Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic data-driven design and 3D printing of custom ocular prostheses
Automatic data-driven design and 3D printing of custom ocular prostheses
Manual processes to produce ocular prostheses are time-consuming and yield varying quality. Here, authors present an automatic digital end-to-end process for custom ocular prostheses. It creates shape and appearance from image data of an OCT device and produces them using a full-colour 3D printer.
- Johann Reinhard
- , Philipp Urban
- & Mandeep S. Sagoo
-
Article
| Open Access Persistence in risk and effect of COVID-19 vaccination on long-term health consequences after SARS-CoV-2 infection
Persistence in risk and effect of COVID-19 vaccination on long-term health consequences after SARS-CoV-2 infection
The long-term health consequences of COVID-19 infection are not fully understood. In this retrospective cohort study from Hong Kong, the authors describe changes in the risk of various clinical outcomes including all-cause mortality for one year following COVID-19 infection and how they vary by vaccination status.
- Ivan Chun Hang Lam
- , Ran Zhang
- & Eric Yuk Fai Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid deep learning-assisted predictive diagnostics for point-of-care testing
Rapid deep learning-assisted predictive diagnostics for point-of-care testing
A key aim in the development of diagnostic assays is improving diagnostic speed while maintaining sensitivity. Here the authors report an approach for the rapid and accurate analysis of lateral flow tests, which integrates time-series deep learning and AI verification, achieving a diagnostic time of 1-2 minutes.
- Seungmin Lee
- , Jeong Soo Park
- & Jeong Hoon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Concordance of randomised controlled trials for artificial intelligence interventions with the CONSORT-AI reporting guidelines
Concordance of randomised controlled trials for artificial intelligence interventions with the CONSORT-AI reporting guidelines
The CONSORT-AI extension was developed to provide specific guidance for randomised controlled trials involving Artificial Intelligence (AI) interventions. Here, the authors show that since publication of CONSORT-AI, several AI-specific considerations remain systematically underreported.
- Alexander P. L. Martindale
- , Benjamin Ng
- & Xiaoxuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Data encoding for healthcare data democratization and information leakage prevention
Data encoding for healthcare data democratization and information leakage prevention
Healthcare data democratization is often hampered by privacy constraints governing the sensitive healthcare data. Here, the authors show that encoding healthcare data could be a potential solution for achieving healthcare democratization within the context of deep learning.
- Anshul Thakur
- , Tingting Zhu
- & David A. Clifton
-
Article
| Open Access Leisure engagement in older age is related to objective and subjective experiences of aging
Leisure engagement in older age is related to objective and subjective experiences of aging
The benefits of different leisure activities for different aspects of aging remain unclear. Here, authors show that performing physical or creative activities is associated with important aging metrics and could help to prevent age-related decline.
- Jessica K. Bone
- , Feifei Bu
- & Daisy Fancourt
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible and cost-effective genomic surveillance of P. falciparum malaria with targeted nanopore sequencing
Flexible and cost-effective genomic surveillance of P. falciparum malaria with targeted nanopore sequencing
Genomic surveillance of Plasmodium falciparum could improve monitoring of drug resistance, but implementation has been hampered due to the large and complex genome. Here, de Cesare et al. develop a flexible and cost-effective nanopore sequencing approach to detect drug resistance and diagnostic escape for P. falciparum malaria.
- Mariateresa de Cesare
- , Mulenga Mwenda
- & Jason A. Hendry
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing emergence risk of double-resistant and triple-resistant genotypes of Plasmodium falciparum
Assessing emergence risk of double-resistant and triple-resistant genotypes of Plasmodium falciparum
Emergence of malaria parasites resistant to artemisinin has prompted the need for new drug regimens to ensure effective treatment. In this simulation study, the authors evaluate the risk of multidrug resistance under regimens with either concurrent or cyclic use of different first-line therapies.
- Eric Zhewen Li
- , Tran Dang Nguyen
- & Maciej F. Boni
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic epidemiology reveals geographical clustering of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli ST131 associated with bacteraemia in Wales
Genomic epidemiology reveals geographical clustering of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli ST131 associated with bacteraemia in Wales
Escherichia coli ST131 is a globally dominant multidrug resistant clone associated with high rates of recurring urinary tract infections. In this genomic epidemiology study, the authors describe the evolution, population structure, and antimicrobial resistance in 142 E. coli ST131 samples from Wales, UK.
- Rhys T. White
- , Matthew J. Bull
- & Scott A. Beatson
-
Article
| Open Access A deep-learning-based framework for identifying and localizing multiple abnormalities and assessing cardiomegaly in chest X-ray
A deep-learning-based framework for identifying and localizing multiple abnormalities and assessing cardiomegaly in chest X-ray
Accurate localization of abnormalities is crucial in the interpretation of chest X-rays. Here the authors present a deep learning framework for simultaneous localization of 14 thoracic abnormalities and calculation of cardiothoracic ratio, based on large X-ray dataset with bounding boxes created via a human-in-the-loop approach.
- Weijie Fan
- , Yi Yang
- & Dong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Income determines the impact of cash transfers on HIV/AIDS: cohort study of 22.7 million Brazilians
Income determines the impact of cash transfers on HIV/AIDS: cohort study of 22.7 million Brazilians
Brazil has operated a conditional cash transfer program to support families living in precarious conditions since 2004. Here, the authors use linked administrative and health data to investigate the impacts of the program on HIV/AIDS-related outcomes, demonstrating strong positive associations.
- Andréa F. Silva
- , Inês Dourado
- & Davide Rasella
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative effectiveness of alternative intervals between first and second doses of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines
Comparative effectiveness of alternative intervals between first and second doses of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines
The optimal timing between first and second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses has not been established. Here, the authors use electronic health record data from Georgia, USA in a target trial emulation study to estimate vaccine effectiveness against infection for different dose intervals.
- Kayoko Shioda
- , Alexander Breskin
- & Elizabeth T. Rogawski McQuade
-
Article
| Open Access Contribution of climate change to the spatial expansion of West Nile virus in Europe
Contribution of climate change to the spatial expansion of West Nile virus in Europe
West Nile Virus is emerging as an important pathogen in Europe, likely driven by recent climate and land-use changes. Here, the authors estimate the extent of the climate change-driven impact by modelling the change in West Nile Virus ecological suitability across the continent in the absence of climate change.
- Diana Erazo
- , Luke Grant
- & Simon Dellicour
-
Article
| Open Access A multicenter clinical AI system study for detection and diagnosis of focal liver lesions
A multicenter clinical AI system study for detection and diagnosis of focal liver lesions
Early detection and accurate diagnosis of focal liver lesions are crucial for effective treatment and prognosis. Here, the authors present a fully automated diagnostic system that leverages multi-phase CT scans and clinical features, for diagnosing liver lesions.
- Hanning Ying
- , Xiaoqing Liu
- & Xiujun Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the risk and speed of drug resistance emerging in soil-transmitted helminths during preventive chemotherapy
Predicting the risk and speed of drug resistance emerging in soil-transmitted helminths during preventive chemotherapy
Resistance to chemotherapy for soil-transmitted helminth infection has been detected in veterinary settings but not yet in human infections. Here, the authors investigate the risk of resistance in humans and how it may change as a result of scaling-up preventative deworming programs.
- Luc E. Coffeng
- , Wilma A. Stolk
- & Sake J. de Vlas
-
Article
| Open Access Early onset diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease patients via amyloid-β oligomers-sensing probe in cerebrospinal fluid
Early onset diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease patients via amyloid-β oligomers-sensing probe in cerebrospinal fluid
In this work, the authors characterize a small molecule fluorescent probe pioneering early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease through identification of amyloid-β oligomers in patients’ cerebrospinal fluid, demonstrating potential for clinical application.
- Jusung An
- , Kyeonghwan Kim
- & Jong Seung Kim
-
Editorial
| Open AccessHealth in Africa
Africa is undergoing a demographic transition
1 that has led to significant reductions in the number of individuals living in extreme poverty, and to positive shifts in related health outcomes, across its diverse populations2 . Building on these successes requires a consideration of intersecting factors that impact health metrics, which is the focus of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals3 . To support researchers in their efforts towards reaching these goals, Nature Communications, Communications Medicine and Scientific Reports invite submissions of papers that advance our understanding of all aspects of health in Africa. -
Article
| Open Access Congenital heart disease detection by pediatric electrocardiogram based deep learning integrated with human concepts
Congenital heart disease detection by pediatric electrocardiogram based deep learning integrated with human concepts
Congenital heart disease is life threatening, and its screening is complex and costly. Here, authors use AI to detect the disease based on pediatric electrocardiogram, suggesting superior performance over cardiologists.
- Jintai Chen
- , Shuai Huang
- & Huiying Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Maternal pertussis immunization and the blunting of routine vaccine effectiveness: a meta-analysis and modeling study
Maternal pertussis immunization and the blunting of routine vaccine effectiveness: a meta-analysis and modeling study
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women has been introduced to protect newborns, but immunological evidence suggests that this lessens subsequent infant immune response to vaccination. Here, the authors assess the epidemiological impacts of both consequences of maternal immunisation on infant infection.
- Michael Briga
- , Elizabeth Goult
- & Matthieu Domenech de Cellès
-
Article
| Open Access Dimethyl fumarate in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial
Dimethyl fumarate in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) is an anti-inflammatory drug proposed as a treatment for COVID19. Here the results are reported from a randomised trial testing DMF treatment in 713 patients hospitalised with COVID-19. DMF was not associated with any improvement in day 5 outcomes.
- Peter Sandercock
- , Janet Darbyshire
- & Martin J. Landray
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal quantification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals late colonization in the infant gut independent of maternal milk HMO composition
Longitudinal quantification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals late colonization in the infant gut independent of maternal milk HMO composition
Here, the authors develop a high-throughput method to quantify Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis (BL. infantis), a proficient HMO-utilizer, from metagenomic sequencing, and applied it to a longitudinal cohort consisting of 21 mother-infant dyads, suggesting BL. infantis colonization to start late in the breast-feeding period.
- Dena Ennis
- , Shimrit Shmorak
- & Moran Yassour
-
Comment
| Open AccessAfrican leadership is critical in responding to public health threats
The African continent demonstrated decisive leadership throughout its response to the COVID-19 pandemic, leveraging lessons learned from previous outbreaks and acting quickly to limit the impact of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. We propose a framework to build on these successes that calls for greater collaboration between African leaders, and greater inclusion of African voices in the global health ecosystem.
- Nicaise Ndembi
- , Aggrey Aluso
- & Jean Kaseya
-
Article
| Open Access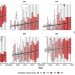 Global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in food animals using priority drugs maps
Global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in food animals using priority drugs maps
Monitoring antimicrobial resistance in food animals is challenging due to limited surveillance systems. Here, the authors combine data from point prevalence surveys in lower- and middle-income settings to map resistance to seven antimicrobials and predict which are likely to exceed key resistance thresholds.
- Cheng Zhao
- , Yu Wang
- & Thomas P. Van Boeckel
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and visual identification of β-lactamase subtypes for precision antibiotic therapy
Rapid and visual identification of β-lactamase subtypes for precision antibiotic therapy
The rapid identification of drug-resistant bacteria is vital for effective treatment and to avoid antibiotic misuse. Here authors report a paper-based sensor which utilises chromogenic carbapenem and cephalosporin substrates for the identification and discrimination of β-lactamase subtypes.
- Wenshuai Li
- , Jingqi Li
- & Dingbin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Segment anything in medical images
Segment anything in medical images
Segmentation is an important fundamental task in medical image analysis. Here the authors show a deep learning model for efficient and accurate segmentation across a wide range of medical image modalities and anatomies.
- Jun Ma
- , Yuting He
- & Bo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access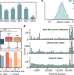 Using big sequencing data to identify chronic SARS-Coronavirus-2 infections
Using big sequencing data to identify chronic SARS-Coronavirus-2 infections
Chronic SARS-CoV-2 infections have been hypothesised to be sources of new variants. Here, the authors use large-scale genome sequencing data to identify mutations predictive of chronic infections, which may therefore be relevant in future variants.
- Sheri Harari
- , Danielle Miller
- & Adi Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Markets as drivers of selection for highly virulent poultry pathogens
Markets as drivers of selection for highly virulent poultry pathogens
Live poultry markets in rural areas can be hotspots for transmission of pathogens, but the effects of markets on selection of viral virulence are not known. This study demonstrates through mathematical modelling that high turnover rate and persistence of viral particles can select for highly virulent pathogens in markets.
- Justin K. Sheen
- , Fidisoa Rasambainarivo
- & C. Jessica E. Metcalf
-
Article
| Open Access Determinants of epidemic size and the impacts of lulls in seasonal influenza virus circulation
Determinants of epidemic size and the impacts of lulls in seasonal influenza virus circulation
Seasonal influenza levels were unusually low when non-pharmaceutical interventions for COVID-19 were in place. Here, the authors analyse serological and epidemiological evidence for the hypothesis that such lulls in influenza transmission lead to reduced immunity and therefore larger epidemics in subsequent seasons.
- Simon P. J. de Jong
- , Zandra C. Felix Garza
- & Colin A. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access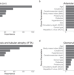 A Machine Learning-Driven Virtual Biopsy System For Kidney Transplant Patients
A Machine Learning-Driven Virtual Biopsy System For Kidney Transplant Patients
Despite being recommended, day-zero biopsies are often not performed, due to the cost and time. Here, the authors show that machine learning and donor’s basic parameters can predict the biopsy, offering a reliable virtual estimation of the day-zero biopsy findings.
- Daniel Yoo
- , Gillian Divard
- & Alexandre Loupy
-
Article
| Open Access Dermatologist-like explainable AI enhances trust and confidence in diagnosing melanoma
Dermatologist-like explainable AI enhances trust and confidence in diagnosing melanoma
Artificial intelligence has become popular as a cancer classification tool, but there is distrust of such systems due to their lack of transparency. Here, the authors develop an explainable AI system which produces text- and region-based explanations alongside its classifications which was assessed using clinicians’ diagnostic accuracy, diagnostic confidence, and their trust in the system.
- Tirtha Chanda
- , Katja Hauser
- & Titus J. Brinker
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic detection of co-infection and intra-host recombination in more than 2 million global SARS-CoV-2 samples
Systematic detection of co-infection and intra-host recombination in more than 2 million global SARS-CoV-2 samples
SARS-CoV-2 coinfections may lead to recombination events which could be important in the emergence of new variants. Here, the authors develop an automated bioinformatics pipeline to identify coinfections in genomic data and test it on >2 million publicly available raw read data sets collected globally.
- Orsolya Anna Pipek
- , Anna Medgyes-Horváth
- & István Csabai
-
Article
| Open Access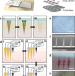 Digital automation of transdermal drug delivery with high spatiotemporal resolution
Digital automation of transdermal drug delivery with high spatiotemporal resolution
Microneedle patches that can actively address individual needles are challenging to realize. Here, the authors introduce a spatiotemporal on-demand patch for precise and personalized drug delivery, utilizing electrically triggered control with drug-loaded microneedles and biocompatible metallic membranes.
- Yihang Wang
- , Zeka Chen
- & Wubin Bai
-
Article
| Open Access A randomized trial looking at planning prompts to reduce opioid prescribing
A randomized trial looking at planning prompts to reduce opioid prescribing
A personalized letter from the Medical Examiner-Coroner in Los Angeles County has proven effective at reducing opioid and benzodiazepine prescribing. Here the authors show that the introduction of if/when-then planning prompts in to the letter further reduced opioid prescribing by 12.85% and benzodiazepine prescribing by 8.32%; they were most effective for clinicians with multiple patient deaths due to accidental opioid-related overdose.
- Jason N. Doctor
- , Marcella A. Kelley
- & Emily P. Stewart
-
Article
| Open Access Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Prelithiation can introduce controllable amounts of lithium within porous silicon, however it yields a highly reactive material unsuitable for biomedicine. In this study, the authors present a strategy to lithiate porous silicon nanowires, resulting in a biocompatible and bioresorbable material.
- Martti Kaasalainen
- , Ran Zhang
- & Ciro Chiappini
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous artificial intelligence increases screening and follow-up for diabetic retinopathy in youth: the ACCESS randomized control trial
Autonomous artificial intelligence increases screening and follow-up for diabetic retinopathy in youth: the ACCESS randomized control trial
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that can be prevented through screening, yet adherence is low. Here, the authors show that autonomous AI increases diabetic eye exam completion in a diverse cohort of youth with diabetes.
- Risa M. Wolf
- , Roomasa Channa
- & Michael D. Abramoff
-
Article
| Open Access Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Many diseases can display distinct brain imaging phenotypes across individuals, potentially reflecting disease subtypes. However, biological interpretability is limited if the derived subtypes are not associated with genetic drivers or susceptibility factors. Here, the authors describe a deep-learning method that links imaging phenotypes with genetic factors, thereby conferring genetic correlations to the disease subtypes.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Junhao Wen
- & Christos Davatzikos
-
Article
| Open Access Convergence of resistance and evolutionary responses in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica co-inhabiting chicken farms in China
Convergence of resistance and evolutionary responses in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica co-inhabiting chicken farms in China
Bacteria in the same environment can share genetic material but the extent to which this influences development of antimicrobial resistance is unclear. Here, the authors investigate the evidence for co-evolution of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria found coexisting in animals and the environment in chicken farms and slaughterhouses in China.
- Michelle Baker
- , Xibin Zhang
- & Tania Dottorini
-
Article
| Open Access Quick model-based viscoelastic clot strength predictions from blood protein concentrations for cybermedical coagulation control
Quick model-based viscoelastic clot strength predictions from blood protein concentrations for cybermedical coagulation control
Available viscoelastic models of blood flow and blood coagulation are unsuited for a cybermedical input-output type of control system application. Here the authors present validated viscoelastic coagulation models that use quickly-measurable protein concentrations to forecast slow clot strength curves for future automation.
- Damon E. Ghetmiri
- , Alessia J. Venturi
- & Amor A. Menezes
-
Article
| Open Access AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
The unequal distribution of medical resources means that bronchoscopic services are often unavailable in underdeveloped areas. Here, the authors present an AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot that features a user-friendly plug-and-play catheter and an AI-human shared control algorithm, to enable novice doctors to conduct lung examinations safely.
- Jingyu Zhang
- , Lilu Liu
- & Haojian Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic predictors of COVID-19 vaccination uptake and their interconnections over two years in Hong Kong
Dynamic predictors of COVID-19 vaccination uptake and their interconnections over two years in Hong Kong
Understanding factors associated with COVID-19 vaccine uptake in an evolving pandemic context is important for future vaccine campaigns. Here, the authors investigate the main drivers of vaccine hesitancy in Hong Kong at different stages of the pandemic, where uptake was initially low despite high availability.
- Jiehu Yuan
- , Yucan Xu
- & Qiuyan Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 in the treatment of functional dyspepsia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 in the treatment of functional dyspepsia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common chronic gastrointestinal disorder. Here, in a randomized, parallel-group, positive-drug, and placebo-controlled clinical trial, the authors show that supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 (BL-99) improves FD clinical response rate and promotes accumulation of SCFA-producing microbiota.
- Qi Zhang
- , Guang Li
- & Fazheng Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbiota facilitate chronic spontaneous urticaria
Gut microbiota facilitate chronic spontaneous urticaria
Chronic spontaneous urticarial is an inflammatory skin disease which has been linked to intestinal dysbiosis. Here the authors implicate intestinal dysbiosis with the inflammatory response in a murine model of urticaria.
- Lei Zhu
- , Xingxing Jian
- & Jie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Mucosal TLR5 activation controls healthspan and longevity
Mucosal TLR5 activation controls healthspan and longevity
Understanding how the immune system’s functionality declines with age is crucial for addressing aging-related health issues. Here, the authors demonstrate that activating TLR5 in the mucosal layer can significantly improve healthspan and longevity, suggesting a novel approach for aging interventions.
- Jae Sung Lim
- , Eun Jae Jeon
- & Kyung A Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Incidence and transmission of respiratory syncytial virus in urban and rural South Africa, 2017-2018
Incidence and transmission of respiratory syncytial virus in urban and rural South Africa, 2017-2018
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes a high burden of disease in children, particularly in lower- and middle-income countries. In this prospective household-based observational cohort study in South Africa, the authors estimate the incidence of RSV and identify risk factors for transmission.
- Cheryl Cohen
- , Jackie Kleynhans
- & Stefano Tempia
-
Article
| Open Access Myeloid-derived grancalcin instigates obesity-induced insulin resistance and metabolic inflammation in male mice
Myeloid-derived grancalcin instigates obesity-induced insulin resistance and metabolic inflammation in male mice
The mechanism by which the cross-talk between bone and adipose tissue regulates metabolic homeostasis is unknown. Here, the authors show a mechanism whereby bone marrow factor GCA initiates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance, showing how GCA targeting could potentially treat metainflammation.
- Tian Su
- , Yue He
- & Xianghang Luo
-
Article
| Open Access BCG vaccination-induced acquired control of mycobacterial growth differs from growth control preexisting to BCG vaccination
BCG vaccination-induced acquired control of mycobacterial growth differs from growth control preexisting to BCG vaccination
Bacillus Calmette-Guèrin vaccination prevents tuberculosis but some individuals control infection without immunization. Here the authors employ functional assessment of effector responses against mycobacteria to find that distinct gene expression profiles for pre-existing capacity to control and control induced by BCG vaccination.
- Krista E. van Meijgaarden
- , Wenchao Li
- & Simone A. Joosten
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitatively assessing early detection strategies for mitigating COVID-19 and future pandemics
Quantitatively assessing early detection strategies for mitigating COVID-19 and future pandemics
Monitoring samples from hospital patients, wastewater, or air travel may enable early detection of pathogens. Here, the authors assess how these surveillance systems could have impacted detection of COVID-19 and their potential benefits for detection of other emerging pathogens.
- Andrew Bo Liu
- , Daniel Lee
- & Michael Springer
-
Article
| Open AccessDietary circadian rhythms and cardiovascular disease risk in the prospective NutriNet-Santé cohort
The relation between daily meal and fasting timing with cardiovascular disease incidence remains unclear. Here, authors show that a later daily meal timing is associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk, especially in women. This study suggests that adopting earlier daily eating patterns may be beneficial for cardiovascular prevention.
- Anna Palomar-Cros
- , Valentina A. Andreeva
- & Bernard Srour
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinomas (cHCC-CCA) are challenging to diagnose, as they exhibit features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICCA). Here, the authors use deep learning to re-classify cHCC-CCA tumours into HCC or ICCA based on histopathology images.
- Julien Calderaro
- , Narmin Ghaffari Laleh
- & Jakob Nikolas Kather

 Dispersion patterns of SARS-CoV-2 variants Gamma, Lambda and Mu in Latin America and the Caribbean
Dispersion patterns of SARS-CoV-2 variants Gamma, Lambda and Mu in Latin America and the Caribbean