Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable image processing metasurfaces with phase-change materials
Reconfigurable image processing metasurfaces with phase-change materials
Researchers demonstrate that image-processing metasurfaces can be dynamically reconfigured by using phase-change materials. The work might lead to novel tunable devices for compact optical computing for applications in AR/VR and bio-medical imaging.
- Michele Cotrufo
- , Shaban B. Sulejman
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Non-thermal emission in gap-mode plasmon photoluminescence
Non-thermal emission in gap-mode plasmon photoluminescence
Photoluminescence from plasmonic nanostructures exhibits diverse wavelength dependent nonlinear behaviors with debated origins. Here, authors use plasmonic gap mode resonators with precise nanoscale confinement to show this nonlinear emission can become dominated by non-Fermi carrier contributions.
- Robert Lemasters
- , Manoj Manjare
- & Hayk Harutyunyan
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid architectures for terahertz molecular polaritonics
Hybrid architectures for terahertz molecular polaritonics
Metasurface-based architectures enhance light-matter interactions between a terahertz photonic mode and glucose vibrational resonance. This platform allows new physical and chemical properties of hybrid light-matter states to be exploited.
- Ahmed Jaber
- , Michael Reitz
- & Jean-Michel Ménard
-
Article
| Open Access Transparent radiative cooling cover window for flexible and foldable electronic displays
Transparent radiative cooling cover window for flexible and foldable electronic displays
In this work, authors synthesize transparent radiative cooling cover windows for flexible and foldable electronic devices. Besides demonstrated enhanced mechanical and moisture-impermeable properties, these mitigate temperature rise of devices under solar irradiation and improve overall thermal management.
- Kang Won Lee
- , Jonghun Yi
- & Dong Rip Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Centimeter-scale nanomechanical resonators with low dissipation
Centimeter-scale nanomechanical resonators with low dissipation
Exploring new mechanics regime, researchers created centimeter-long, nanometer-thin resonators, achieving unmatched room temperature mechanical isolation via cutting edge nanoengineering and machine learning design; rivaling cryogenic counterparts.
- Andrea Cupertino
- , Dongil Shin
- & Richard A. Norte
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically stable radiation pressure propulsion of flexible lightsails for interstellar exploration
Dynamically stable radiation pressure propulsion of flexible lightsails for interstellar exploration
Ultrathin laser-driven lightsails represent a unique vision for interstellar space exploration. Here, the authors show how spinning flexible membranes can be both shape- and trajectory-stable with multiphysics structural and nanophotonic engineering.
- Ramon Gao
- , Michael D. Kelzenberg
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong magnon-magnon coupling and chiral spin-texture control in a dipolar 3D multilayered artificial spin-vortex ice
Ultrastrong magnon-magnon coupling and chiral spin-texture control in a dipolar 3D multilayered artificial spin-vortex ice
Extending magnetic nanostructures into three dimensions offers a vast increase in potential functionalities, but this typically comes at the expense of ease of fabrication and measurement. Here, Dion et al. demonstrate an approach to creating three dimensional magnetic nanostructures while retaining easy fabrication and readout of established two dimensional approaches.
- Troy Dion
- , Kilian D. Stenning
- & Jack C. Gartside
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-narrowband and rainbow-free mid-infrared thermal emitters enabled by a flat band design in distorted photonic lattices
Ultra-narrowband and rainbow-free mid-infrared thermal emitters enabled by a flat band design in distorted photonic lattices
Narrowband thermal emitters realized with photonic nanostructures usually suffer from the rainbow effect. Here, the authors demonstrate rainbow-free thermal emissions with high temporal coherence through harnessing flatband high-Q resonances.
- Kaili Sun
- , Yangjian Cai
- & Zhanghua Han
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient characterizations of multiphoton states with an ultra-thin optical device
Efficient characterizations of multiphoton states with an ultra-thin optical device
Shadow tomography is efficient for quantum state characterization. Here, the authors implement shadow tomography on photonic states with a single metasurface, which alleviates the complexity in measurement
- Kui An
- , Zilei Liu
- & He Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Radiative cooling and indoor light management enabled by a transparent and self-cleaning polymer-based metamaterial
Radiative cooling and indoor light management enabled by a transparent and self-cleaning polymer-based metamaterial
Transparent roofs offer a solution for harnessing natural light in sustainable buildings. Here, authors demonstrate a polymer-based metamaterial with micro-pyramid surface structures that diffuses sunlight while offering passive cooling and self-cleaning properties.
- Gan Huang
- , Ashok R. Yengannagari
- & Bryce S. Richards
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the broadband enhanced light chirality with L-shaped dielectric metamaterials
Controlling the broadband enhanced light chirality with L-shaped dielectric metamaterials
L-shaped silicon metamaterials are realized exhibiting broadband and enhanced chirality. The current work sets new benchmarks in the assembly of ultrathin dielectric chiral metamaterials that can efficiently control chiral light-matter interactions.
- Ufuk Kilic
- , Matthew Hilfiker
- & Christos Argyropoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Arbitrary engineering of spatial caustics with 3D-printed metasurfaces
Arbitrary engineering of spatial caustics with 3D-printed metasurfaces
Caustics, as a unique type of singularity in wave phenomena, occur in diverse physical systems. Here, the authors realize multi-dimensional customization of caustics with 3D-printed metasurfaces. This arbitrary caustic engineering is poised to bring new revolutions to many domains.
- Xiaoyan Zhou
- , Hongtao Wang
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic steering of thermal emission with active metasurface control of delocalized modes
Electrostatic steering of thermal emission with active metasurface control of delocalized modes
Dynamic angular tuning of thermal emission is a problem in the field of thermal metasurfaces. Here, the authors make a thermal emission device using electrostatic gates, opening an avenue for radiative heat management and mid-infrared communication.
- Joel Siegel
- , Shinho Kim
- & Victor Watson Brar
-
Article
| Open Access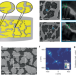 Ultrastrong exciton-plasmon couplings in WS2 multilayers synthesized with a random multi-singular metasurface at room temperature
Ultrastrong exciton-plasmon couplings in WS2 multilayers synthesized with a random multi-singular metasurface at room temperature
Here, the authors fabricate a metasurface with nanometre-sized plasmonic hotspots that interact coherently with WS2 excitons, achieving ultrastrong exciton-plasmon coupling.
- Tingting Wu
- , Chongwu Wang
- & Yu Luo
-
Article
| Open Access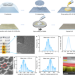 All-silicon multidimensionally-encoded optical physical unclonable functions for integrated circuit anti-counterfeiting
All-silicon multidimensionally-encoded optical physical unclonable functions for integrated circuit anti-counterfeiting
The researchers introduce an all-silicon optical PUF that enhances IoT device security through CMOS-compatible fabrication, showcasing five unique optical responses per pixel for advanced authentication and high information entropy.
- Kun Wang
- , Jianwei Shi
- & Deren Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A terahertz meta-sensor array for 2D strain mapping
A terahertz meta-sensor array for 2D strain mapping
The researchers showcase a flexible meta-sensor array based on classical Mie resonance, enabling precise detection of in-plane strain direction and magnitude using dynamically transmitted terahertz (THz) signals. The sensor array holds immense promise for the real-life applications as it possesses high sensor density and has a very large size up to (110 ×130 mm2).
- Xueguang Lu
- , Feilong Zhang
- & Qiang Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access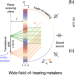 Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Achieving a wide angular response in single layer acoustic metalenses is challenging. By leveraging perfect acoustic symmetry conversion, the authors realize an aberration free metalens with a wide field-of-hearing, up to 140 degrees.
- Dongwoo Lee
- , Beomseok Oh
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access A metasurface-based full-color circular auto-focusing Airy beam transmitter for stable high-speed underwater wireless optical communications
A metasurface-based full-color circular auto-focusing Airy beam transmitter for stable high-speed underwater wireless optical communications
Authors present an adaptive underwater optical communication (UWOC) technology based on multi-wavelength lasers and a full-color metasurface for converting visible-band Gaussian to circular autofocusing Airy beams. The potential of Airy beams to mitigate optical power degradation is demonstrated, enabling stable data rate transmission via 4 K video transmission for these systems.
- Junhui Hu
- , Zeyuan Guo
- & Chao Shen
-
Article
| Open Access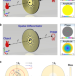 Compact meta-differentiator for achieving isotropically high-contrast ultrasonic imaging
Compact meta-differentiator for achieving isotropically high-contrast ultrasonic imaging
High-contrast ultrasonic imaging holds significant importance in biomedical and engineering applications. Here, the authors present a compact spatial differentiator tailored for underwater isotropic edge-enhanced imaging, facilitating the realization of high-contrast ultrasonic imaging.
- Yurou Jia
- , Suying Zhang
- & Xiaojun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Experimentally realized physical-model-based frugal wave control in metasurface-programmable complex media
Experimentally realized physical-model-based frugal wave control in metasurface-programmable complex media
Using a compact physics-based model, the authors experimentally achieve coherent wave control in metasurface-programmable complex systems with surprisingly frugal protocols (e.g., without ever measuring phase).
- Jérôme Sol
- , Hugo Prod’homme
- & Philipp del Hougne
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic switching from coherent perfect absorption to parametric amplification in a nonlinear spoof plasmonic waveguide
Dynamic switching from coherent perfect absorption to parametric amplification in a nonlinear spoof plasmonic waveguide
The authors propose a nonlinear spoof plasmonic waveguide to realize coherent perfect absorption and parametric amplification at the same frequency, which opens a new route to actively modulate the electromagnetic waves with giant amplification-to-absorption contrast.
- Wen Yi Cui
- , Jingjing Zhang
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Intelligent wireless power transfer via a 2-bit compact reconfigurable transmissive-metasurface-based router
Intelligent wireless power transfer via a 2-bit compact reconfigurable transmissive-metasurface-based router
The rapid emergence of the Internet of Things has led to new power supply challenges. Here, authors propose a compact wireless power transfer framework that can intelligently deliver wireless power to devices in dynamic environments and simultaneously transfer information.
- Wenzhi Li
- , Qiyue Yu
- & Jiaran Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperbolic metamaterial empowered controllable photonic Weyl nodal line semimetals
Hyperbolic metamaterial empowered controllable photonic Weyl nodal line semimetals
One-dimensional photonic crystals provide a platform to modulate Weyl quasiparticles with properties of bound states in the continuum both dynamically (transition and rotation) and topologically (singularities in bilateral drumhead surface states).
- Shengyu Hu
- , Zhiwei Guo
- & Hong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access High-security learning-based optical encryption assisted by disordered metasurface
High-security learning-based optical encryption assisted by disordered metasurface
In this work, the employment of disordered metasurface as an ultra-stable and actively polarized speckle generator in a passive manner, coupled with a double-secure treatment to the plaintext, enables a highly secure speckle-based cryptosystem.
- Zhipeng Yu
- , Huanhao Li
- & Puxiang Lai
-
Article
| Open Access Amber rainbow ribbon effect in broadband optical metamaterials
Amber rainbow ribbon effect in broadband optical metamaterials
The researchers showcased a negative Goos-Hänchen effect in film samples across the entire visible spectrum and discovered an amber rainbow ribbon and an optical black hole where little light leaks out due to perfect back reflection.
- Jing Zhao
- , Xianfeng Wu
- & Xiaopeng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast all-optical second harmonic wavefront shaping
Ultrafast all-optical second harmonic wavefront shaping
Enhancing the data encoding into the orbital angular momentum of light beams could enable faster and more efficient optical communications. This work demonstrates complex control of the second harmonic wavefront with dynamics solely limited by the pulse duration.
- Artem Sinelnik
- , Shiu Hei Lam
- & Isabelle Staude
-
Article
| Open Access Twisted photonic Weyl meta-crystals and aperiodic Fermi arc scattering
Twisted photonic Weyl meta-crystals and aperiodic Fermi arc scattering
Fermi arcs show unpredictable diffraction features resulting from their long-range scattering order in aperiodic systems. Here, authors continuously twist a bi-block Weyl meta-crystal and experimentally observe the twisted Fermi arc reconstruction.
- Hanyu Wang
- , Wei Xu
- & Biao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Poincaré sphere trajectory encoding metasurfaces based on generalized Malus’ law
Poincaré sphere trajectory encoding metasurfaces based on generalized Malus’ law
Polarization serves as an excellent information encoding carrier. Here, authors expand the metasurface encoding dimensionality of polarization information by engineering the Poincaré Sphere trajectory with generalized Malus’ law, unveiling new opportunities for advanced polarization optics.
- Zi-Lan Deng
- , Meng-Xia Hu
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous and Chern topological waves in hyperbolic networks
Anomalous and Chern topological waves in hyperbolic networks
Here the authors experimentally demonstrate the anomalous and Chern topological phases in a hyperbolic non-reciprocal scattering network, establishing unidirectional channels to induce new and exciting wave transport properties in curved spaces.
- Qiaolu Chen
- , Zhe Zhang
- & Romain Fleury
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband angular spectrum differentiation using dielectric metasurfaces
Broadband angular spectrum differentiation using dielectric metasurfaces
Metasurfaces processing incoming images have been proposed in the context of real space operations. Here, the authors demonstrate mathematical operations, such as differentiation, on the angular spectrum of an image using metasurfaces, which can be used to enhance spectral features of an image.
- Ming Deng
- , Michele Cotrufo
- & Lin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Twisted moiré conductive thermal metasurface
Twisted moiré conductive thermal metasurface
Authors control heat transfer through twisting moiré conductive thermal metasurface, showcasing the potential for manipulating thermal conductivity and temperature gradients with imitated magic angles, thereby realizing multifunctional thermal metadevices.
- Huagen Li
- , Dong Wang
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Wandering principal optical axes in van der Waals triclinic materials
Wandering principal optical axes in van der Waals triclinic materials
Principal optical axes define light-matter interactions in crystals and they are usually assumed to be stationary. Here, the authors report the observation of wavelength-dependent principal optical axes in ternary van der Waals crystals (ReS2 and ReSe2), leading to wavelength-switchable propagation directions of their waveguide modes.
- Georgy A. Ermolaev
- , Kirill V. Voronin
- & Kostya S. Novoselov
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of continuum Landau modes in non-Hermitian electric circuits
Observation of continuum Landau modes in non-Hermitian electric circuits
Non-Hermitian systems have many physical properties without Hermitian counterparts. Here, the authors demonstrate a non-Hermitian topolectrical circuit hosting continuous bound states under pseudomagnetic fields with no counterparts in Hermitian systems.
- Xuewei Zhang
- , Chaohua Wu
- & Gang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband thermal imaging using meta-optics
Broadband thermal imaging using meta-optics
Exploring the miniaturization of imaging systems, researchers use inverse-design for broadband meta-optics in the LWIR spectrum. Here, authors achieve a six-fold Strehl ratio improvement in image quality over conventional metalenses using a novel design and computational techniques.
- Luocheng Huang
- , Zheyi Han
- & Arka Majumdar
-
Article
| Open Access Vision-driven metasurfaces for perception enhancement
Vision-driven metasurfaces for perception enhancement
Authors showcase a framework for visual perception enhancement system based on vision-driven metasurfaces. It can help humans obtain information in multiple frequency bands and allows the metasurface platform with more interesting functions.
- Tianshuo Qiu
- , Qiang An
- & Shaobo Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring entanglement entropy and its topological signature for phononic systems
Measuring entanglement entropy and its topological signature for phononic systems
Entanglement entropy exhibits rich phenomenology connected to different kinds of phases in condensed matter. Here, the authors confirm some of these predictions by experimentally probing nonlocal correlations in 1D and 2D phononic crystal based on interconnected resonating acoustic cavities.
- Zhi-Kang Lin
- , Yao Zhou
- & Jian-Hua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic light manipulation via silicon-organic slot metasurfaces
Dynamic light manipulation via silicon-organic slot metasurfaces
In this work, the authors present an active optical metasurface based on a silicon-organic platform. The metasurface can modulate the amplitude of a reflected beam via electric voltage actuation lower than ± 17V.
- Tianzhe Zheng
- , Yiran Gu
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of all-band-flat photonic lattices
Realization of all-band-flat photonic lattices
Here the authors experimentally realized a systematic approach to synthesize arbitrary-size two-dimensional all-band-flat photonic lattices, which pave a route for investigating flat-band related physics such as slow-light, nonlinear breathing, and dispersionless image transmission.
- Jing Yang
- , Yuanzhen Li
- & Fei Gao
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of echoes interference on phonon attenuation in a nanophononic membrane
The effect of echoes interference on phonon attenuation in a nanophononic membrane
Coherent scattering of phonons in a periodic nanostructure leads to interference, which modifies phonon energies. Here, authors observed that a strong interference effect also influences phonon lifetime. Despite its reduction, energy transport is conserved thanks to a hopping of energy among the reflected waves.
- Mohammad Hadi
- , Haoming Luo
- & Valentina M. Giordano
-
Article
| Open Access Optical Tellegen metamaterial with spontaneous magnetization
Optical Tellegen metamaterial with spontaneous magnetization
Here the authors propose an isotropic three-dimensional metamaterial with nonreciprocal magnetoelectric resonant responses at visible and mid-infrared frequencies. The proposed metamaterials do not require external magnetization.
- Shadi Safaei Jazi
- , Ihar Faniayeu
- & Viktar Asadchy
-
Article
| Open Access Linear and phase controllable terahertz frequency conversion via ultrafast breaking the bond of a meta-molecule
Linear and phase controllable terahertz frequency conversion via ultrafast breaking the bond of a meta-molecule
The time-varying metasurfaces show promise for exploring exotic physics and photonic applications. The authors introduce a time-varying metasurface with superconductor-metal hybrid meta-molecules, demonstrating phase-controllable frequency conversion with high efficiency.
- Siyu Duan
- , Xin Su
- & Peiheng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Clocked dynamics in artificial spin ice
Clocked dynamics in artificial spin ice
Artificial spin ices are nanomagnetic metamaterials, whose collective magnetization self-organizes into extended domains. However, controlling when, where and how domains change has proven difficult, yet is crucial for technological applications. Here, Jensen and Strømberg et al. introduce astroid clocking, which enables controlled, stepwise growth and reversal of magnetic domains, using only global fields.
- Johannes H. Jensen
- , Anders Strømberg
- & Erik Folven
-
Article
| Open Access A dual-selective thermal emitter with enhanced subambient radiative cooling performance
A dual-selective thermal emitter with enhanced subambient radiative cooling performance
Radiative cooling is a sustainable subambient cooling technology. Here, authors show a scalable and practical design of a dual-selective thermal emitter that is shown to have enhanced radiative cooling potential over existing typical designs.
- Xueke Wu
- , Jinlei Li
- & Rufan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation
Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation
The authors report the chiral inversion of exceptional points (EPs) through a structural mirror-symmetric operation, extending the application of EP to any desired polarization states, surpassing the inherent limitation of conventional EP systems.
- Zijin Yang
- , Po-Sheng Huang
- & Qinghua Song
-
Perspective
| Open Access Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials
Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials
In this Perspective, the authors illustrate the physics of hyperbolic polaritons in anisotropic 2D and 1D materials, proposing new potential material candidates, forward looking opportunities and technological applications.
- Hongwei Wang
- , Anshuman Kumar
- & Tony Low
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
The requirement for sophisticated objective lenses hinders the miniaturisation of single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy for portable sensing applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a dual-wavelength metalens for real-time monitoring of individual fluorescent nanoparticles.
- Aleksandr Barulin
- , Yeseul Kim
- & Inki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
Wavefront manipulation with metasurfaces is typically limited to low quality factors. Here, the authors show how higher-order Mie modes can be leveraged to design high quality factor optical metasurfaces for wavefront manipulation in two dimensions.
- Claudio U. Hail
- , Morgan Foley
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical geometric image transformations enabled by ultrathin metasurfaces
All-optical geometric image transformations enabled by ultrathin metasurfaces
Metasurfaces enable all-optical geometric coordinate transformations, converting images with altered pixel spatial relations, which can facilitate fast, energy-efficient preprocessing for tasks like object tracking, or aid in laser manufacturing.
- Xingwang Zhang
- , Xiaojie Zhang
- & Xingjie Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
The authors demonstrate how flexible metasurfaces powered by artificial neural network can dynamically manipulate the EM scattering behavior from an arbitrary surface - an ultimate ambition for many EM stealth and communication problems.
- Erda Wen
- , Xiaozhen Yang
- & Daniel F. Sievenpiper

 Microwave-transparent metallic metamaterials for autonomous driving safety
Microwave-transparent metallic metamaterials for autonomous driving safety