Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Heavy-atom tunnelling in singlet oxygen deactivation predicted by instanton theory with branch-point singularities
Heavy-atom tunnelling in singlet oxygen deactivation predicted by instanton theory with branch-point singularities
Singlet oxygen relaxes in water to its triplet ground state. Here, the authors show that heavy-atom tunnelling speeds up this reaction from time scales longer than the age of the universe to microseconds.
- Imaad M. Ansari
- , Eric R. Heller
- & Jeremy O. Richardson
-
Article
| Open Access Active droplets through enzyme-free, dynamic phosphorylation
Active droplets through enzyme-free, dynamic phosphorylation
Despite the importance of dynamic phosphorylation in biology, enzyme-free, synthetic systems that use dynamic phosphorylation to regulate supramolecular processes are unexplored. Here, the authors report an enzyme-free chemical reaction cycle that can dynamically phosphorylate amino acids and peptides using simple phosphorylating agents and regulate supramolecular functions.
- Simone M. Poprawa
- , Michele Stasi
- & Job Boekhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of structural preorganization and conformational sampling in UDP-glucuronic acid 4-epimerase catalysis
Interplay of structural preorganization and conformational sampling in UDP-glucuronic acid 4-epimerase catalysis
Enzymes involve structural flexibility in their function, but understanding enzyme catalysis as connected to protein motions is a major challenge. Here, the authors obtain energetic description of C-H activation in nicotinamide coenzyme-dependent UDP-glucuronic acid C4 epimerase based on temperature kinetic studies and isotope effect measurements.
- Christian Rapp
- , Annika Borg
- & Bernd Nidetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the activated complex of the F + NH3 reaction via a dipole-bound state
Probing the activated complex of the F + NH3 reaction via a dipole-bound state
Experimental characterization of the transition state in chemical reactions is challenging due to its transient nature. Here, Zhang et al. observe quantum states near the activated complex region of the F + NH3 → HF + NH2 reaction via a dipole-bound state of the FNH3- anion formed upon photodetachment, which allows probing regions of reactive potential energy surfaces out of the Franck-Condon-active areas.
- Rui Zhang
- , Shuaiting Yan
- & Chuangang Ning
-
Article
| Open Access Selenium catalysis enables negative feedback organic oscillators
Selenium catalysis enables negative feedback organic oscillators
Multiple autocatalytic reactions producing thiols are known, but negative feedback loop motifs are unavailable for thiol chemistry. Here, the authors develop a negative feedback loop based on the selenocarbonates, in which thiols induce the release of aromatic selenols that catalyze the oxidation of thiols by organic peroxides.
- Xiuxiu Li
- , Polina Fomitskaya
- & Sergey N. Semenov
-
Article
| Open Access Universal inter-molecular radical transfer reactions on metal surfaces
Universal inter-molecular radical transfer reactions on metal surfaces
Radicals are expected to be inactive on metal surfaces. Here the authors describe general intermolecular radical transfer reactions on Ag and Cu surfaces and confirm the reaction mechanism by extensive control experiments.
- Junbo Wang
- , Kaifeng Niu
- & Lifeng Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aluminum corrosion–passivation regulation prolongs aqueous batteries life
Aqueous batteries have a short lifespan due to Al current collector corrosion and Li loss from side reactions on the anode. Here, the authors propose a prototype of self-prolonging aqueous Li-ion batteries by introducing hydrolyzation-type anodic additives to regulate Al corrosion-passivation.
- Binghang Liu
- , Tianshi Lv
- & Liumin Suo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast photoinduced C-H bond formation from two small inorganic molecules
Ultrafast photoinduced C-H bond formation from two small inorganic molecules
The formation of C–H bonds via reaction of small inorganic molecules is of great interest for understanding the transition from inorganic to organic matter, but the detailed mechanisms remain elusive. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time visualization and coherent control of the ultrafast C–H bond formation dynamics in a light-induced bimolecular reaction from inorganic species.
- Zhejun Jiang
- , Hao Huang
- & Jian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Hairpin trimer transition state of amyloid fibril
Hairpin trimer transition state of amyloid fibril
Amyloid fibrils are ordered protein assemblies implicated in neurodegenerative disease. Here the authors show that hairpin trimers can be transition states of fibril nucleation, explaining how different fibril isoforms may arise from alternative nucleation sites.
- Levent Sari
- , Sofia Bali
- & Milo M. Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Squeezing formaldehyde into C60 fullerene
Squeezing formaldehyde into C60 fullerene
The interconversion of the two spin isomers of formaldehyd has been studied in the gas phase but has never been observed experimentally in the condensed phase. Here the authors report the encapsulation of formaldehyde inside C60 cages and observe spin-isomer conversion of the formaldehyde guest molecules in the cryogenic solid state.
- Vijyesh K. Vyas
- , George R. Bacanu
- & Richard J. Whitby
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic insight into the competition between interfacial and bulk reactions in microdroplets through N2O5 ammonolysis and hydrolysis
Mechanistic insight into the competition between interfacial and bulk reactions in microdroplets through N2O5 ammonolysis and hydrolysis
The authors report a computational strategy to simulate the hydrolysis and ammonolysis of N2O5 in aerosols using high-level quantum chemical methods. The computational results reveal a complete picture of the reactive uptake of N2O5 by atmospheric aerosols with or without NH3.
- Ye-Guang Fang
- , Bo Tang
- & Wei-Hai Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of geometric phase effect through backward angular oscillations in the H + HD → H2 + D reaction
Observation of geometric phase effect through backward angular oscillations in the H + HD → H2 + D reaction
In a combined experimental and theoretical study of the H + HD → H2 + D reaction at low collision energy (1.72 eV), the authors obtain detailed information on the quantum reaction dynamics surrounding a conical intersection.
- Shihao Li
- , Jiayu Huang
- & Xueming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the state-to-state charge-transfer dynamics between the spin-orbit excited Ar+(2P1/2) ion and N2
Imaging the state-to-state charge-transfer dynamics between the spin-orbit excited Ar+(2P1/2) ion and N2
The charge-transfer reaction Ar++N2 → Ar+N2+ has been largely studied as a model gas-phase reaction but many aspects remain to be understood. Here, differential cross sections of the reaction are measured and calculated with Ar+ prepared in 2P1/2 state, showing that the charge-transfer dynamics differs significantly for Ar+(2P1/2) compared to Ar+(2P3/2) when colliding with N2.
- Guodong Zhang
- , Dandan Lu
- & Hong Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of the multi-phasic quenching dynamics in the BLUF domains across the species
Origin of the multi-phasic quenching dynamics in the BLUF domains across the species
Here the authors combine 19 F NMR and femtosecond transient absorption to characterise the structural origin of the multiphasic quenching dynamics in various species of BLUF domains, highlighting the importance of the heterogeneous active-site H-bond network.
- Yalin Zhou
- , Siwei Tang
- & Dongping Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating protonation pathways in CO2 photoreduction using the kinetic isotope effect
Elucidating protonation pathways in CO2 photoreduction using the kinetic isotope effect
Yin et al. reveal a protonation pathway in CO2 photoreduction on TiO2, challenging electron activation theories and diversifying photocatalyst design, distinct from Fischer-Tropsch and Sabatier processes.
- Shikang Yin
- , Yiying Zhou
- & Pengwei Huo
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopy and dynamics of the hydrated electron at the water/air interface
Spectroscopy and dynamics of the hydrated electron at the water/air interface
Hydrated electrons at the water/air interface participate in natural and synthetic processes, but investigation of their properties remains challenging. Here the authors show that most of their electron density is solvated below the dividing surface and solvates into the bulk in around 10 picoseconds, leaving its phenoxyl radical source at the interface.
- Caleb J. C. Jordan
- , Marc P. Coons
- & Jan R. R. Verlet
-
Article
| Open Access Selective amide bond formation in redox-active coacervate protocells
Selective amide bond formation in redox-active coacervate protocells
Coacervate droplets are promising protocells that sequester nutrients, but how new peptides could be synthesized inside coacervates remains a mystery. Here, the authors develop redox-active coacervates that facilitate the formation of new peptide bonds.
- Jiahua Wang
- , Manzar Abbas
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access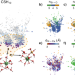 Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
The nucleation of calcium silicate hydrate is a crucial step in cement hydration, but is still a poorly understood process. Here the authors use atomistic simulations to study primary particles and their aggregation, revealing a potential C-S-H “basic building block”.
- Xabier M. Aretxabaleta
- , Jon López-Zorrilla
- & Hegoi Manzano
-
Article
| Open Access Generalised analytical method unravels framework-dependent kinetics of adsorption-induced structural transition in flexible metal–organic frameworks
Generalised analytical method unravels framework-dependent kinetics of adsorption-induced structural transition in flexible metal–organic frameworks
The kinetics of guest-induced structural transition shown by flexible metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) remain poorly understood despite being crucial for process design. Here, three MOFs are studied to reveal the framework-dependent kinetic nature.
- Yuta Sakanaka
- , Shotaro Hiraide
- & Satoshi Watanabe
-
Article
| Open Access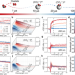 Direct time-resolved observation of surface-bound carbon dioxide radical anions on metallic nanocatalysts
Direct time-resolved observation of surface-bound carbon dioxide radical anions on metallic nanocatalysts
Understanding the activity and selectivity of metal catalysts requires elucidating the dynamics of CO2•− radicals bound to the surface. Here, the authors use pulse radiolysis to directly observe the stabilization process of CO2•− radicals at nanoscale metallic sites from nanoseconds to seconds.
- Zhiwen Jiang
- , Carine Clavaguéra
- & Mehran Mostafavi
-
Article
| Open Access Universal machine learning for the response of atomistic systems to external fields
Universal machine learning for the response of atomistic systems to external fields
External fields, despite their significant influence on chemical processes, have been largely ignored in current machine learning potentials. Here, the authors introduce a field-induced model that captures system-field interactions rigorously.
- Yaolong Zhang
- & Bin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric control of olefin isomerization kinetics via remote metal binding and its mechanochemical analysis
Allosteric control of olefin isomerization kinetics via remote metal binding and its mechanochemical analysis
The mechanisms by which changes in local geometries of receptor sites lower activation reaction barriers in electronically uncoupled, remote reaction moieties remain relatively unexplored. Here, the authors demonstrate allosteric acceleration in the thermal isomerization of an alkene triggered by the binding of a metal ion to a remote receptor site.
- Yichen Yu
- , Robert T. O’Neill
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article
| Open Access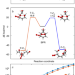 Molecular rearrangement of bicyclic peroxy radicals is a key route to aerosol from aromatics
Molecular rearrangement of bicyclic peroxy radicals is a key route to aerosol from aromatics
The oxidation of aromatics contributes significantly to the formation of atmospheric aerosol. Using toluene as an example the authors demonstrate a molecular rearrangement channel in the oxidation mechanism and show that the bicyclic peroxy radicals are much less stable than previously thought and can lead to aerosol-forming low-volatility products with up to 9 oxygen atoms on sub-second timescales
- Siddharth Iyer
- , Avinash Kumar
- & Matti Rissanen
-
Article
| Open Access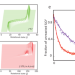 Enhancing reactivity of SiO+ ions by controlled excitation to extreme rotational states
Enhancing reactivity of SiO+ ions by controlled excitation to extreme rotational states
Control of chemical reactivity through excitation of rotational states is a relatively unexplored process that may play a role in interstellar chemistry. Here the authors show a marked acceleration of the hydrogen abstraction reaction between SiO+ and H2 by exciting super-rotor states of SiO+, in a joint experimental and theoretical study.
- Sruthi Venkataramanababu
- , Anyang Li
- & Brian C. Odom
-
Article
| Open Access Oxidation kinetics and non-Marcusian charge transfer in dimensionally confined semiconductors
Oxidation kinetics and non-Marcusian charge transfer in dimensionally confined semiconductors
In this study, the authors correlate the kinetics of lateral photooxidation in WS2 and MoS2 monolayers with their crystallographic defects and environmental parameters, showing a charge transfer mechanism that does not follow the Marcus-Gerischer charge transfer theory.
- Ning Xu
- , Li Shi
- & Songlin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulating hydrogen bond dissociation rates and mechanisms in water dimer through vibrational strong coupling
Manipulating hydrogen bond dissociation rates and mechanisms in water dimer through vibrational strong coupling
Mechanistic understanding of how light-matter interaction alters chemical reactivities remains a challenge. Here, the authors show both hydrogen bond dissociation rate and pathways can be modified through cavity-modified molecular coupling patterns.
- Qi Yu
- & Joel M. Bowman
-
Article
| Open Access Lanthanide-doped MoS2 with enhanced oxygen reduction activity and biperiodic chemical trends
Lanthanide-doped MoS2 with enhanced oxygen reduction activity and biperiodic chemical trends
Oxygen reduction reaction plays a key role in many applications of MoS2-based materials. Here, using first-principles simulations, the authors find the enhanced oxygen-reduction activity with a biperiodic chemical trend on the lanthanide-doped MoS2.
- Yu Hao
- , Liping Wang
- & Liang-Feng Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Rehybridization dynamics into the pericyclic minimum of an electrocyclic reaction imaged in real-time
Rehybridization dynamics into the pericyclic minimum of an electrocyclic reaction imaged in real-time
Electrocyclic reactions proceed through critical geometries, which are known as pericyclic transition states in thermal reactions and pericyclic minima in photochemical reactions. Here, the authors image the structure of a pericyclic minimum in real time using a combination of ultrafast electron diffraction and ab initio dynamics simulations.
- Y. Liu
- , D. M. Sanchez
- & T. J. A. Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Ferricyanide photo-aquation pathway revealed by combined femtosecond Kβ main line and valence-to-core x-ray emission spectroscopy
Ferricyanide photo-aquation pathway revealed by combined femtosecond Kβ main line and valence-to-core x-ray emission spectroscopy
Reliably identifying transient intermediates is crucial to elucidate chemical reaction mechanisms. Here, the authors use femtosecond Fe Kβ main line and valence-to-core x-ray emission spectroscopy to characterize a short-lived intermediate of the aqueous ferricyanide photo-aquation reaction.
- Marco Reinhard
- , Alessandro Gallo
- & Dimosthenis Sokaras
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic evolution of the active center driven by hemilabile coordination in Cu/CeO2 single-atom catalyst
Dynamic evolution of the active center driven by hemilabile coordination in Cu/CeO2 single-atom catalyst
This work explores the concept of hemilability in single atom catalysts. The results imply that this effect can promote reactant activation and product desorption simultaneously to provide a potential approach to circumvent the Sabatier volcano.
- Zheng Chen
- , Zhangyun Liu
- & Xin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Gas phase synthesis of the C40 nano bowl C40H10
Gas phase synthesis of the C40 nano bowl C40H10
Nanobowls represent building blocks of fullerenes and nanotubes as detected in combustion systems and deep space, but their formation mechanisms in these environments have remained elusive. Here, the authors explore the gas-phase formation of benzocorannulene and beyond to the C40 nanobowl.
- Lotefa B. Tuli
- , Shane J. Goettl
- & Ralf I. Kaiser
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction of transition state structures of gas-phase chemical reactions via machine learning
Prediction of transition state structures of gas-phase chemical reactions via machine learning
Obtaining good initial structures is the main challenge for the computational study of transition states. Here, fast and accurate predictions for transition state of gas phase reactions are achieved by machine learning based on interatomic distances.
- Sunghwan Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient stabilization of cyanonaphthalene by fast radiative cooling and implications for the resilience of small PAHs in interstellar clouds
Efficient stabilization of cyanonaphthalene by fast radiative cooling and implications for the resilience of small PAHs in interstellar clouds
The abundances of small Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) observed in interstellar clouds has surprised astronomers and confounded astrochemical models. Here, the authors show that fast radiative cooling by Recurrent Fluorescence efficiently stabilizes the small PAH cation 1-cyanonaphthalene.
- Mark H. Stockett
- , James N. Bull
- & Boxing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Shining light on the microscopic resonant mechanism responsible for cavity-mediated chemical reactivity
Shining light on the microscopic resonant mechanism responsible for cavity-mediated chemical reactivity
Hybridization of dark optical cavity modes with vibrational states of molecules can alter chemical reactions. Here, the authors use ab-initio methods to shine light on the associated mechanism and highlight the role of the optical mode to redistribute the vibrational energy.
- Christian Schäfer
- , Johannes Flick
- & Angel Rubio
-
Article
| Open Access Green synthesis of propylene oxide directly from propane
Green synthesis of propylene oxide directly from propane
Propylene and propylene oxide are formed over boron nitride or SiO2 in the gas phase without yielding large amounts of CO2. Conversion at non-specific interfaces can thus be a successful strategy for the synthesis of oxidation-sensitive products.
- Pierre Kube
- , Jinhu Dong
- & Annette Trunschke
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast light-induced dynamics in the microsolvated biomolecular indole chromophore with water
Ultrafast light-induced dynamics in the microsolvated biomolecular indole chromophore with water
Experimentally following the ultrafast dynamics of microsolvated molecules is challenging due to the inherently produced soup mix of various gas-phase aggregates. Here, the authors exploit neutral-species selection to reveal intimate details of the UV-induced ultrafast dynamics in the prototypical indole-water system.
- Jolijn Onvlee
- , Sebastian Trippel
- & Jochen Küpper
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of hydronium ions on the Pd-catalyzed furfural hydrogenation
Impact of hydronium ions on the Pd-catalyzed furfural hydrogenation
Hydrogen binding and furfural adsorption are critical steps in Pd-catalyzed furfural hydrogenation reactions in aqueous phases. Here, the authors explore how hydronium ion at different pH values modifies the rate constant for this reaction.
- Iris K. M. Yu
- , Fuli Deng
- & Johannes A. Lercher
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking through water-splitting bottlenecks over carbon nitride with fluorination
Breaking through water-splitting bottlenecks over carbon nitride with fluorination
Graphitic carbon nitride has long been considered a poor oxygen evolution catalyst. Here, the authors report a simple fluorination strategy to prevent the accumulation of inert C=O on carbon nitride to break through this bottleneck.
- Ji Wu
- , Zhonghuan Liu
- & Yongsheng Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Effective screening of Coulomb repulsions in water accelerates reactions of like-charged compounds by orders of magnitude
Effective screening of Coulomb repulsions in water accelerates reactions of like-charged compounds by orders of magnitude
The reaction speed of like-charged compounds in water is extremely slow due to Coulomb repulsions. Here, the authors boost kinetics up to 5 million times by screening these interactions and increasing the local concentration of reactants using positively charged micelles. They show the effect for two independent systems and present a theoretical explanation.
- Adam Kowalski
- , Krzysztof Bielec
- & Robert Holyst
-
Article
| Open Access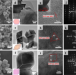 Facet effect of hematite on the hydrolysis of phthalate esters under ambient humidity conditions
Facet effect of hematite on the hydrolysis of phthalate esters under ambient humidity conditions
With a combined experimental and computational study, Jin et al. demonstrate that hematite nanoparticles can efficiently degrade phthalates under ambient humidity conditions, with a rate strongly dependent on the exposed facet via bidentate coordination involving neighbor Fe atoms, suggesting their possible use for indoor air purification
- Xin Jin
- , Dingding Wu
- & Cheng Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Towards fully ab initio simulation of atmospheric aerosol nucleation
Towards fully ab initio simulation of atmospheric aerosol nucleation
Atmosphere aerosol nucleation contributes to climate change, air pollution, and human health, however the mechanisms are complex and elusive. Here the authors propose a general workflow based on deep neural network-based force field, paving the way towards fully ab initio simulation of atmospheric aerosol nucleation.
- Shuai Jiang
- , Yi-Rong Liu
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Triple ionization and fragmentation of benzene trimers following ultrafast intermolecular Coulombic decay
Triple ionization and fragmentation of benzene trimers following ultrafast intermolecular Coulombic decay
Higher-order aromatic clusters are prevalent in biochemical systems, but a full understanding of their structural and dynamical properties is lacking. Here, the authors demonstrate that inner-valence ionization can induce ultrafast relaxation and further fragmentation mechanisms in benzene trimers.
- Jiaqi Zhou
- , Xitao Yu
- & Xueguang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Step-by-step state-selective tracking of fragmentation dynamics of water dications by momentum imaging
Step-by-step state-selective tracking of fragmentation dynamics of water dications by momentum imaging
Determining the time evolution of reactions at the quantum mechanical level improves our understanding of molecular dynamics. Here, authors separate the breakup of water, one bond at a time, from other processes leading to the same final products and experimentally identify, separate, and follow step by step two breakup paths of the transient OD+ fragment.
- Travis Severt
- , Zachary L. Streeter
- & Itzik Ben-Itzhak
-
Article
| Open Access A Ziegler-type spherical cap model reveals early stage ethylene polymerization growth versus catalyst fragmentation relationships
A Ziegler-type spherical cap model reveals early stage ethylene polymerization growth versus catalyst fragmentation relationships
Ziegler-type polyolefin catalysts have proven to be hard to characterize. Here the authors present a model system consisting of patterned LaOCl spherical caps, simulating bulk particles while facilitating the use of micro(-spectro)scopic characterization techniques specifically aimed at surfaces.
- Koen W. Bossers
- , Laurens D. B. Mandemaker
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected steric hindrance failure in the gas phase F− + (CH3)3CI SN2 reaction
Unexpected steric hindrance failure in the gas phase F− + (CH3)3CI SN2 reaction
Base-induced elimination (E2) and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2) are of significant importance in physical organic chemistry. Here, the authors show that the competing factor of E2 as opposed to steric hindrance determines the low reactivity of SN2 in the F− + (CH3)3CI reaction.
- Xiaoxiao Lu
- , Chenyao Shang
- & Dong H. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral signatures of excess-proton waiting and transfer-path dynamics in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions
Spectral signatures of excess-proton waiting and transfer-path dynamics in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions
The spectroscopic signatures of excess protons in HCl solutions are studied by ab initio simulations and THz experiments. Two contributions beyond the normal-mode scenario are identified that reflect proton-waiting and proton-transfer processes.
- Florian N. Brünig
- , Manuel Rammler
- & Roland R. Netz
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the molecular mechanism of MIL-53(Al) crystallization
Unraveling the molecular mechanism of MIL-53(Al) crystallization
The discovery and control of the synthesis of metal–organic frameworks remains challenging due to the lack of understanding of their nucleation and growth. Here, the authors report a detailed molecular-level mechanism of the formation of MIL-53(Al).
- Daniil Salionov
- , Olesya O. Semivrazhskaya
- & Vitaly L. Sushkevich
-
Article
| Open Access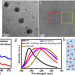 Identification of a quasi-liquid phase at solid–liquid interface
Identification of a quasi-liquid phase at solid–liquid interface
Solid–liquid interfaces are ubiquitous in natural and technological processes, but their imaging at the atomic scale has been challenging. The authors, using liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy, identify a quasi-liquid phase and the mass transport between the surface of In and Sn nanocrystals and an aqueous solution.
- Xinxing Peng
- , Fu-Chun Zhu
- & Haimei Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Generation and direct observation of a triplet arylnitrenium ion
Generation and direct observation of a triplet arylnitrenium ion
Nitrenium ions are highly electrophilic reactive intermediates of formula R−N−R+, nitrogen analogue of carbenes. Here the authors report the detection of a triplet nitrenium ion using time-resolved spectroscopic methods and ab initio computations, allowing a glimpse at the properties and behavior of this important class of intermediates.
- Lili Du
- , Juanjuan Wang
- & Arthur H. Winter

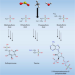 Abiotic formation of alkylsulfonic acids in interstellar analog ices and implications for their detection on Ryugu
Abiotic formation of alkylsulfonic acids in interstellar analog ices and implications for their detection on Ryugu