Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cold-induced urticarial autoinflammatory syndrome related to factor XII activation
Cold-induced urticarial autoinflammatory syndrome related to factor XII activation
Systemic autoinflammatory syndromes such as cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS) are rare and often involve genes related to the inflammasome. Here, the authors report a syndrome characterised by systemic inflammation and cold-induced urticarial rash associated with a Factor XII-activating mutation.
- Jörg Scheffel
- , Niklas A. Mahnke
- & Karoline Krause
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into malaria susceptibility using genome-wide data on 17,000 individuals from Africa, Asia and Oceania
Insights into malaria susceptibility using genome-wide data on 17,000 individuals from Africa, Asia and Oceania
Four genome-wide associated loci are currently known for malaria susceptibility. Here, the authors expand on earlier work by combining data from 11 malaria-endemic countries and additional population sequencing informing an African-enriched imputation reference panel, with findings including a previously unreported association on chromosome 6.
- Gavin Band
- , Quang Si Le
- & Dominic P. Kwiatkowski
-
Article
| Open Access A network-based approach to identify deregulated pathways and drug effects in metabolic syndrome
A network-based approach to identify deregulated pathways and drug effects in metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by complex phenotypes that increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Here the authors’ integrative network analysis suggests BTK inhibitor ibrutinib to be a promising treatment through its obesity-associated inflammation lowering effect.
- Karla Misselbeck
- , Silvia Parolo
- & Corrado Priami
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis reveals genomic loci stratified by ANCA status
Genome-wide association study of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis reveals genomic loci stratified by ANCA status
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare inflammatory disorder characterised by asthma, eosinophilia and vasculitis. Here, the authors describe a genome-wide association study of EGPA that reveals clinical and genetic differences between subgroups stratified by autoantibody status (ANCA).
- Paul A Lyons
- , James E Peters
- & Kenneth G. C. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Synergized regulation of NK cell education by NKG2A and specific Ly49 family members
Synergized regulation of NK cell education by NKG2A and specific Ly49 family members
MHC-I-induced signalling of various natural killer (NK) inhibitory receptors is critical for regulation NK cell education, but clear genetic evidence is still lacking. Here the authors generate multiple lines of mice differentially deficient in Ly49 family and/or NKG2A NK receptors, and find that self-MHCI specific Ly49 members and NKG2A synergize to regulate NK education.
- Xiaoqian Zhang
- , Jin Feng
- & Zhongjun Dong
-
Article
| Open Access A human immune dysregulation syndrome characterized by severe hyperinflammation with a homozygous nonsense Roquin-1 mutation
A human immune dysregulation syndrome characterized by severe hyperinflammation with a homozygous nonsense Roquin-1 mutation
Roquin-1 is a posttranscriptional regulator that controls the expression of many immune-related genes such as ICOS and TNFA. Here, the authors report a homozygous R688* loss of function mutation in Roquin-1 in a patient with syndromic uncontrolled hyperinflammation associated with immune cell activation and hypercytokinemia.
- S. J. Tavernier
- , V. Athanasopoulos
- & F. Haerynck
-
Article
| Open Access Context-specific regulation of surface and soluble IL7R expression by an autoimmune risk allele
Context-specific regulation of surface and soluble IL7R expression by an autoimmune risk allele
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) is a central cytokine in T cell homeostasis. Here the authors show that allelic variation at rs6897932, an autoimmune GWAS risk allele at IL7R, regulates surface and soluble IL-7R in stimulated monocytes, indicating a function of monocytes in IL-7-related autoimmunity.
- Hussein Al-Mossawi
- , Nicole Yager
- & Benjamin P. Fairfax
-
Article
| Open Access ImmGen report: sexual dimorphism in the immune system transcriptome
ImmGen report: sexual dimorphism in the immune system transcriptome
Sexual dimorphism is observed frequently in immune disorders, but the underlying insights are still unclear. Here the authors analyze transcriptome and epigenome changes induced by interferon in various mouse immune cell types, and find only a restricted set of sexual dimorphism genes in innate immunity and macrophages.
- Shani Talia Gal-Oz
- , Barbara Maier
- & Tal Shay
-
Article
| Open Access DNA methylation loss promotes immune evasion of tumours with high mutation and copy number load
DNA methylation loss promotes immune evasion of tumours with high mutation and copy number load
Demethylation of the genome is found in cancer. Here, the authors show that genomic demethylation entails changes in promoter methylation and gene expression associated with immune escape and suggest that the epigenetic alterations may be an important determinant of responses to immunotherapy.
- Hyunchul Jung
- , Hong Sook Kim
- & Jung Kyoon Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Early progression to active tuberculosis is a highly heritable trait driven by 3q23 in Peruvians
Early progression to active tuberculosis is a highly heritable trait driven by 3q23 in Peruvians
Between 5 and 15% of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections develop into active tuberculosis (TB). Here, Luo et al. report a genome-wide association study for early TB progression in a total of 4002 active TB cases and their household contacts in Peru and they identify a locus on 3q23 in which ATP1B3 is mapped as the likely causal gene.
- Yang Luo
- , Sara Suliman
- & Soumya Raychaudhuri
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of drug-specific public TCR driving severe cutaneous adverse reactions
Identification of drug-specific public TCR driving severe cutaneous adverse reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) is a T cell-mediated, potentially lethal drug hypersensitivity (DH). Here, the authors identify a carbamazepine-specific TCR common among patients with carbamazepine-induced SCAR that confers SCAR-like pathology in mice upon carbamazepine exposure, thereby implicating specific TCRs in DH etiology.
- Ren-You Pan
- , Mu-Tzu Chu
- & Shuen-Iu Hung
-
Article
| Open Access Stochastic search and joint fine-mapping increases accuracy and identifies previously unreported associations in immune-mediated diseases
Stochastic search and joint fine-mapping increases accuracy and identifies previously unreported associations in immune-mediated diseases
Statistical fine-mapping to pinpoint likely causal variants in a genomic region is complicated by linkage disequilibrium (LD). Here, Asimit et al. compare stepwise and stochastic approaches to fine-mapping and propose a Bayesian multinomial stochastic search method which they apply to six immune-mediated diseases.
- Jennifer L. Asimit
- , Daniel B. Rainbow
- & Chris Wallace
-
Article
| Open Access Functional rare and low frequency variants in BLK and BANK1 contribute to human lupus
Functional rare and low frequency variants in BLK and BANK1 contribute to human lupus
Function-altering variants of immune-related genes cause rare autoimmune syndromes, whereas their contribution to common autoimmune diseases remains uncharacterized. Here the authors show that rare variants of lupus-associated genes are present in the majority of lupus patients and healthy controls, but only the variants found in lupus patients alter gene function.
- Simon H. Jiang
- , Vicki Athanasopoulos
- & Carola G. Vinuesa
-
Article
| Open Access Joint sequencing of human and pathogen genomes reveals the genetics of pneumococcal meningitis
Joint sequencing of human and pathogen genomes reveals the genetics of pneumococcal meningitis
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a causative agent of meningitis and bacteremia. In a combined pathogen and host GWAS, Lees et al. find that host genetic variation is associated with both susceptibility and severity of pneumococcal meningitis, and specific bacterial genetic variation associated with susceptibility.
- John A. Lees
- , Bart Ferwerda
- & Diederik van de Beek
-
Article
| Open Access Interferon inducible X-linked gene CXorf21 may contribute to sexual dimorphism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Interferon inducible X-linked gene CXorf21 may contribute to sexual dimorphism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) shows a striking bias towards higher prevalence in females. Here, the authors perform fine-mapping of an SLE-associated locus at Xp21.2 and characterise a candidate gene, CXorf21, as IFN-responsive in immune cells that shows sexually dimorphic expression.
- Christopher A. Odhams
- , Amy L. Roberts
- & Timothy J. Vyse
-
Article
| Open Access Defining the genetic and evolutionary architecture of alternative splicing in response to infection
Defining the genetic and evolutionary architecture of alternative splicing in response to infection
Genetic ancestry might influence immunological response to infection at different regulatory levels. Here, the authors use RNA-Seq to investigate the variability of alternative splicing patterns in resting and stimulated monocytes of African- and European-descent.
- Maxime Rotival
- , Hélène Quach
- & Lluis Quintana-Murci
-
Article
| Open Access A CRISPR-Cas9 delivery system for in vivo screening of genes in the immune system
A CRISPR-Cas9 delivery system for in vivo screening of genes in the immune system
The use of functional genomics in primary immune cells has been limited by inefficient vector delivery and risk of perturbing cell states. Here the authors present CHimeric IMmune Editing (CHIME) for in vivo evaluation of gene function and pooled screening approaches.
- Martin W. LaFleur
- , Thao H. Nguyen
- & Arlene H. Sharpe
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study in frontal fibrosing alopecia identifies four susceptibility loci including HLA-B*07:02
Genome-wide association study in frontal fibrosing alopecia identifies four susceptibility loci including HLA-B*07:02
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) features lichenoid cutaneous inflammation and scarring hair loss. Here, Tziotzios et al. identify four genetic loci associated with FFA by GWAS followed by Bayesian fine-mapping, co-localisation and HLA imputation which highlights HLA-B*07:02 as a risk factor.
- Christos Tziotzios
- , Christos Petridis
- & John A. McGrath
-
Article
| Open Access Genome wide analysis for mouth ulcers identifies associations at immune regulatory loci
Genome wide analysis for mouth ulcers identifies associations at immune regulatory loci
Oral ulcerations are sores of the mucous membrane of the mouth and highly prevalent in the population. Here, in a genome-wide association study, the authors identify 97 loci associated with mouth ulcers highlighting genes involved in T cell-mediated immunity and TH1 responses.
- Tom Dudding
- , Simon Haworth
- & Nicholas J. Timpson
-
Article
| Open Access Association study in African-admixed populations across the Americas recapitulates asthma risk loci in non-African populations
Association study in African-admixed populations across the Americas recapitulates asthma risk loci in non-African populations
The burden of asthma varies between ancestries, but GWAS have so far focused on mainly European ancestry populations. Here, Daya et al. perform GWAS for asthma in 14,654 individuals of African ancestry and, besides confirming previously known loci, identify two potentially African ancestry-specific loci.
- Michelle Daya
- , Nicholas Rafaels
- & Maria Yazdanbakhsh
-
Article
| Open Access Mosaic deletion patterns of the human antibody heavy chain gene locus shown by Bayesian haplotyping
Mosaic deletion patterns of the human antibody heavy chain gene locus shown by Bayesian haplotyping
High-throughput sequencing and analyzes of antibody repertoire provide important information on immune responses, but current methodologies are limited in sequence assembly precision and haplotype inference validity. Here the authors propose a new Bayesian haplotyping method, and attest its broad application with a large, multi-individual dataset.
- Moriah Gidoni
- , Omri Snir
- & Gur Yaari
-
Article
| Open Access TGFβ/BMP immune signaling affects abundance and function of C. elegans gut commensals
TGFβ/BMP immune signaling affects abundance and function of C. elegans gut commensals
Host genetics modulates gut microbiota composition, which in turn affects host health, but little is known about the specific genes involved. Here, Berg et al. show that TGFβ/BMP immune signalling affects abundance and function of commensal Enterobacter species in C. elegans.
- Maureen Berg
- , David Monnin
- & Michael Shapira
-
Article
| Open Access Early-onset autoimmune vitiligo associated with an enhancer variant haplotype that upregulates class II HLA expression
Early-onset autoimmune vitiligo associated with an enhancer variant haplotype that upregulates class II HLA expression
GWAS have led to the identification of 49 genetic loci associated with vitiligo. Here, the authors observe a bimodal distribution of age-of-onset and find a novel genetic locus specifically associated with early-onset vitiligo, located in a regulatory element in the MHC class II region.
- Ying Jin
- , Genevieve H. L. Roberts
- & Richard A. Spritz
-
Article
| Open Access Proteasomal degradation of NOD2 by NLRP12 in monocytes promotes bacterial tolerance and colonization by enteropathogens
Proteasomal degradation of NOD2 by NLRP12 in monocytes promotes bacterial tolerance and colonization by enteropathogens
Mutations in nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 12 (NLRP12) are known to effect inflammatory processes. Here the authors show that NLRP12-mediated proteasomal degradation of NOD2 in monocytes promotes bacterial tolerance and colonisation in a model of enteric infection.
- Sylvain Normand
- , Nadine Waldschmitt
- & Mathias Chamaillard
-
Article
| Open Access HLA-B57 micropolymorphism defines the sequence and conformational breadth of the immunopeptidome
HLA-B57 micropolymorphism defines the sequence and conformational breadth of the immunopeptidome
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) are multi-allelic and polymorphic genes that present antigens to immune cells for inducing protective immunity. Here, using systems biology and structural approaches, the authors show that micropolymorphism of three HLA has effects beyond the modulation of antigen diversity.
- Patricia T. Illing
- , Phillip Pymm
- & Anthony W. Purcell
-
Article
| Open Access A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease
A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease
Mutations in genes encoding NAPDH oxidase subunits are known to be causative for the primary immunodeficiency chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Here, the authors identify CYBC1 mutations in patients with CGD and show that CYBC1 is important for formation of the NADPH complex and respiratory burst.
- Gudny A. Arnadottir
- , Gudmundur L. Norddahl
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Sequencing HIV-neutralizing antibody exons and introns reveals detailed aspects of lineage maturation
Sequencing HIV-neutralizing antibody exons and introns reveals detailed aspects of lineage maturation
Knowledge on how antibody responses have evolved is critical for the induction of protective immunity. Here the authors analyse, using high-throughput sequencing of both exon and intron regions, the mutation and lineage development of an HIV-neutralizing antibody to find an unexpected early emergence of broadly neutralizing species.
- Erik L. Johnson
- , Nicole A. Doria-Rose
- & George Georgiou
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study identifies two risk loci for tuberculosis in Han Chinese
Genome-wide association study identifies two risk loci for tuberculosis in Han Chinese
Genetic risk loci for tuberculosis (TB) have so far been identified in African and Russian populations. Here, the authors perform a three-stage GWAS for TB in Han Chinese populations and find two risk loci near ESRRB and TGM6 and further demonstrate that tgm6 protects mice from Mtb infection.
- Ruijuan Zheng
- , Zhiqiang Li
- & Baoxue Ge
-
Article
| Open Access IBD risk loci are enriched in multigenic regulatory modules encompassing putative causative genes
IBD risk loci are enriched in multigenic regulatory modules encompassing putative causative genes
Most of the more than 200 known genetic risk loci for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) reside in regulatory regions. Here, the authors provide eQTL datasets for six circulating immune cell types and ileal, colonic and rectal biopsies to map regulatory modules and identify potential causative genes for IBD.
- Yukihide Momozawa
- , Julia Dmitrieva
- & Michel Georges
-
Article
| Open Access AID/APOBEC-like cytidine deaminases are ancient innate immune mediators in invertebrates
AID/APOBEC-like cytidine deaminases are ancient innate immune mediators in invertebrates
The AID/APOBEC cytidine deaminase family are nucleic acid editors, important for antigen receptor expression and thought to have evolved along with vertebrate adaptive immunity. Here the authors show this family may have evolved prior to adaptive immunity as members with cytidine deaminase activity are present and functional in invertebrate sea urchins and brachiopods.
- Mei-Chen Liu
- , Wen-Yun Liao
- & Sebastian D. Fugmann
-
Article
| Open Access B cell activation and plasma cell differentiation are inhibited by de novo DNA methylation
B cell activation and plasma cell differentiation are inhibited by de novo DNA methylation
DNA methylation is known to contribute to B cell differentiation, but de novo methylation has not been studied in this context. Here the authors use a conditional Dnmt3a/b knockout mouse to map the function of de novo DNA methylation in B cell differentiation and the development of humoral immunity.
- Benjamin G. Barwick
- , Christopher D. Scharer
- & Jeremy M. Boss
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient DNA study reveals HLA susceptibility locus for leprosy in medieval Europeans
Ancient DNA study reveals HLA susceptibility locus for leprosy in medieval Europeans
Leprosy, caused by infection with Mycobacterium leprae, was common in Europe in the Middle Ages. Here, Krause-Kyora et al. analyze ancient DNA from a medieval Danish leprosarium to assemble 10 complete bacterial genomes and perform association analysis of the DRB1*15:01 allele with risk of leprosy infection.
- Ben Krause-Kyora
- , Marcel Nutsua
- & Almut Nebel
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput immune repertoire analysis with IGoR
High-throughput immune repertoire analysis with IGoR
B and T cell receptor diversity can be studied by high-throughput immune receptor sequencing. Here, the authors develop a software tool, IGoR, that calculates the likelihoods of potential V(D)J recombination and somatic hypermutation scenarios from raw immune sequence reads.
- Quentin Marcou
- , Thierry Mora
- & Aleksandra M. Walczak
-
Article
| Open Access Type I interferon-mediated autoinflammation due to DNase II deficiency
Type I interferon-mediated autoinflammation due to DNase II deficiency
Nucleic acid sensing is important to ensure that an innate immune response is only mounted against microbial nucleic acid. Here, the authors identify loss-of-function mutations in the DNASE2 gene that cause type I interferon-mediated autoinflammation due to enhanced systemic interferon signaling.
- Mathieu P. Rodero
- , Alessandra Tesser
- & Yanick J. Crow
-
Article
| Open Access Three distinct developmental pathways for adaptive and two IFN-γ-producing γδ T subsets in adult thymus
Three distinct developmental pathways for adaptive and two IFN-γ-producing γδ T subsets in adult thymus
Mouse γδ T cells have diverse functional subsets, but how these subsets are programmed during their development is still unclear. Here the authors show that three surface markers, CD117, CD200 and CD371, refine the development of γδ T cells in the thymus into three pathways programming distinct γδ T cell subsets.
- Terkild Brink Buus
- , Niels Ødum
- & Jens Peter Holst Lauritsen
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study of classical Hodgkin lymphoma identifies key regulators of disease susceptibility
Genome-wide association study of classical Hodgkin lymphoma identifies key regulators of disease susceptibility
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer that originates in lymph nodes. Little is known about its genetic susceptibility. Here, the authors combined existing and new genome-wide association studies to identify risk loci for classical Hodgkin lymphoma at 6q22.33, and nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma at 3q28, 6q23.3, 10p14, 13q34, 16p13.13.
- Amit Sud
- , Hauke Thomsen
- & Richard S. Houlston
-
Article
| Open Access T cell receptor β-chains display abnormal shortening and repertoire sharing in type 1 diabetes
T cell receptor β-chains display abnormal shortening and repertoire sharing in type 1 diabetes
T cell receptors are generated by somatic gene recombination, and are normally selected against autoreactivity. Here the authors show that CD4 T cells from patients with autoimmune type 1 diabetes have shorter TCRβ sequences, broader repertoire diversity, and more repertoire sharing than those from healthy individuals.
- Iria Gomez-Tourino
- , Yogesh Kamra
- & Mark Peakman
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary genetics of immunological supertypes reveals two faces of the Red Queen
Evolutionary genetics of immunological supertypes reveals two faces of the Red Queen
Host-parasite coevolution can lead to arms races favouring novel immunogenetic alleles or the maintenance of diversity in a balanced polymorphism. Here, Lighten et al. combine data on MHC diversity across three guppy species and simulations to show that polymorphisms of immunogenetic supertypes may persist even as alleles within supertypes are involved in an arms race.
- Jackie Lighten
- , Alexander S. T. Papadopulos
- & Cock van Oosterhout
-
Article
| Open Access Mef2C restrains microglial inflammatory response and is lost in brain ageing in an IFN-I-dependent manner
Mef2C restrains microglial inflammatory response and is lost in brain ageing in an IFN-I-dependent manner
Microglia cells in the brain regulate immune responses, but in ageing can negatively affect brain function. Here the authors show that the chronic presence of type I interferon in aged mouse brain impedes cognitive ability by altering microglia transcriptome and limiting Mef2C, a microglia ‘off’ signal.
- Aleksandra Deczkowska
- , Orit Matcovitch-Natan
- & Michal Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access IgG1 memory B cells keep the memory of IgE responses
IgG1 memory B cells keep the memory of IgE responses
IgE is an important mediator of protective immunity as well as allergic reaction, but how high affinity IgE antibodies are produced in memory responses is not clear. Here the authors show that IgE can be generated via class-switch recombination in IgG1 memory B cells without additional somatic hypermutation.
- Jin-Shu He
- , Sharrada Subramaniam
- & Maria A. Curotto de Lafaille
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association and HLA region fine-mapping studies identify susceptibility loci for multiple common infections
Genome-wide association and HLA region fine-mapping studies identify susceptibility loci for multiple common infections
Susceptibility to infectious diseases is, among others, influenced by the genetic landscape of the host. Here, Tian and colleagues perform genome-wide association studies for 23 common infections and find 59 risk loci for 17 of these, both within the HLA region and non-HLA loci.
- Chao Tian
- , Bethann S. Hromatka
- & David A. Hinds
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide association study identifies a novel susceptibility locus for the immunogenicity of polyethylene glycol
A genome-wide association study identifies a novel susceptibility locus for the immunogenicity of polyethylene glycol
Some individuals develop antibodies against the polyethylene glycol that is commonly used in therapeutic preparations. Here the authors conduct a GWAS in Han Chinese and find the IGH locus is associated with anti-PEG IgM.
- Chia-Jung Chang
- , Chien-Hsiun Chen
- & Jer-Yuarn Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic regulatory effects modified by immune activation contribute to autoimmune disease associations
Genetic regulatory effects modified by immune activation contribute to autoimmune disease associations
Insight into the genetic influence on the immune response is important for the understanding of interindividual variability in human pathologies. Here, the authors generate transcriptome data from human blood monocytes stimulated with various immune stimuli and provide a time-resolved response eQTL map.
- Sarah Kim-Hellmuth
- , Matthias Bechheim
- & Veit Hornung
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and regulatory diversity shape HLA-C protein expression levels
Structural and regulatory diversity shape HLA-C protein expression levels
HLA-C expression levels correlate with immune responses to pathogens and autoimmunity, and vary in an allele-specific manner across individuals. Here the authors identify factors that drive differential expression of HLA-C allomorphs at the cell surface, and influence the structure of the peptide-binding cleft and diversity of peptides bound by HLA-C molecules.
- Gurman Kaur
- , Stephanie Gras
- & Lars Fugger
-
Article
| Open Access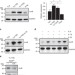 JunB is essential for IL-23-dependent pathogenicity of Th17 cells
JunB is essential for IL-23-dependent pathogenicity of Th17 cells
T helper 17 (Th17) cells can be pathogenic, but what controls this phenotype is unclear. Here the authors show that the transcription factor JunB promotes proinflammatory Th17 function by regulating the transcription of multiple Th17-related genes.
- Zafrul Hasan
- , Shin-ichi Koizumi
- & Hiroki Ishikawa
-
Article
| Open Access Clonally stable Vκ allelic choice instructs Igκ repertoire
Clonally stable Vκ allelic choice instructs Igκ repertoire
B cell development involves sequential rearrangement of the immunoglobulin chains, but fine control over the selection process remains a mystery. Here the authors show that individual alleles in pre-B cells are clonally unique and result from stochastic activation of V gene segments to induce optimal generation of a diverse repertoire.
- Rena Levin-Klein
- , Shira Fraenkel
- & Yehudit Bergman
-
Article
| Open Access Large scale meta-analysis characterizes genetic architecture for common psoriasis associated variants
Large scale meta-analysis characterizes genetic architecture for common psoriasis associated variants
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated skin disease with a complex genetic architecture. Here, Elder and colleagues identify 16 novel psoriasis susceptibility loci using GWAS meta-analysis with a combined effective sample size of over 39,000 individuals.
- Lam C. Tsoi
- , Philip E. Stuart
- & James T Elder
-
Article
| Open Access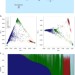 Association between a common immunoglobulin heavy chain allele and rheumatic heart disease risk in Oceania
Association between a common immunoglobulin heavy chain allele and rheumatic heart disease risk in Oceania
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is a chronic auto-inflammatory reaction to group A streptococcal infection, and frequently occurs in individuals from the South Pacific. This study finds a novel association between an immunoglobulin heavy chain allele and risk of RHD in Pacific Islanders and South Asians.
- Tom Parks
- , Mariana M. Mirabel
- & Brenton Ward
-
Article
| Open Access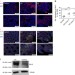 Elevated levels of Bcl-3 inhibits Treg development and function resulting in spontaneous colitis
Elevated levels of Bcl-3 inhibits Treg development and function resulting in spontaneous colitis
Bcl-3 modulates effector T cell responses, but the importance of Bcl-3 in T regulatory cells and autoimmunity is not clear. Here the authors show that Bcl-3 impedes NF-κB DNA binding to alter T regulatory cell development and function, causing spontaneous colitis in mice.
- Sonja Reißig
- , Yilang Tang
- & Nadine Hövelmeyer

 Eighty-eight variants highlight the role of T cell regulation and airway remodeling in asthma pathogenesis
Eighty-eight variants highlight the role of T cell regulation and airway remodeling in asthma pathogenesis