Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Pelagic barite precipitation at micromolar ambient sulfate
Pelagic barite precipitation at micromolar ambient sulfate
The question of how significant barite deposits were able to form from early Earth’s low-sulfate seas remains controversial. Here, the authors show pelagic barite precipitation within a strongly barite-undersaturated ecosystem, highlighting the importance of particle-associated microenvironments.
- Tristan J. Horner
- , Helena V. Pryer
- & Richard D. Ricketts
-
Article
| Open Access Timing anthropogenic stressors to mitigate their impact on marine ecosystem resilience
Timing anthropogenic stressors to mitigate their impact on marine ecosystem resilience
Stressors such as sediment dredging can harm marine organisms, but this impact could be minimised if targeted within ‘ecological windows’. Here, Wu and colleagues develop a modelling framework to identify ecological windows that maximise seagrass resilience under varying dredging schedules.
- Paul Pao-Yen Wu
- , Kerrie Mengersen
- & M. Julian Caley
-
Article
| Open Access Contribution of livestock H2S to total sulfur emissions in a region with intensive animal production
Contribution of livestock H2S to total sulfur emissions in a region with intensive animal production
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from agricultural sources is generally omitted from sulfur emission estimates despite its abundance in livestock emissions. Here, the authors show that agriculture is the most important source of sulfur in Denmark using proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry measurements of H2S.
- Anders Feilberg
- , Michael Jørgen Hansen
- & Tavs Nyord
-
Article
| Open Access The impact of anthropogenic land use and land cover change on regional climate extremes
The impact of anthropogenic land use and land cover change on regional climate extremes
Land use and land cover change has led to more frequent hot, dry summers in parts of the mid-latitudes. Here the authors use an Earth system model to show that regions converted to crops and pastures experience hot, dry summers 2 to 4 times more frequently than they would if native forests had remained.
- Kirsten L. Findell
- , Alexis Berg
- & Elena Shevliakova
-
Article
| Open Access Organic coating on biochar explains its nutrient retention and stimulation of soil fertility
Organic coating on biochar explains its nutrient retention and stimulation of soil fertility
Biochar promotes plant growth via a slow release of nutrients; however, a mechanistic understanding of nutrient storage in biochar is lacking. Here, using high-resolution spectromicroscopy and mass spectrometry, the authors identify an organic coating on co-composted particles that enhances nutrient retention.
- Nikolas Hagemann
- , Stephen Joseph
- & Andreas Kappler
-
Article
| Open Access Mining drives extensive deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon
Mining drives extensive deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon
Industrial mining contributes to deforestation in the Amazon, and the extent of effect could occur beyond areas of land explicitly permitted for mining. Here, Sonter et al. show that deforestation in 70-km buffer zones around mines has led to an estimated 9% of Brazilian Amazon deforestation since 2005.
- Laura J. Sonter
- , Diego Herrera
- & Britaldo S. Soares-Filho
-
Article
| Open Access Atmospheric observations show accurate reporting and little growth in India’s methane emissions
Atmospheric observations show accurate reporting and little growth in India’s methane emissions
India’s methane emissions have been quantified using atmospheric measurements to provide an independent comparison with reported emissions. Here Ganesan et al. find that derived methane emissions are consistent with India’s reports and no significant trend has been observed between 2010–2015.
- Anita L. Ganesan
- , Matt Rigby
- & Paul B. Krummel
-
Article
| Open Access Trade-driven relocation of air pollution and health impacts in China
Trade-driven relocation of air pollution and health impacts in China
International and domestic interprovincial trade of China are entangled, but their health impacts have been treated separately in earlier studies. Here Wang. quantify the complex impacts of trade on public health across China within an integrative framework.
- Haikun Wang
- , Yanxu Zhang
- & Michael B. McElroy
-
Article
| Open Access A surface-stabilized ozonide triggers bromide oxidation at the aqueous solution-vapour interface
A surface-stabilized ozonide triggers bromide oxidation at the aqueous solution-vapour interface
Heterogeneous oxidation of bromide in atmospheric aqueous environments has long been suspected to be accelerated at the interface between aqueous solution and air. Here, the authors provide spectroscopic, kinetic and theoretical evidence for a rate limiting, surface active ozonide formed at the interface.
- Luca Artiglia
- , Jacinta Edebeli
- & Markus Ammann
-
Article
| Open Access Low carbon renewable natural gas production from coalbeds and implications for carbon capture and storage
Low carbon renewable natural gas production from coalbeds and implications for carbon capture and storage
Coalbeds produce natural gas, which has been observed to be enhanced by in situ microbes. Here, the authors add plant-derived carbohydrates (monosaccharides) to coal seams to be converted by indigenous microbes into natural gas, thus demonstrating a potential low carbon renewable natural gas resource.
- Zaixing Huang
- , Christine Sednek
- & Shengpin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Aerosols as a source of dissolved black carbon to the ocean
Aerosols as a source of dissolved black carbon to the ocean
The contribution of atmospheric deposition to the oceanic dissolved black carbon pool (DBC) is unclear. Here, the authors show that water-soluble black carbon is positively correlated with water-soluble organic carbon in marine aerosols, and that atmospheric deposition is a significant source of oceanic DBC.
- Hongyan Bao
- , Jutta Niggemann
- & Shuh-Ji Kao
-
Article
| Open Access Statistical modelling predicts almost complete loss of major periglacial processes in Northern Europe by 2100
Statistical modelling predicts almost complete loss of major periglacial processes in Northern Europe by 2100
Cryogenic land surface processes characterise the periglacial realm and control landscape development and ecosystem functioning. Here, via statistical modelling, the authors predict a 72% reduction of the periglacial realm in Northern Europe by 2050, and almost complete disappearance by 2100.
- Juha Aalto
- , Stephan Harrison
- & Miska Luoto
-
Article
| Open Access Developing a molecular picture of soil organic matter–mineral interactions by quantifying organo–mineral binding
Developing a molecular picture of soil organic matter–mineral interactions by quantifying organo–mineral binding
Most molecular scale knowledge on soil organo–mineral interactions remains qualitative due to instrument limitations. Here, the authors use force spectroscopy to directly measure free binding energy between organic ligands and minerals and find that both chemistry and environmental conditions affect binding.
- C. J. Newcomb
- , N. P. Qafoku
- & J. J. De Yoreo
-
Article
| Open Access Agricultural pesticide use and adverse birth outcomes in the San Joaquin Valley of California
Agricultural pesticide use and adverse birth outcomes in the San Joaquin Valley of California
The health consequences of exposure to pesticides are uncertain and subject to much debate. Here, the effect of exposure during pregnancy is investigated in an agriculturally dominated residential area, showing that an increase in adverse birth outcomes is observed with very high levels of pesticide exposure.
- Ashley E. Larsen
- , Steven D. Gaines
- & Olivier Deschênes
-
Article
| Open Access Redox reactions and weak buffering capacity lead to acidification in the Chesapeake Bay
Redox reactions and weak buffering capacity lead to acidification in the Chesapeake Bay
The potential contribution of redox reactions to acidification in coastal waters is unclear. Here, using measurements from the Chesapeake Bay, the authors show that pH minimum occurs at mid-depths where acids are produced via hydrogen sulfide oxidation in waters mixed upward from anoxic depths.
- Wei-Jun Cai
- , Wei-Jen Huang
- & W. Michael Kemp
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and ramifications of incidental Magnéli phase generation and release from industrial coal-burning
Discovery and ramifications of incidental Magnéli phase generation and release from industrial coal-burning
Solid-state emissions from coal burning remain an environmental concern. Here, the authors have found that TiO2 minerals present in coal are converted into titanium suboxides during burning, and initial biotoxicity screening suggests that further testing is needed to look into human lung consequences.
- Yi Yang
- , Bo Chen
- & Michael F. Hochella Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access Reduced ultrafine particle levels in São Paulo’s atmosphere during shifts from gasoline to ethanol use
Reduced ultrafine particle levels in São Paulo’s atmosphere during shifts from gasoline to ethanol use
The biofuel ethanol has been introduced into urban transportation in many countries. Here, by measuring aerosols in São Paulo, the authors find that high ethanol prices coincided with an increase in harmful nanoparticles by a third, as drivers switched from ethanol to cheaper gasoline, showing a benefit of ethanol.
- Alberto Salvo
- , Joel Brito
- & Franz M. Geiger
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of snow-fed rivers affects flow regimes more than climate change
Regulation of snow-fed rivers affects flow regimes more than climate change
Global warming and hydropower regulations are major threats to future fresh-water availability and biodiversity. Here, the authors show that their impact on flow regime over a large landmass result in similar changes, but hydropower is more critical locally and may have potential for climate adaptation in floodplains.
- B. Arheimer
- , C. Donnelly
- & G. Lindström
-
Article
| Open Access Iron-mediated soil carbon response to water-table decline in an alpine wetland
Iron-mediated soil carbon response to water-table decline in an alpine wetland
The response of soil organic carbon in wetlands to water-table decline remains uncertain. Here, the authors examine the role of iron in mediating soil enzyme activity and lignin stabilization and find that iron protecting lignin phenols in soils exposed to air acts as an iron gate against the enzyme latch.
- Yiyun Wang
- , Hao Wang
- & Xiaojuan Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Current rates and mechanisms of subsea permafrost degradation in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf
Current rates and mechanisms of subsea permafrost degradation in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf
The rate of subsea permafrost degradation is a key factor controlling marine methane emissions in the Arctic. Here, using re-drilled boreholes, the authors show that the ice-bonded permafrost table in the near-shore East Siberian Arctic Shelf has deepened by ∼14 cm per year over the past 31–32 years.
- Natalia Shakhova
- , Igor Semiletov
- & Denis Chernykh
-
Article
| Open Access Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century
Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century
Water scarcity threatens a growing number of global catchments. Here, the authors examine how human interventions (HI) affected water scarcity between 1971 and 2010 and find that HI caused increases in the average duration and occurrence of water scarcity for 32% and 34% of the global population, respectively.
- T.I.E. Veldkamp
- , Y. Wada
- & P. J. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Anthropogenic climate change has altered primary productivity in Lake Superior
Anthropogenic climate change has altered primary productivity in Lake Superior
The impacts of climate change on the Great Lakes’ ecosystems compared to historical records are unclear. Here, using paleolimnological evidence, the authors show that Lake Superior experienced a slow increase in productivity throughout the Holocene, but that this rate has increased in the last century.
- M. D. O’Beirne
- , J. P. Werne
- & E. D. Reavie
-
Article
| Open Access Seepage from an arctic shallow marine gas hydrate reservoir is insensitive to momentary ocean warming
Seepage from an arctic shallow marine gas hydrate reservoir is insensitive to momentary ocean warming
The degree to which warming bottom waters will destabilize shallow gas hydrate reservoirs in the Arctic remains unclear. Here, Honget al. observe and model porewater profiles from a gas-hydrate-bearing system south of Spitsbergen, and conclude episodic emissions are not warming induced.
- Wei-Li Hong
- , Marta E. Torres
- & Pavel Serov
-
Article
| Open Access River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans
River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans
Rivers provide a major pathway for ocean plastic waste, but effective mitigation is dependent on a quantification of active sources. Here, the authors present a global model of riverine plastic inputs, and estimate annual plastic waste of almost 2.5 million tonnes, with 86% sourced from Asia.
- Laurent C. M. Lebreton
- , Joost van der Zwet
- & Julia Reisser
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for fungal and chemodenitrification based N2O flux from nitrogen impacted coastal sediments
Evidence for fungal and chemodenitrification based N2O flux from nitrogen impacted coastal sediments
Predicting nitrous oxide emissions (N2O) remains difficult due to the numerous N2O production pathways. Here, the authors use incubations simulating high nitrate inputs to show that, in intertidal sediments, increases in N2O flux are largely mediated by fungal denitrification and/or chemodenitrification.
- Scott D. Wankel
- , Wiebke Ziebis
- & Karsten Zengler
-
Article
| Open Access Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits
Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits
Crystalline uraninite is believed to be the dominant form in uranium deposits. Here, the authors find that non-crystalline U(IV) generated through biologically mediated U(VI) reduction is the predominant U(IV)species in ore deposits, implying that biogenic processes are more important than previously thought.
- Amrita Bhattacharyya
- , Kate M. Campbell
- & Thomas Borch
-
Article
| Open Access Amazonian forest-savanna bistability and human impact
Amazonian forest-savanna bistability and human impact
Deforestation and edge effects around cleared areas impact forest stability. Here, the authors examine human impacts on Amazonian forest-savanna bistability and show that tree cover bimodality is enhanced in regions close to human activities and is nearly absent in regions unaffected by human activities.
- Bert Wuyts
- , Alan R. Champneys
- & Joanna I. House
-
Article
| Open Access Coral calcification in a changing World and the interactive dynamics of pH and DIC upregulation
Coral calcification in a changing World and the interactive dynamics of pH and DIC upregulation
Coral reefs are biologically diverse and productive ecosystems, yet our understanding of the impacts of ocean acidification on biocalcification is limited. Here, the authors show that pH upregulation and the biological control of dissolved inorganic carbon in calcifying fluids ofPoritescorals are linked.
- Malcolm T. McCulloch
- , Juan Pablo D’Olivo
- & Julie A. Trotter
-
Article
| Open Access Airborne observations reveal elevational gradient in tropical forest isoprene emissions
Airborne observations reveal elevational gradient in tropical forest isoprene emissions
Isoprene emissions are commonly estimated using satellite measurements and model simulations. Here, using eddy covariance, the authors report higher emission rates over the Amazon forest than those estimated with these techniques and a relationship between terrain elevation and isoprene emissions.
- Dasa Gu
- , Alex B. Guenther
- & Zhiyuan Hu
-
Article
| Open Access The effects of forest canopy shading and turbulence on boundary layer ozone
The effects of forest canopy shading and turbulence on boundary layer ozone
Fully quantifying the influence of vegetation on atmospheric chemistry remains challenging. Here, the authors show that forest canopy shading and turbulence significantly modify air pollution throughout the atmospheric boundary layer, and must be taken into account in models of the atmosphere.
- P. A. Makar
- , R. M. Staebler
- & Q. Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Global perturbation of organic carbon cycling by river damming
Global perturbation of organic carbon cycling by river damming
The damming of rivers has large impacts on the balance of riverine carbon (C) processes and fluxes to the oceans. Here, the authors use decadal riverine organic C loads and model C transformations to quantify in-reservoir organic C burial, mineralization and assess decreases in riverine exports to the oceans.
- Taylor Maavara
- , Ronny Lauerwald
- & Philippe Van Cappellen
-
Article
| Open Access Anthropogenic iron oxide aerosols enhance atmospheric heating
Anthropogenic iron oxide aerosols enhance atmospheric heating
Iron oxide nanoparticles contribute to shortwave absorption in the form of desert dust. Motekiet al. show that iron oxide particles of anthropogenic origin, potentially from motor vehicles and blast furnaces, also contribute to atmospheric heating over East Asia.
- Nobuhiro Moteki
- , Kouji Adachi
- & Yutaka Kondo
-
Article
| Open Access Dust-wind interactions can intensify aerosol pollution over eastern China
Dust-wind interactions can intensify aerosol pollution over eastern China
Anthropogenic aerosol and calm conditions give rise to winter haze episodes in eastern China. Yanget al. show that these weak winds also decrease natural dust emissions, reducing the land–ocean temperature difference and associated winds, enhancing air stagnation and pollution in this region.
- Yang Yang
- , Lynn M. Russell
- & Steven J. Ghan
-
Article
| Open Access Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line
Actively evolving subglacial conduits and eskers initiate ice shelf channels at an Antarctic grounding line
The formation mechanisms of ice-shelf channels remain poorly understood. Here, using ice-penetrating radar data, the authors propose that ice-shelf channel morphology in the Roi Baudouin Ice Shelf, East Antarctica, is seeded by esker ridges, indenting the ice from below.
- R. Drews
- , F. Pattyn
- & N. Neckel
-
Article
| Open Access Global distribution of particle phase state in atmospheric secondary organic aerosols
Global distribution of particle phase state in atmospheric secondary organic aerosols
Secondary organic aerosols (SOA) are important for climate and aerosol quality, but the phase state is unclear. Here, the authors show that SOA is liquid in tropical and polar air, semi-solid in the mid-latitudes, solid over dry lands and in a glassy solid phase state in the middle and upper troposphere.
- Manabu Shiraiwa
- , Ying Li
- & Ulrich Pöschl
-
Article
| Open Access Life cycle assessment needs predictive spatial modelling for biodiversity and ecosystem services
Life cycle assessment needs predictive spatial modelling for biodiversity and ecosystem services
Life cycle assessments are used by corporations to determine the sustainability of raw source materials. Here, Chaplin-Krameret al. develop an improved life cycle assessment approach incorporating spatial variation in land-use change, and apply this framework to a bioplastic case study.
- Rebecca Chaplin-Kramer
- , Sarah Sim
- & Gretchen Daily
-
Article
| Open Access Pathways for balancing CO2 emissions and sinks
Pathways for balancing CO2 emissions and sinks
COP21 led to a global commitment to decarbonization before 2100 to combat climate change, but leaves the timing and scale of mitigation efforts to individual countries. Here, the authors show that global carbon emissions need to peak within a decade to maintain realistic pathways for achieving the Paris Agreement.
- Brian Walsh
- , Philippe Ciais
- & Michael Obersteiner
-
Article
| Open Access Past penguin colony responses to explosive volcanism on the Antarctic Peninsula
Past penguin colony responses to explosive volcanism on the Antarctic Peninsula
Changes in penguin populations on the Antarctic Peninsula in recent decades have been linked to environmental factors such as sea ice. Here, the authors show that penguin colony change on Ardley Island, NW Antarctic Peninsula during the last 8,500 years was primarily driven by volcanic activity.
- Stephen J. Roberts
- , Patrick Monien
- & Dominic A. Hodgson
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term trends in the intensity and relative toxicity of herbicide use
Long-term trends in the intensity and relative toxicity of herbicide use
Quantifying the toxicity of herbicides applied in the field is difficult. Here, the author applies a quotient to evaluate changes in relative toxicity over the past 25 years and finds that increased herbicide use does not necessarily constitute increased toxicity.
- Andrew R. Kniss
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid electron transfer by the carbon matrix in natural pyrogenic carbon
Rapid electron transfer by the carbon matrix in natural pyrogenic carbon
Electron transfer reactions govern most biogeochemical processes, yet we have a limited knowledge of the electrochemistry of pyrogenic carbon, a major component of organic matter. Here, the authors quantify electron transfers between pyrogenic carbon and mineral phases under different pyrolysis temperatures.
- Tianran Sun
- , Barnaby D. A. Levin
- & Johannes Lehmann
-
Article
| Open Access Vulnerability of Louisiana’s coastal wetlands to present-day rates of relative sea-level rise
Vulnerability of Louisiana’s coastal wetlands to present-day rates of relative sea-level rise
Coastal Louisiana wetlands face some of the world’s highest rates of relative sea-level rise and loss. Here, the authors show that there is a strong regional component to coastal Louisiana wetland vulnerability to relative sea-level rise as well as contributing to the understanding of subsidence in the region.
- Krista L. Jankowski
- , Torbjörn E Törnqvist
- & Anjali M Fernandes
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental conditions regulate the impact of plants on cloud formation
Environmental conditions regulate the impact of plants on cloud formation
Volatile organic compounds (VOC) emitted by vegetation influence cloud formation, yet the impact of environmental stresses remains little known. Here, manipulation experiments reveal insect infestation and heat stress are linked to induced VOC and constitutive VOC emissions shifts, respectively.
- D. F. Zhao
- , A. Buchholz
- & Th. F. Mentel
-
Article
| Open Access Mismatch between marine plankton range movements and the velocity of climate change
Mismatch between marine plankton range movements and the velocity of climate change
Marine plankton are the basis of the oceanic food chain. Here, Chivers and colleagues use ocean-basin wide plankton population data over six decades to show huge differences in the response of different plankton groups to climate change with major implications for the marine ecosystem and fisheries.
- William J. Chivers
- , Anthony W. Walne
- & Graeme C. Hays
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular composition of organic matter controls methylmercury formation in boreal lakes
Molecular composition of organic matter controls methylmercury formation in boreal lakes
Neurotoxic methylmercury can be found in high levels in aquatic systems, but the role of organic matter in methylmercury formation is not well understood. Here, Bravoet al. show that plankton-derived organic compounds enhance formation rates in boreal lakes.
- Andrea G. Bravo
- , Sylvain Bouchet
- & Stefan Bertilsson
-
Article
| Open Access Proton pumping accompanies calcification in foraminifera
Proton pumping accompanies calcification in foraminifera
Despite their role in oceanic CaCO3production, the physiological processes responsible for calcification in foraminifera are poorly understood Here, the authors show that calcification is driven by rapid transformation of bicarbonate to carbonate inside the cytoplasm, achieved by active outward proton pumping.
- Takashi Toyofuku
- , Miki Y. Matsuo
- & Hiroshi Kitazato
-
Article
| Open Access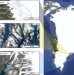 Ice sheets as a missing source of silica to the polar oceans
Ice sheets as a missing source of silica to the polar oceans
Glacial runoff often has relatively low dissolved silica concentrations and therefore ice sheets have been thought insignificant in the global silicon cycle. Here, the authors show that ice sheets likely play an important role in the production and export of dissolved and dissolvable amorphous silica downstream.
- Jon R. Hawkings
- , Jemma L. Wadham
- & Rob Raiswell
-
Article
| Open Access Super-emitters in natural gas infrastructure are caused by abnormal process conditions
Super-emitters in natural gas infrastructure are caused by abnormal process conditions
A large proportion of methane emissions from natural gas production sites are released by a fraction of high-emitting sources. Here, using Monte Carlo simulations, the authors reveal that super-emitters occur due to abnormal process conditions, explaining component and site-based inventory discrepancies.
- Daniel Zavala-Araiza
- , Ramón A Alvarez
- & Steven P. Hamburg
-
Article
| Open Access Observational evidence for cloud cover enhancement over western European forests
Observational evidence for cloud cover enhancement over western European forests
Forests impact continental-scale moisture recycling, but their impact on regional-scale cloud cover is little known. Here, using satellite observations, Teulinget al. illustrate enhanced cloud cover over regional forested areas in western Europe due to the establishment of a forest-breeze circulation.
- Adriaan J. Teuling
- , Christopher M. Taylor
- & Jordi Vilà-Guerau de Arellano
-
Article
| Open Access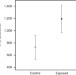 GABAergic anxiolytic drug in water increases migration behaviour in salmon
GABAergic anxiolytic drug in water increases migration behaviour in salmon
Fish migration is influenced by various environmental factors such as chemicals in water. Here, Hellstrom et al. show that an anxiolytic drug in the benzodiazepine family, oxazepam, can promote migratory behaviour of Atlantic salmon smolts in both laboratory setting and river tributary in Sweden.
- Gustav Hellström
- , Jonatan Klaminder
- & Tomas Brodin

 Polymorphic regenerated silk fibers assembled through bioinspired spinning
Polymorphic regenerated silk fibers assembled through bioinspired spinning