors report an inorganic electride material with a high concentration of near-surface electrons that is capable of adsorbing and decomposing carbon dioxide.
- Yoshitake Toda
- , Hiroyuki Hirayama
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Article |
 Trinuclear zinc complexes for biologically relevant μ3-oxoanion binding and carbon dioxide fixation
Trinuclear zinc complexes for biologically relevant μ3-oxoanion binding and carbon dioxide fixation
Molecular models of the biologically relevant oxoanion-bridged trinuclear zinc cluster found in numerous enzymatic active sites are desirable. Cao et al. report the synthesis of a trinuclear zinc scaffold, pre-organized to capture oxoanions, and its ability to catalytically convert CO2to carbonates in solution.
- Xiao Liu
- , Pingwu Du
- & Rui Cao
-
Article |
 Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as non-metal electrocatalysts for water oxidation
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as non-metal electrocatalysts for water oxidation
Efficient and economical water splitting is desirable for energy conversion, but it is limited by high overpotential and the need for noble metals. Zhao et al. report that nitrogen-doped graphite materials function as a promising electrocatalyst, with efficiency comparable to that of benchmark metal oxides.
- Yong Zhao
- , Ryuhei Nakamura
- & Kazuhito Hashimoto
-
Article |
 A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries
A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries
Anode materials in sodium-ion batteries can undergo significant volume change upon sodium insertion and extraction, leading to deteriorated cycling performance. Wang et al. report a layered metal oxide anode with zero-strain characteristics, which may lead to extended battery cycle life.
- Yuesheng Wang
- , Xiqian Yu
- & Xuejie Huang
-
Article |
 Reductive assembly of cyclobutadienyl and diphosphacyclobutadienyl rings at uranium
Reductive assembly of cyclobutadienyl and diphosphacyclobutadienyl rings at uranium
Despite their prevalence in the d-block, f-block cyclobutadienyl complexes are hitherto unknown. Here, the authors report the syntheses of inverted sandwich cyclobutadienyl dianion uranium(IV) complexes and show computational analysis that suggests the bonding is predominantly electrostatic.
- Dipti Patel
- , Jonathan McMaster
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
Article |
 Membrane-less hydrogen bromine flow battery
Membrane-less hydrogen bromine flow battery
Membrane-less electrochemical systems eliminate the need for costly ion-exchange membranes, but typically suffer from low-power densities. Braff et al.propose a hydrogen bromine laminar flow battery, which rivals the performance of the best membrane-based systems.
- William A. Braff
- , Martin Z. Bazant
- & Cullen R. Buie
-
Article |
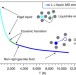 Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
A physical description of supercritical fluids remains challenging because common approximations for solids and gases do not apply to liquids. Bolmatov et al. identify a liquid/gas dynamic crossover of specific heat above the critical point, and formulate a theory to shed light on its nature.
- Dima Bolmatov
- , V. V. Brazhkin
- & K. Trachenko
-
Article |
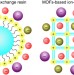 Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Crystalline porous materials are commonly based around negatively charged frameworks, so ion-exchange is limited to cations. Here, the authors report a series of positive metal-organic frameworks, capable of ion exchange of large organic anions, with potential in separation and purification applications.
- Xiang Zhao
- , Xianhui Bu
- & Pingyun Feng
-
Article |
 Polymeric pseudo-crown ether for cation recognition via cation template-assisted cyclopolymerization
Polymeric pseudo-crown ether for cation recognition via cation template-assisted cyclopolymerization
Cyclopolymers have potentially interesting molecular recognition properties due to their in-chain multiple rings. Here, the authors report cation-templated, controlled radical cyclopolymerization of poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylates, yielding polymeric pseudo-crown ethers with large in-chain cavities.
- Takaya Terashima
- , Minami Kawabe
- & Mitsuo Sawamoto
-
Article |
 Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Compositionally and geometrically complex nano-objects are an important goal in medicinal, photonic and electronic materials research. Here, the authors fabricate disk-sphere and disk-cylinder nanoparticles with defined multicompartments from binary mixtures of block copolymers.
- Jiahua Zhu
- , Shiyi Zhang
- & Darrin J. Pochan
-
Article |
 Structured cone arrays for continuous and effective collection of micron-sized oil droplets from water
Structured cone arrays for continuous and effective collection of micron-sized oil droplets from water
Effective methods for the removal of micro-droplets of oil from water are sought-after to combat oil spills. Here, the authors report cactus-inspired oleophilic conical needle arrays capable of capturing micron-sized oil droplets with both high continuity and high throughput.
- Kan Li
- , Jie Ju
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article |
 Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Techniques for shape-controlling of hydrogels, that is, crosslinked networks of polymers, could make possible various biomimetic applications. Palleau et al.propose a strategy to pattern three-dimensional hydrogels using electric potential, which allows directed bending and fast controllable actuation.
- Etienne Palleau
- , Daniel Morales
- & Orlin D. Velev
-
Article
| Open Access Stable platinum nanoclusters on genomic DNA–graphene oxide with a high oxygen reduction reaction activity
Stable platinum nanoclusters on genomic DNA–graphene oxide with a high oxygen reduction reaction activity
Platinum nanoclusters are well-known catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction, although the performance of clusters smaller than 2 nm is poorly studied. Here, the authors report 1.4 nm platinum clusters supported on DNA–graphene oxide composites and demonstrate promising electrochemical activity and stability.
- Jitendra N. Tiwari
- , Krishna Nath
- & Kwang S. Kim
-
Article |
 Nitrate formation from atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen photocatalysed by nano-sized titanium dioxide
Nitrate formation from atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen photocatalysed by nano-sized titanium dioxide
Nitrate pollutants are known to contribute to a variety of environmental problems. Here, the authors suggest that nano-sized titanium dioxide, as used in numerous surface coatings, may catalyse the formation of nitrate via the photochemical reaction of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen.
- Shi-Jie Yuan
- , Jie-Jie Chen
- & Han-Qing Yu
-
Article |
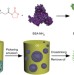 Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Proteins are ideal building blocks for self-assembly of artificial cell-like architectures, but their realization is rare. Huang et al.report an interfacial assembly of protein–polymer conjugates, which exhibit cellular properties such as encapsulating guest molecules and switching enzyme activity.
- Xin Huang
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Role of point defects on the reactivity of reconstructed anatase titanium dioxide (001) surface
Role of point defects on the reactivity of reconstructed anatase titanium dioxide (001) surface
Theory suggests that the anatase (001) surface is the most catalytically reactive of all the crystal facets of titanium dioxide. Wang et al.show that the active sites are four-coordinated titanium states and in their absence this surface is even inert for water adsorption at room temperature.
- Yang Wang
- , Huijuan Sun
- & J. G. Hou
-
Article
| Open Access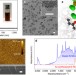 Hypervalent surface interactions for colloidal stability and doping of silicon nanocrystals
Hypervalent surface interactions for colloidal stability and doping of silicon nanocrystals
Electrically insulating ligands and doping of colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals continue to be significant challenges for practical nanocrystal-based optoelectronics. Wheeler et al.demonstrate a new surface chemistry technique that confronts both of these challenges simultaneously.
- Lance M. Wheeler
- , Nathan R. Neale
- & Uwe R. Kortshagen
-
Article |
 Probing the nature of gold–carbon bonding in gold–alkynyl complexes
Probing the nature of gold–carbon bonding in gold–alkynyl complexes
Fundamental understanding of gold–carbon bonding in homogeneous catalysts is vital for improved catalyst design, although spectroscopic information is limited. Here, the authors probe the bonding in gold–alkyne complexes using a combination of photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initiocalculations.
- Hong-Tao Liu
- , Xiao-Gen Xiong
- & Lai-Sheng Wang
-
Article |
 A green lead hydrometallurgical process based on a hydrogen-lead oxide fuel cell
A green lead hydrometallurgical process based on a hydrogen-lead oxide fuel cell
Lead-acid batteries are used worldwide, but their recycling remains challenging because of lead pollution and high energy consumption. Pan et al. solve these problems in a high-yield, hydrometallurgical process based on hydrogen-lead oxide fuel cell reactions, which produce water as the by-product.
- Junqing Pan
- , Yanzhi Sun
- & Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article |
 Understanding the role of phase in chemical bond breaking with coincidence angular streaking
Understanding the role of phase in chemical bond breaking with coincidence angular streaking
Ultrafast laser pulses are useful to study electron dynamics in chemical bonds, but their influence on bond breaking is not fully understood. Wu et al. study H2 bond breaking with coincidence techniques, and find a phase-dependent anisotropy of the H+fragmentation even for isotropic multicycle laser pulses.
- J. Wu
- , M. Magrakvelidze
- & R. Dörner
-
Article
| Open Access Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Many interesting chemical problems like photosynthesis and photovoltaics involve non-adiabatic dynamical phenomena, which are difficult to predict theoretically. Here, the authors develop a new numerical method capable of recovering quantum interferences that are neglected by conventional methods.
- Vyacheslav N. Gorshkov
- , Sergei Tretiak
- & Dmitry Mozyrsky
-
Article |
 Interfacial liquid-state surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Interfacial liquid-state surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Assembly of functional colloidal nanoparticles has many technological applications, but its three-dimensional realization remains challenging. Kim et al.report a spontaneous self-orientation of gold nanorods at an oil/water interface and use it to amplify signal in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
- Kihoon Kim
- , Hye Soo Han
- & Taewook Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Femtolitre chemistry assisted by microfluidic pen lithography
Femtolitre chemistry assisted by microfluidic pen lithography
Chemical reactions on femtolitre scales are necessary to study confined biological processes. Here, the authors use a microfluidic pen lithography technique to perform a series of discrete femtoscale acid-base and synthetic reactions, and crystallizations on a surface with high registration accuracy.
- Carlos Carbonell
- , Kyriakos C. Stylianou
- & Daniel Maspoch
-
Article
| Open Access NMR spectroscopic detection of chirality and enantiopurity in referenced systems without formation of diastereomers
NMR spectroscopic detection of chirality and enantiopurity in referenced systems without formation of diastereomers
The enantiopurity of chiral compounds is key in determining their activity or therapeutic action. Here, the authors present a versatile NMR method of enantiomeric excess determination using a symmetrical achiral molecule as resolving agent, based on complexation with analyte, without formation of diastereomers.
- Jan Labuta
- , Shinsuke Ishihara
- & Jonathan P. Hill
-
Article |
 Gold peroxide complexes and the conversion of hydroperoxides into gold hydrides by successive oxygen-transfer reactions
Gold peroxide complexes and the conversion of hydroperoxides into gold hydrides by successive oxygen-transfer reactions
Gold peroxide-derived complexes are important in oxidation catalysis, although structural information on these species is sparse. Here, the authors have synthesized a range of gold complexes and have shown a reaction pathway from peroxides to hydrides, via oxygen-transfer events.
- Dragoş-Adrian Roşca
- , Joseph A. Wright
- & Manfred Bochmann
-
Article
| Open Access Conducting linear chains of sulphur inside carbon nanotubes
Conducting linear chains of sulphur inside carbon nanotubes
Elemental sulphur is an insulator in the bulk phase, although it may become conducting under ultrahigh-pressure conditions. Here, the authors report a one-dimensional conducting form of sulphur formed by encapsulation inside single-walled and double-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Toshihiko Fujimori
- , Aarón Morelos-Gómez
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article |
 Chemical synthesis of lactic acid from cellulose catalysed by lead(II) ions in water
Chemical synthesis of lactic acid from cellulose catalysed by lead(II) ions in water
The direct transformation of cellulose into high-value chemicals is a key process in the establishment of biomass-derived chemical production. Here, the authors present the lead(II)-catalysed conversion of cellulose into lactic acid via a cascade reaction, which proceeds in water under mild conditions.
- Yanliang Wang
- , Weiping Deng
- & Huilin Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies
Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies
Heparin-like oligosaccharides are implicated in various diseases. Hansen et al. report an efficient two-cycle [4+4+4] tetrasaccharide-iteration-based approach to synthesize a structurally defined heparin dodecasaccharide with a latent aldehyde tag for labelling and conjugation.
- Steen U. Hansen
- , Gavin J. Miller
- & John M. Gardiner
-
Article |
 Direct measurement and modulation of single-molecule coordinative bonding forces in a transition metal complex
Direct measurement and modulation of single-molecule coordinative bonding forces in a transition metal complex
The nature of metal–ligand interactions remains unclear in coordination chemistry. Hao et al. address this question using in situelectrochemically controlled atomic force microscopy, which can monitor and modulate the coordinative bonding in a transition metal complex at a molecular level.
- Xian Hao
- , Nan Zhu
- & Qijin Chi
-
Article |
 Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst
Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst
The rational design of inexpensive and durable oxygen reduction catalysts may lead to enhanced fuel cell performance. Here, the authors report a bio-inspired catalyst in which hybridization of iron 3delectrons with a carbon nanotube alters its electronic structure and improves catalytic performance.
- Ruiguo Cao
- , Ranjit Thapa
- & Jaephil Cho
-
Article |
 Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers
Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers
Postsynthetic modulation of the structural properties of hydrogels is desirable for a range of biomaterials applications. Here, the authors fabricate photolatently modulable polymer hydrogels crosslinked by titania nanosheets, which may be micropatterned with high spatial and temporal resolution.
- Mingjie Liu
- , Yasuhiro Ishida
- & Takuzo Aida
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 Super liquid-repellent gas membranes for carbon dioxide capture and heart–lung machines
Super liquid-repellent gas membranes for carbon dioxide capture and heart–lung machines