Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nestin-dependent mitochondria-ER contacts define stem Leydig cell differentiation to attenuate male reproductive ageing
Nestin-dependent mitochondria-ER contacts define stem Leydig cell differentiation to attenuate male reproductive ageing
The regulatory mechanisms contributing to male reproductive ageing are unknown. Here, the authors show that Nestin-dependent mito-ER contacts (MERCs) regulate stem Leydig cell (SLC) senescence and provide insights into SLCs-targeting therapies.
- Senyu Yao
- , Xiaoyue Wei
- & Jiancheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Functional antagonism between ΔNp63α and GCM1 regulates human trophoblast stemness and differentiation
Functional antagonism between ΔNp63α and GCM1 regulates human trophoblast stemness and differentiation
Trophoblast stem cells can be derived from human blastocysts and first-trimester, but not term, cytotrophoblasts. Here the authors show that induction efficiency of cytotrophoblast is determined by antagonism between GCM1 and ΔNp63α and manipulating this antagonism facilitates derivation of TS cells from term placenta.
- Liang-Jie Wang
- , Chie-Pein Chen
- & Hungwen Chen
-
Article
| Open Access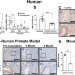 Loss of MIG-6 results in endometrial progesterone resistance via ERBB2
Loss of MIG-6 results in endometrial progesterone resistance via ERBB2
Female subfertility is highly associated with endometriosis. Here the authors show that progesterone-induced MIG-6 is reduced in endometrium of infertile women and non-human primates with endometriosis, and in a mouse model find that Erbb2 is the key mediator of Mig-6 loss induced endometriosis-related infertility.
- Jung-Yoon Yoo
- , Tae Hoon Kim
- & Jae-Wook Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access The RNA landscape of the human placenta in health and disease
The RNA landscape of the human placenta in health and disease
Placental dysfunction can have catastrophic or barely discernible effects ranging from miscarriage to apparently normal birth. Here the authors present a comprehensive analysis of the human placental transcriptome and identify circular RNAs and piRNAs.
- Sungsam Gong
- , Francesca Gaccioli
- & D. Stephen Charnock-Jones
-
Article
| Open Access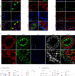 RANKL regulates male reproductive function
RANKL regulates male reproductive function
There are few treatments for male infertility. Here, the authors show that the receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) signalling pathway has important functions in sperm production and maturation, improves fertility in male mice and shows potential as a male infertility target.
- Martin Blomberg Jensen
- , Christine Hjorth Andreassen
- & Anders Juul
-
Article
| Open Access Defining the impact of dietary macronutrient balance on PCOS traits
Defining the impact of dietary macronutrient balance on PCOS traits
Lifestyle interventions are first-line treatment for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), but the optimal diet remains undefined. Here the authors identify an optimum dietary macronutrient balance that can rectify PCOS reproductive traits in a mouse model of PCOS, while metabolic features were less sensitive to diet changes.
- Valentina Rodriguez Paris
- , Samantha M. Solon-Biet
- & Kirsty A. Walters
-
Article
| Open Access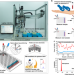 Measuring luteinising hormone pulsatility with a robotic aptamer-enabled electrochemical reader
Measuring luteinising hormone pulsatility with a robotic aptamer-enabled electrochemical reader
Assessment of luteinising hormone pulsatility is important in the diagnosis of reproductive disorders. Here the authors develop a DNA aptamer-based electrochemical analysis integrated into a robotic platform for high-throughput and sensitive analysis.
- Shaolin Liang
- , Andrew B. Kinghorn
- & Julian A. Tanner
-
Article
| Open Access SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
The onset of mammalian puberty is sensitive to metabolic changes and nutritional status, but the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are poorly understood. Here the authors show that the epigenetic regulator of transcription, SIRT1, mediates the effects of under and overnutrition on pubertal timing by controlling the expression of Kiss1 in hypothalamic neurons.
- M. J. Vazquez
- , C. A. Toro
- & M. Tena-Sempere
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the genetic architecture of reproductive ageing in the Japanese population
Elucidating the genetic architecture of reproductive ageing in the Japanese population
The timing of female reproductive capacity is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Here, in genome-wide association studies, the authors identify genetic loci for age at menarche and onset of menopause in Japanese women, and highlight differences with European populations.
- Momoko Horikoshi
- , Felix R. Day
- & John. R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
About a quarter of pre-menopausal women will suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding in their lives. Here, Maybin and colleagues show hypoxia and subsequent activation of HIF-1α during menses are required for normal endometrial repair, and identify pharmacological stabilisation of HIF-1α as a potential therapeutic strategy for this debilitating condition.
- Jacqueline A. Maybin
- , Alison A. Murray
- & Hilary O. D. Critchley
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorene-9-bisphenol is anti-oestrogenic and may cause adverse pregnancy outcomes in mice
Fluorene-9-bisphenol is anti-oestrogenic and may cause adverse pregnancy outcomes in mice
Bisphenol A is used in the production of many plastic products, but has adverse health effects and is therefore being replaced. Here the authors show that its substitute, fluorene-9-bisphenol, is released from commercial plastic bottles into drinking water, and has anti-oestrogenic effects in mice.
- Zhaobin Zhang
- , Ying Hu
- & Jianying Hu

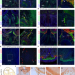 SEMA6A drives GnRH neuron-dependent puberty onset by tuning median eminence vascular permeability
SEMA6A drives GnRH neuron-dependent puberty onset by tuning median eminence vascular permeability