Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access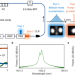 Turnkey photonic flywheel in a microresonator-filtered laser
Turnkey photonic flywheel in a microresonator-filtered laser
Here the authors demonstrate a universal approach to achieve turnkey dissipative Kerr soliton (DKS) frequency comb. Phase insensitivity, self-healing capability, deterministic selection of DKS state, and access to ultralow noise are all successfully accomplished.
- Mingming Nie
- , Jonathan Musgrave
- & Shu-Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A mode-locked random laser generating transform-limited optical pulses
A mode-locked random laser generating transform-limited optical pulses
Pulses of adjustable duration are generated by a mode-locked random fibre laser that can drive advances in sensing. Rayleigh backscattering from cm-long sections of telecom fibre provides laser feedback and spectral selectivity to the Fourier limit.
- Jean Pierre von der Weid
- , Marlon M. Correia
- & Walter Margulis
-
Article
| Open Access Two-photon imaging of soliton dynamics
Two-photon imaging of soliton dynamics
The authors present a moving-parts-free approach for visualizing soliton motion in optical cavities that lifts the wavelength and speed constraints of contemporary pulsed laser diagnostic techniques.
- Łukasz A. Sterczewski
- & Jarosław Sotor
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond-precision electronic clock distribution in CMOS chips by injecting frequency comb-extracted photocurrent pulses
Femtosecond-precision electronic clock distribution in CMOS chips by injecting frequency comb-extracted photocurrent pulses
A clock distribution network (CDN) is a ubiquitous element that provides synchronized clocks to all circuit blocks in the chip. Here the authors demonstrate femtosecond-precision distribution of clocks in CMOS chips using optical frequency combs and driverless CDNs.
- Minji Hyun
- , Hayun Chung
- & Jungwon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling the complexity of spatiotemporal soliton molecules in real time
Unveiling the complexity of spatiotemporal soliton molecules in real time
The authors present the real-time spectral-temporal dynamics of 3D soliton molecules, highlighting the importance of nonlinear spatiotemporal coupling in the dynamics of spatiotemporal mode-locking.
- Yuankai Guo
- , Wei Lin
- & Zhongmin Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Farey tree and devil’s staircase of frequency-locked breathers in ultrafast lasers
Farey tree and devil’s staircase of frequency-locked breathers in ultrafast lasers
Fractal optical solitons were studied in theory while it is cumbersome their experimental realization in optics setups. Here, the authors find that breathing solitons in lasers constitute fractals―the devil’s staircases, which are around 3000 times more stable than classical ones.
- Xiuqi Wu
- , Ying Zhang
- & Heping Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-comb thin-disk oscillator
Dual-comb thin-disk oscillator
Achieving high output powers in dual-comb sources is important for possible applications like deep UV high resolution spectroscopy. Here the authors demonstrate a fully passive scheme of generating a set of high-power dual-combs from a thin-disc gain medium.
- Kilian Fritsch
- , Tobias Hofer
- & Oleg Pronin
-
Article
| Open Access Spatio-temporal-spectral imaging of non-repeatable dissipative soliton dynamics
Spatio-temporal-spectral imaging of non-repeatable dissipative soliton dynamics
Due to three-dimensional, stochastic and non-repeatable transitions of dissipative solitons, it is challenging to monitor their full dynamics. Here, the authors resolve the dynamics by wavelength and along two spatial dimensions with up to trillions of frames per second using compressed ultrafast photography.
- Joseph C. Jing
- , Xiaoming Wei
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent master equation for laser modelocking
Coherent master equation for laser modelocking
Modelocked lasers are typically modeled using the Haus master equation which, albeit powerful, provides only a limited description in certain parameter regimes. The authors introduce another master equation formalism to describe laser modelocking that accounts for coherent effects and overcomes these limitations.
- Auro M. Perego
- , Bruno Garbin
- & Germán J. de Valcárcel
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of optical supramolecular structures in a fibre laser by tailoring long-range soliton interactions
Formation of optical supramolecular structures in a fibre laser by tailoring long-range soliton interactions
Optical solitons have been studied in a variety of systems for their unique properties. Here, the authors report on optically observed solitonic supramolecules, made up of large-scale structures of many solitons interacting within a fiber cavity, and study their fundamental characteristics.
- W. He
- , M. Pang
- & P. St. J. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of laser radiation using the Nonlinear Fourier transform
Analysis of laser radiation using the Nonlinear Fourier transform
Mathematical approaches for simultaneous characterisation of localized and extended fields in optical signals are not well developed. Here, the authors demonstrate the application of the Nonlinear Fourier transform approach based on the Zakharov-Shabat spectral problem for the analysis of fibre laser radiation.
- Srikanth Sugavanam
- , Morteza Kamalian Kopae
- & Sergei K. Turitsyn
-
Article
| Open Access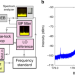 Fully phase-stabilized quantum cascade laser frequency comb
Fully phase-stabilized quantum cascade laser frequency comb
Here, the authors demonstrate full stabilization and control of the two key parameters of a four-wavemixing-based quantum cascade laser comb with metrological precision. These fully-controlled, frequency scalable comb emitters will allow an increasing number of mid- and far-IR applications.
- Luigi Consolino
- , Malik Nafa
- & Saverio Bartalini
-
Article
| Open Access Optical soliton molecular complexes in a passively mode-locked fibre laser
Optical soliton molecular complexes in a passively mode-locked fibre laser
It has recently been shown that optical solitons can form stably bound states, so-called soliton molecules. Here, Wang et al. demonstrate stable soliton molecule complexes and explore the different bonds represented by the inter- and intra-molecular coupling.
- Z. Q. Wang
- , K. Nithyanandan
- & Ph. Grelu
-
Article
| Open Access Watt-level 10-gigahertz solid-state laser enabled by self-defocusing nonlinearities in an aperiodically poled crystal
Watt-level 10-gigahertz solid-state laser enabled by self-defocusing nonlinearities in an aperiodically poled crystal
Ultrafast lasers with multi-gigahertz repetition rates are desirable for applications requiring high sampling rates or resolvable frequency comb lines. Here, Mayer et al. use cascading of quadratic nonlinearities to passively modelock a femtosecond solid-state laser at a repetition rate of 10 GHz.
- A. S. Mayer
- , C. R. Phillips
- & U. Keller
-
Article
| Open Access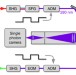 Single ion fluorescence excited with a single mode of an UV frequency comb
Single ion fluorescence excited with a single mode of an UV frequency comb
Frequency combs are useful tools in high precision measurement including atomic transitions and atomic clocks. Here the authors demonstrate direct frequency comb spectroscopy to shorter wavelengths by probing a transition frequency in a trapped Mg+ ion using a single mode of a UV frequency comb.
- Akira Ozawa
- , Josue Davila-Rodriguez
- & Thomas Udem
-
Article
| Open Access A robust and tuneable mid-infrared optical switch enabled by bulk Dirac fermions
A robust and tuneable mid-infrared optical switch enabled by bulk Dirac fermions
Mid-infrared pulsed sources are technologically important for sensing and spectroscopy but their implementation is challenging due to the lack of a tuneable optical switch. Here, the authors address this limitation by engineering the band structure of an emerging Dirac semimetal, Cd3As2.
- Chunhui Zhu
- , Fengqiu Wang
- & Shining Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Active mode locking of quantum cascade lasers in an external ring cavity
Active mode locking of quantum cascade lasers in an external ring cavity
Compact, integrated mode-locked lasers can produce ultrashort pulses of light in the visible and near infrared, but are more difficult to achieve in the mid-infrared. Here, the authors demonstrate active mode locking of an external-cavity quantum cascade laser emitting at 5.2 micrometres at room temperature.
- D. G. Revin
- , M. Hemingway
- & A. Belyanin
-
Article
| Open Access High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator
High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator
An optical frequency comb demodulated on a photodiode can generate a radio frequency signal with high spectral purity at a frequency corresponding to the comb spacing. Here, Liang et al.demonstrate a frequency-comb-based radio frequency photonic oscillator characterized with low phase noise and high frequency stability.
- W. Liang
- , D. Eliyahu
- & L. Maleki
-
Article
| Open Access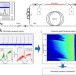 Stochasticity, periodicity and localized light structures in partially mode-locked fibre lasers
Stochasticity, periodicity and localized light structures in partially mode-locked fibre lasers
The interplay of processes with different spatio-temporal scales is present in many physical systems but its study is challenging. Here, Churkin et al. study the dynamics of a partially mode-locked laser where stochastic and periodic processes interplay by mapping the evolution of the intensity autocorrelation function.
- D. V. Churkin
- , S. Sugavanam
- & S. K. Turitsyn
-
Article |
 Picosecond pulses from wavelength-swept continuous-wave Fourier domain mode-locked lasers
Picosecond pulses from wavelength-swept continuous-wave Fourier domain mode-locked lasers
Ultrafast lasers are important in many fields of science, but they typically have high power consumption. Here Eigenwillig et al.realize picosecond laser pulses directly from a semiconductor-based laser. Due to the low repetition rate, high-energy pulses are generated at low average power.
- Christoph M. Eigenwillig
- , Wolfgang Wieser
- & Robert Huber
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity
Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity
Stable, ultrahigh repetition rate optical clocks are critical for applications in high-speed communications, metrology and microchip computing. Pecciantiet al.present a mode-locked laser based on an integrated microcavity, with repetition rate exceeding 200 GHz and narrow linewidth pulses.
- M. Peccianti
- , A. Pasquazi
- & R. Morandotti

 Electrically empowered microcomb laser
Electrically empowered microcomb laser