Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access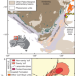 Emplacement of the Argyle diamond deposit into an ancient rift zone triggered by supercontinent breakup
Emplacement of the Argyle diamond deposit into an ancient rift zone triggered by supercontinent breakup
The Argyle deposit erupted 1.3 billion years ago into an ancient rift at the edge of a craton. Argyle coincided with supercontinent breakup, highlighting the link between diamond emplacement, former rifts and continental breakup.
- Hugo K. H. Olierook
- , Denis Fougerouse
- & Michael T. D. Wingate
-
Article
| Open Access Sulfur and chlorine budgets control the ore fertility of arc magmas
Sulfur and chlorine budgets control the ore fertility of arc magmas
Earth’s largest copper deposits form in continental arcs, yet it is not well understood what determines whether a magmatic system generates economic mineralization or not. Here the authors show that the abundance of chlorine and sulfur, rather than the abundance of ore metals controls magmatic ore fertility.
- Carter Grondahl
- & Zoltán Zajacz
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle suspensions from carbon-rich fluid make high-grade gold deposits
Nanoparticle suspensions from carbon-rich fluid make high-grade gold deposits
The authors present novel observations providing insights into the formation of extraordinary gold-rich veins. We discovered metal nanoparticles associated with amorphous silica and carbon indicating their essential contribution to efficient gold deposition.
- Laura Petrella
- , Nicolas Thébaud
- & Sarah Gain
-
Article
| Open Access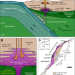 Mobilisation of deep crustal sulfide melts as a first order control on upper lithospheric metallogeny
Mobilisation of deep crustal sulfide melts as a first order control on upper lithospheric metallogeny
The presence and mobility of metal-rich sulfides in lower crustal magma chambers can act as a gateway for metals to be trapped, or released into ascending magmas that are then able to form upper crustal porphyry copper and gold deposits.
- David A. Holwell
- , Marco L. Fiorentini
- & Weronika Gorczyk
-
Article
| Open Access Fluids as primary carriers of sulphur and copper in magmatic assimilation
Fluids as primary carriers of sulphur and copper in magmatic assimilation
Experiments show that when magma heats black shale wall-rock, fluids form and mobilize S and Cu, which can then concentrate and form base metal deposits. The fluids also attach to sulphide droplets and cause them to float in the host silicate melt.
- Ville J. Virtanen
- , Jussi S. Heinonen
- & Karina Moslova
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetically driven successive sodic and potassic alteration of feldspar
Kinetically driven successive sodic and potassic alteration of feldspar
This paper reveals that potassic alteration can be triggered by Na-rich fluids, indicating that pervasive sequential sodic and potassic alterations associated with mineralization in some of the world’s largest ore deposits may not necessarily reflect externally-driven changes in fluid alkali contents.
- Gan Duan
- , Rahul Ram
- & Joël Brugger
-
Article
| Open Access Oxidized sulfur-rich arc magmas formed porphyry Cu deposits by 1.88 Ga
Oxidized sulfur-rich arc magmas formed porphyry Cu deposits by 1.88 Ga
Tectonomagmatic conditions in the Precambrian were hypothesized to be unfavorable for porphyry Cu deposit formation. Here, the authors show that metallogenic processes typify Phanerozoic porphyry Cu deposits operated by ~1.88 Ga, reflecting modification of mantle lithosphere by oxidized slab-derived fluids at that time.
- Xuyang Meng
- , Jackie M. Kleinsasser
- & Richard A. Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Trace element catalyses mineral replacement reactions and facilitates ore formation
Trace element catalyses mineral replacement reactions and facilitates ore formation
Trace amounts of Cerium can act as a catalyst by enhancing fluid-mediated magnetite alteration, which preconditions ore systems and could contribute to the large size and metal content of world-class ore deposits.
- Yanlu Xing
- , Joël Brugger
- & Xiya Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Fluxing of mantle carbon as a physical agent for metallogenic fertilization of the crust
Fluxing of mantle carbon as a physical agent for metallogenic fertilization of the crust
Magmatic systems play a crucial role in enriching the crust with volatiles and elements that reside primarily within the Earth’s mantle. Here, the authors show that carbon, as a buoyant supercritical CO2 fluid, could be a covert agent that may promote the physical transport of sulfides across the mantle-crust transition.
- Daryl E. Blanks
- , David A. Holwell
- & Elena Ferrari
-
Article
| Open Access Fossilized solidification fronts in the Bushveld Complex argue for liquid-dominated magmatic systems
Fossilized solidification fronts in the Bushveld Complex argue for liquid-dominated magmatic systems
Magma storage zones are debated to either be crystal-dominated mush zones or large liquid-dominated magma chambers. Here, the authors discover fossilized solidification fronts of magnetitite in the Bushveld pluton, which indicate nucleation and crystal growth occurred at the magma chamber floor, precluding the existence of a thick crystal mush zone in this region.
- Willem Kruger
- & Rais Latypov
-
Article
| Open Access Exposed soil and mineral map of the Australian continent revealing the land at its barest
Exposed soil and mineral map of the Australian continent revealing the land at its barest
In this study, the authors combine Landsat images spanning 30 years with a new statistical estimator to produce a soil and mineral spectra map of the Australian continent largely unobscured by vegetation or clouds.
- Dale Roberts
- , John Wilford
- & Omar Ghattas
-
Article
| Open Access A metasomatized lithospheric mantle control on the metallogenic signature of post-subduction magmatism
A metasomatized lithospheric mantle control on the metallogenic signature of post-subduction magmatism
Hydrous and alkali rich magmas rise through the lithosphere and may host gold-rich ore deposits – a poorly understood process. Here, the authors present new chalcophile element data across a metallogenic section of the lithosphere and suggest a continuous or staged ascent of magmatic-hydrothermal settings from mantle to upper crust.
- David A. Holwell
- , Marco Fiorentini
- & Marek Locmelis
-
Article
| Open Access Global Fe–O isotope correlation reveals magmatic origin of Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores
Global Fe–O isotope correlation reveals magmatic origin of Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores
The origin of giant Kiruna-type iron ores has been debated for nearly 100 years. This study employs extensive stable isotope data from Kiruna-type ores worldwide and magmatic and hydrothermal reference materials to show that iconic Kiruna-type ores originate primarily from ortho-magmatic processes.
- Valentin R. Troll
- , Franz A. Weis
- & Katarina P. Nilsson
-
Article
| Open Access Uranium transport in acidic brines under reducing conditions
Uranium transport in acidic brines under reducing conditions
Ore deposits and nuclear reactors are greatly affected by the solubility and speciation of uranium at elevated (>100 °C) temperature. Here, the authors identify a new uranium chloride species (UCl40), which is mobile under reducing conditions, thereby necessitating a re-evaluation of uranium mobility.
- Alexander Timofeev
- , Artaches A. Migdisov
- & Hongwu Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Lithium enrichment in intracontinental rhyolite magmas leads to Li deposits in caldera basins
Lithium enrichment in intracontinental rhyolite magmas leads to Li deposits in caldera basins
Lithium is increasingly being utilized for modern technology in the form of lithium-ion batteries. Here, using in situ measurements of quartz-hosted melt inclusions, the authors demonstrate that preserved lake sediments within rhyolitic calderas have the potential to host large lithium-rich clay deposits.
- Thomas R. Benson
- , Matthew A. Coble
- & Gail A. Mahood
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of heavy rare earth mineralization in South China
Origin of heavy rare earth mineralization in South China
Heavy rare earth elements (HREE) are an important global resource for many industries. Here, Xuet al. have discovered new REE minerals, which represent oxidized REE-rich fluids that metasomatized granites resulting in an enrichment of HREE, therefore contributing to our knowledge of global REE resources.
- Cheng Xu
- , Jindřich Kynický
- & Wenlei Song
-
Article
| Open Access Secondary migration and leakage of methane from a major tight-gas system
Secondary migration and leakage of methane from a major tight-gas system
As shale and tight gas basins are increasingly used to extract natural gas, understanding how gas migrates is important. Wood and Sanei find that secondary migration in a tight-gas basin leads to up-dip transmission of enriched methane into surficial strata which may leak into groundwater and the atmosphere.
- James M. Wood
- & Hamed Sanei

 Magmatic immiscibility and the origin of magnetite-(apatite) iron deposits
Magmatic immiscibility and the origin of magnetite-(apatite) iron deposits