Featured
-
-
Comment
| Open Access Population imaging cerebellar growth for personalized neuroscience
Population imaging cerebellar growth for personalized neuroscience
Growth chart studies of the human cerebellum, which is increasingly recognized as pivotal for cognitive development, are rare. Gaiser and colleagues utilized population-level neuroimaging to unveil cerebellar growth charts from childhood to adolescence, offering insights into brain development.
- Zi-Xuan Zhou
- & Xi-Nian Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of four biotypes in temporal lobe epilepsy via machine learning on brain images
Identification of four biotypes in temporal lobe epilepsy via machine learning on brain images
Brain imaging-based disease progression modelling is a promising technique for disease stratification. Here the authors characterize distinct ‘trajectories’ of brain atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy and identify four subtypes with distinct neuroanatomical signatures.
- Yuchao Jiang
- , Wei Li
- & Dongmei An
-
Article
| Open Access Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Many diseases can display distinct brain imaging phenotypes across individuals, potentially reflecting disease subtypes. However, biological interpretability is limited if the derived subtypes are not associated with genetic drivers or susceptibility factors. Here, the authors describe a deep-learning method that links imaging phenotypes with genetic factors, thereby conferring genetic correlations to the disease subtypes.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Junhao Wen
- & Christos Davatzikos
-
Article
| Open Access A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
Real-time MRI provides accurate navigation and targeting for neurological interventions. Here, the authors propose a deep unrolled neural network for MRI reconstruction that enables real-time monitoring of remote-controlled brain interventions and can be integrated into diagnostic scanners.
- Zhao He
- , Ya-Nan Zhu
- & Yuan Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association analysis of left ventricular imaging-derived phenotypes identifies 72 risk loci and yields genetic insights into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Genome-wide association analysis of left ventricular imaging-derived phenotypes identifies 72 risk loci and yields genetic insights into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Changes of left ventricular structure are used to predict morbidity and mortality in cardiovascular diseases. Here the authors conducted a study using advanced deep learning technology to analyze left ventricular regional wall thickness (LVRWT) in a large population, identifying 72 significant genetic loci linked to LVRWT traits.
- Caibo Ning
- , Linyun Fan
- & Xiaoping Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Joint multi-ancestry and admixed GWAS reveals the complex genetics behind human cranial vault shape
Joint multi-ancestry and admixed GWAS reveals the complex genetics behind human cranial vault shape
The genetic architecture of normal-range cranial vault shape in humans is poorly understood. Here, the authors extract cranial vault shape from MRI and conduct a multi-ancestry GWAS, identifying 30 independently associated genomic loci of which 29 are novel.
- Seppe Goovaerts
- , Hanne Hoskens
- & Peter Claes
-
Article
| Open Access Automated temporalis muscle quantification and growth charts for children through adulthood
Automated temporalis muscle quantification and growth charts for children through adulthood
Temporalis muscle thickness is a promising marker of lean muscle mass but has had limited utility due to its unknown normal growth trajectory and lack of standardized measurement. Here, the authors develop an automated deep learning pipeline to accurately measure temporalis muscle thickness from routine brain magnetic resonance imaging.
- Anna Zapaishchykova
- , Kevin X. Liu
- & Benjamin H. Kann
-
Article
| Open Access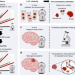 Non-invasive assessment of normal and impaired iron homeostasis in the brain
Non-invasive assessment of normal and impaired iron homeostasis in the brain
Assessment of different iron compounds in the living brain remains an open challenge. Here, the authors present a magnetic resonance imaging method which is sensitive to the iron homeostasis in the brain, and increases the detection of tumor tissue.
- Shir Filo
- , Rona Shaharabani
- & Aviv A. Mezer
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging of pH, perfusion and renal filtration using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled Z-OMPD
Simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging of pH, perfusion and renal filtration using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled Z-OMPD
pH alterations are a hallmark of many pathologies including cancer and kidney disease. Here the authors describe [1,5- 13 C2]Z-OMPD as a probe for hyperpolarized 13C-MRI with good pH sensitivity and hyperpolarization properties which combined with tailored MRI protocols allow sub-minute imaging of pH, renal perfusion and filtration simultaneously.
- Martin Grashei
- , Pascal Wodtke
- & Franz Schilling
-
Article
| Open Access Bone marrow adiposity modulation after long duration spaceflight in astronauts
Bone marrow adiposity modulation after long duration spaceflight in astronauts
Bone marrow adiposity is linked to disease, and it is unknown how it is modulated during space travel. Here, the authors show that astronauts returning from ISS missions had decreased marrow fat and increased hematopoiesis and bone formation, suggesting that adipose reserves in the bone marrow might be used as an energy source to counteract anemia and bone loss associated with space flight.
- Tammy Liu
- , Gerd Melkus
- & Guy Trudel
-
Article
| Open Access Biodegradable polyphosphoester micelles act as both background-free 31P magnetic resonance imaging agents and drug nanocarriers
Biodegradable polyphosphoester micelles act as both background-free 31P magnetic resonance imaging agents and drug nanocarriers
MRI agents can result in environmental pollution and organ accumulation. Here, the authors show that modifying the molecular structure of biodegradable polyphosphoesters and tailoring the polymers’ microstructure to adjust MRI relaxation times can overcome challenges in 31P MR imaging.
- Olga Koshkina
- , Timo Rheinberger
- & Frederik R. Wurm
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic macroscale oscillatory modes driving long range functional connectivity in female rat brains detected by ultrafast fMRI
Intrinsic macroscale oscillatory modes driving long range functional connectivity in female rat brains detected by ultrafast fMRI
The mechanisms which generate fMRI signal correlations across the brain are not fully understood. Here, the authors record ultrafast fMRI signals in anesthetized female rats to demonstrate intrinsic macroscale oscillatory modes which drive correlated activity between distant regions.
- Joana Cabral
- , Francisca F. Fernandes
- & Noam Shemesh
-
Article
| Open Access Non-metallic T2-MRI agents based on conjugated polymers
Non-metallic T2-MRI agents based on conjugated polymers
The toxicity of heavy metals for MRI contrast agents is an issue. Here, the authors report on the development of conjugated polymers nanoparticles based on paramagnetic polypyrrole to generate T2 MRI contrast effects by changing the interactions between polarons and water protons.
- Qinrui Lin
- , Yuhong Yang
- & Zhengzhong Shao
-
Article
| Open Access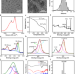 Carbonized paramagnetic complexes of Mn (II) as contrast agents for precise magnetic resonance imaging of sub-millimeter-sized orthotopic tumors
Carbonized paramagnetic complexes of Mn (II) as contrast agents for precise magnetic resonance imaging of sub-millimeter-sized orthotopic tumors
Improving the imaging of cancer may enhance the treatment of patients, Here, the authors develop a Mn(II) based nanoparticle contrast agent for MRI imaging and show that the nanoparticles can cross the brain barrier and image glioma cells.
- Ruixue Qin
- , Shi Li
- & Hongmin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access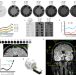 Non-invasive MR imaging of human brain lymphatic networks with connections to cervical lymph nodes
Non-invasive MR imaging of human brain lymphatic networks with connections to cervical lymph nodes
Studies in animal models have visualized drainage of interstitial or cerebrospinal fluid via lymphatic vessels, but there is limited data on in humans. Here, the authors non-invasively visualize lymphatic structures in the human brain, including evidence of lymphatic flow from cranial nerves to cervical lymph nodes, and differences by age and sex, without use of contrast agents.
- Mehmet Sait Albayram
- , Garrett Smith
- & Onder Albayram
-
Article
| Open Access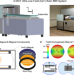 A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner
A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner
A low cost MRI scanner may have the potential to meet clinical needs at point of care or in low and middle income countries. Here the authors describe a low cost 0.055 Tesla MRI scanner that operates using a standard AC power outlet, and demonstrate its preliminary feasibility in diagnosing brain tumor and stroke.
- Yilong Liu
- , Alex T. L. Leong
- & Ed X. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
Alzheimer’s disease is heterogeneous in its neuroimaging and clinical phenotypes. Here the authors present a semi-supervised deep learning method, Smile-GAN, to show four neurodegenerative patterns and two progression pathways providing prognostic and clinical information.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Ilya M. Nasrallah
- & Balebail Ashok Raj
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-targeted 1H/19F MRI unmasks specific danger patterns for emerging cardiovascular disorders
Multi-targeted 1H/19F MRI unmasks specific danger patterns for emerging cardiovascular disorders
The prediction of major cardiovascular events is still an unsolved problem. Here, the authors present a multi-color, multi-targeted non-invasive imaging technology that allows reliable in vivo identification of silent but prognostically highly relevant danger patterns prior to myocardial infarction in mice.
- Ulrich Flögel
- , Sebastian Temme
- & Bodo Levkau
-
Article
| Open Access Lowering the thermal noise barrier in functional brain mapping with magnetic resonance imaging
Lowering the thermal noise barrier in functional brain mapping with magnetic resonance imaging
The signal-to-noise ratio is a key consideration when selecting a magnetic resonance imaging protocol. Thermal noise is major issue, especially in high resolution functional images. Here the authors introduce a method to suppress thermal noise in functional images without losses in spatial precision, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio.
- Luca Vizioli
- , Steen Moeller
- & Kamil Uğurbil
-
Article
| Open Access Associations between frontal lobe structure, parent-reported obstructive sleep disordered breathing and childhood behavior in the ABCD dataset
Associations between frontal lobe structure, parent-reported obstructive sleep disordered breathing and childhood behavior in the ABCD dataset
Parents often report behavioral problems in children with symptoms of sleep disordered breathing (oSDB), such as snoring. Here, the authors show that lower brain volumes within the frontal lobe are associated with parent-reported problem behaviors in children with parent-reported symptoms of oSDB.
- Amal Isaiah
- , Thomas Ernst
- & Linda Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting treatment response from longitudinal images using multi-task deep learning
Predicting treatment response from longitudinal images using multi-task deep learning
Radiographic imaging is routinely used to evaluate treatment response in solid tumors. Here, the authors present a multi-task deep learning approach that allows simultaneous tumor segmentation and response prediction from longitudinal images in a multi-center study on rectal cancer.
- Cheng Jin
- , Heng Yu
- & Ruijiang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Ceramic resonators for targeted clinical magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
Ceramic resonators for targeted clinical magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
Here, the authors present a concept for targeted clinical magnetic resonance imaging for relatively small targets in the body. They use an artificial resonator for spatial redistribution and passive focusing of the radiofrequency magnetic flux and demonstrate feasibility for targeted breast imaging.
- Alena Shchelokova
- , Viacheslav Ivanov
- & Anna Andreychenko
-
Article
| Open Access Iron imaging in myocardial infarction reperfusion injury
Iron imaging in myocardial infarction reperfusion injury
Restoration of coronary blood flow after a heart attack may lead to reperfusion injury and pathologic iron deposition. Here, the authors perform magnetic susceptibility imaging showing its association with iron in a large animal model of myocardial infarction during wound healing, and showing feasibility in acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.
- Brianna F. Moon
- , Srikant Kamesh Iyer
- & Walter R. Witschey
-
Article
| Open Access Motion corrected MRI differentiates male and female human brain growth trajectories from mid-gestation
Motion corrected MRI differentiates male and female human brain growth trajectories from mid-gestation
The human fetal brain may exhibit early sex differences. Here, the authors present MRI based analysis female and male brain growth. Cortical development follows very similar trajectories at larger scales, while differing in focal regions. White matter growth differs at both large and small scales.
- Colin Studholme
- , Christopher D. Kroenke
- & Manjiri Dighe
-
Article
| Open Access Early stratification of radiotherapy response by activatable inflammation magnetic resonance imaging
Early stratification of radiotherapy response by activatable inflammation magnetic resonance imaging
Non-invasive approaches to stratify early responses to therapy are of great value to improve cancer patient management. Here the authors design a hybrid nanovesicle-based activatable inflammation magnetic resonance method for the early prediction of response to radiotherapy.
- Zijian Zhou
- , Hongzhang Deng
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo imaging of phosphocreatine with artificial neural networks
In vivo imaging of phosphocreatine with artificial neural networks
Phosphocreatine plays a vital role in cellular energetic homeostasis, but there are no routine diagnostic tests to noninvasively map the distribution with clinically relevant spatial resolution. Here, the authors develop and validate a noninvasive approach for quantifying and imaging phosphocreatine, without contrast agents, on widely available clinical MRI scanners with artificial neural networks.
- Lin Chen
- , Michael Schär
- & Jiadi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Image-guided neural activity manipulation with a paramagnetic drug
Image-guided neural activity manipulation with a paramagnetic drug
Targeted manipulations of neural activity in the living brain remain a significant challenge. In this study the authors introduce a paramagnetic analog of the drug muscimol that enables targeted neural inactivation to be performed with feedback from magnetic resonance imaging
- Sarah Bricault
- , Ali Barandov
- & Alan Jasanoff
-
Article
| Open Access The SIGMA rat brain templates and atlases for multimodal MRI data analysis and visualization
The SIGMA rat brain templates and atlases for multimodal MRI data analysis and visualization
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely used to study the rat brain. Here, the authors provide standardized MRI brain templates and descriptive atlases for the rat, incorporating both structural and functional MRI data, along with associated resources.
- D. A. Barrière
- , R. Magalhães
- & S. Mériaux
-
Article
| Open Access Brain age prediction using deep learning uncovers associated sequence variants
Brain age prediction using deep learning uncovers associated sequence variants
Machine learning algorithms can be trained to estimate age from brain structural MRI. Here, the authors introduce a new deep-learning-based age prediction approach, and then carry out a GWAS of the difference between predicted and chronological age, revealing two associated variants.
- B. A. Jonsson
- , G. Bjornsdottir
- & M. O. Ulfarsson
-
Article
| Open Access Network curvature as a hallmark of brain structural connectivity
Network curvature as a hallmark of brain structural connectivity
The brain can often continue to function despite lesions in many areas, but damage to particular locations may have serious effects. Here, the authors use the concept of Ollivier-Ricci curvature to investigate the robustness of brain networks.
- Hamza Farooq
- , Yongxin Chen
- & Christophe Lenglet
-
Article
| Open Access Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent
Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent
Non-invasive early diagnosis of liver fibrosis is important to prevent disease progression and direct treatment strategies. Here the authors developed a collagen-targeting contrast agent for the detection of early stage fibrosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by magnetic resonance and tested it in animal models.
- Mani Salarian
- , Ravi Chakra Turaga
- & Jenny J. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Brainstem and spinal cord MRI identifies altered sensorimotor pathways post-stroke
Brainstem and spinal cord MRI identifies altered sensorimotor pathways post-stroke
There are few studies of structural changes in ascending and descending sensorimotor pathways after stroke, beyond the corticospinal tract, in the brain. Here the authors identify changes in white matter structure in brainstem and spinal cord following stroke, and show its relationship to motor impairment.
- Haleh Karbasforoushan
- , Julien Cohen-Adad
- & Julius P. A. Dewald
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling molecular alterations from water-content changes in the aging human brain using quantitative MRI
Disentangling molecular alterations from water-content changes in the aging human brain using quantitative MRI
MRI has been used for the non-invasive imaging of human brain aging but is sensitive to both tissue molecular composition and water content. Here the authors present a quantitative MRI method that discriminates these factors and describe region-specific changes in the molecular composition of the aging human brain.
- Shir Filo
- , Oshrat Shtangel
- & Aviv A. Mezer
-
Article
| Open Access Weakly supervised classification of aortic valve malformations using unlabeled cardiac MRI sequences
Weakly supervised classification of aortic valve malformations using unlabeled cardiac MRI sequences
The availability of labelled training data is one of the practical obstacles towards wide application of machine learning models in medicine. Here the authors develop a weakly supervised deep learning model for the classification of aortic malformations using unlabelled cardiac MRI sequences from the UK biobank.
- Jason A. Fries
- , Paroma Varma
- & James R. Priest
-
Article
| Open Access Brain leptin reduces liver lipids by increasing hepatic triglyceride secretion and lowering lipogenesis
Brain leptin reduces liver lipids by increasing hepatic triglyceride secretion and lowering lipogenesis
Obesity is associated with leptin resistance and rising blood leptin levels while central leptin exposure may be limited. Here, the authors show that brain leptin infusion reduces hepatic lipid content in rats by increasing hepatic VLDL secretion and lowering liver de novo lipogenesis via a vagal mechanism.
- Martina Theresa Hackl
- , Clemens Fürnsinn
- & Thomas Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access The architecture of functional lateralisation and its relationship to callosal connectivity in the human brain
The architecture of functional lateralisation and its relationship to callosal connectivity in the human brain
Many functions of the human brain are lateralised i.e. associated more strongly with either the left or the right hemisphere of the brain. Here, the authors report the first complete map of functional asymmetries in the human brain, and its relationship with structural inter-hemispheric connectivity.
- Vyacheslav R. Karolis
- , Maurizio Corbetta
- & Michel Thiebaut de Schotten
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate autocorrelation modeling substantially improves fMRI reliability
Accurate autocorrelation modeling substantially improves fMRI reliability
There has been recent controversy over the validity of commonly-used software packages for functional MRI (fMRI) data analysis. Here, the authors compare the performance of three leading packages (AFNI, FSL, SPM) in terms of temporal autocorrelation modeling, a key statistical step in fMRI analysis.
- Wiktor Olszowy
- , John Aston
- & Guy B. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Sensing intracellular calcium ions using a manganese-based MRI contrast agent
Sensing intracellular calcium ions using a manganese-based MRI contrast agent
There are only few MRI-compatible calcium reporters and they are limited to measuring extracellular calcium levels. Here the authors develop and validate a cell-permeable, manganese-based paramagnetic MRI contrast agent that enables monitoring intracellular calcium signals in vivo in the rat brain.
- Ali Barandov
- , Benjamin B. Bartelle
- & Alan Jasanoff
-
Article
| Open Access Self-decoupled radiofrequency coils for magnetic resonance imaging
Self-decoupled radiofrequency coils for magnetic resonance imaging
Conventional coil arrays require complex decoupling technologies to reduce electromagnetic coupling between coil elements. Here, the authors report a self-decoupled RF coil design that achieves high inter-coil isolation between adjacent and non-adjacent elements and mixed arrays of loops and dipoles
- Xinqiang Yan
- , John C. Gore
- & William A. Grissom
-
Article
| Open Access MAP1B mutations cause intellectual disability and extensive white matter deficit
MAP1B mutations cause intellectual disability and extensive white matter deficit
Intellectual disability (ID) is characterized by an intelligence quotient of below 70 and impaired adaptive skills. Here, analyzing whole genome sequences from 31,463 Icelanders, Walters et al. identify variants in MAP1B associated with ID and extensive brain-wide white matter deficits.
- G. Bragi Walters
- , Omar Gustafsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and powerful genome wide association of dense genetic data with high dimensional imaging phenotypes
Fast and powerful genome wide association of dense genetic data with high dimensional imaging phenotypes
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of neuroimaging data pose a significant computational burden because of the need to correct for multiple testing in both the genetic and the imaging data. Here, Ganjgahi et al. develop WLS-REML which significantly reduces computation running times in brain imaging GWAS.
- Habib Ganjgahi
- , Anderson M. Winkler
- & Thomas E. Nichols
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral DOTA chelators as an improved platform for biomedical imaging and therapy applications
Chiral DOTA chelators as an improved platform for biomedical imaging and therapy applications
MRI contrast agents containing the rare earth metal gadolinium are very effective, yet unstable and thus potentially hazardous. Here, the authors developed complexes between gadolinium and the scaffolding compound DOTA with increased stability, which also lend themselves to radiometal labelling.
- Lixiong Dai
- , Chloe M. Jones
- & Ga-Lai Law
-
Article
| Open Access Zika virus infection in pregnant rhesus macaques causes placental dysfunction and immunopathology
Zika virus infection in pregnant rhesus macaques causes placental dysfunction and immunopathology
Zika virus infection during pregnancy can result in birth defects, but underlying pathogenesis at the maternal-fetal interface is unclear. Here, the authors use non-invasive in vivo imaging of Zika-infected rhesus macaques and show that infection results in abnormal oxygen transport across the placenta.
- Alec J. Hirsch
- , Victoria H. J. Roberts
- & Daniel N. Streblow
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the microscale origins of magnetic resonance image contrast with subcellular diamond magnetometry
Mapping the microscale origins of magnetic resonance image contrast with subcellular diamond magnetometry
Magnetic resonance imaging derives its contrast from local magnetic fields, however the connection between these fields and macroscale contrast has not been established through direct experiments. Here, Davis et al. use diamond magnetometry to map local magnetic fields within mammalian cells with sub-micron resolution and predict macroscale contrast.
- Hunter C. Davis
- , Pradeep Ramesh
- & Mikhail G. Shapiro
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging of pH in vivo using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled zymonic acid
Imaging of pH in vivo using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled zymonic acid
Local pH alterations can be manifestations of pathologies such as cancer, inflammation and ischaemia. Here Düwelet al. show hyperpolarized 13C-labelled zymonic acid can be used as a non-invasive probe to map and measure pH in vivo, suggesting it as a candidate for clinical imaging and a diagnostic tool.
- Stephan Düwel
- , Christian Hundshammer
- & Franz Schilling
-
Article
| Open Access Nanodiamond-enhanced MRI via in situ hyperpolarization
Nanodiamond-enhanced MRI via in situ hyperpolarization
Hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging can enhance imaging contrast by orders of magnitude, but applications are limited by the thermal relaxation of hyperpolarized states. Here, Waddingtonet al. demonstrate the on-demand hyperpolarization of hydrogen spins through the Overhauser effect with nanodiamonds.
- David E. J. Waddington
- , Mathieu Sarracanie
- & Matthew S. Rosen
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-state carbon-13 hyperpolarization generated in an MRI system for fast imaging
Liquid-state carbon-13 hyperpolarization generated in an MRI system for fast imaging
Hyperpolarized MRI uses molecules with a nuclear spin polarization beyond the thermodynamic equilibrium to enhance imaging contrast. Here, Schmidtet al. enable a single MRI system to both generate a hyperpolarized tracer and perform imaging, eliminating the need for an external polarizer.
- A. B. Schmidt
- , S. Berner
- & J. -B. Hövener
-
Article
| Open Access Covalent assembly of nanoparticles as a peptidase-degradable platform for molecular MRI
Covalent assembly of nanoparticles as a peptidase-degradable platform for molecular MRI
Iron oxide microparticles (MPIO) are better MRI contrast agents than nanoparticles, but are of limited clinical use as they are not degradable and so risk toxicity. Here the authors present an iron oxide microparticle MRI contrast agent with peptide linkers that enable degradation into non-toxic nanoparticlesin vivo.
- Francisco Perez-Balderas
- , Sander I. van Kasteren
- & Benjamin G. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Light controls cerebral blood flow in naive animals
Light controls cerebral blood flow in naive animals
Combination of optogenetics and BOLD fMRI is routinely used to map neuronal activity upon photostimulation. Here the authors show that light, shone at intensities used in optogenetic studies, dilates vessels and increases blood flow independently of exogenous light-sensitive proteins in the mouse brain.
- Ravi L Rungta
- , Bruno-Félix Osmanski
- & Serge Charpak

 Human connectome topology directs cortical traveling waves and shapes frequency gradients
Human connectome topology directs cortical traveling waves and shapes frequency gradients