Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of DNA origami folding elucidated by mesoscopic simulations
Mechanism of DNA origami folding elucidated by mesoscopic simulations
The self-assembly process of DNA nanostructures is still not well understood, especially for DNA origami. Here, the authors present a mesoscopic model that uses a switchable force field to capture the mechanical behavior of single- and double-stranded DNA motifs and transition between them, allowing access to the long assembly timescales of DNA origami up to several kilobases in size.
- Marcello DeLuca
- , Daniel Duke
- & Gaurav Arya
-
Article
| Open Access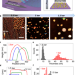 Crystallization of molecular layers produced under confinement onto a surface
Crystallization of molecular layers produced under confinement onto a surface
Molecules arranged in close proximity to a surface form molecular layers, exhibiting distinct properties. However, the creation of these layers is challenging. Here, the authors present a technique for generating molecular layers through crystallization induced by gas blowing onto a surface.
- Jincheng Tong
- , Nathan de Bruyn
- & Cinzia Casiraghi
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
The assembly of oligopeptide and polypeptide molecules can reconstruct various ordered advanced structures. Here the authors develop a “molecular velcro”-inspired amphiphilic supramolecular co-assembly strategy, which improves the mechanical strength and cartilaginous regeneration efficiency through conformation transition.
- Chengkun Zhao
- , Xing Li
- & Yong Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Functional features in the spatiotemporal regulation of blood chemistry are not much explored. Here authors show vascular network-inspired fluidics, functionalizable for different region-specific trans-wall transport to regulate fluids over space and time.
- Yafeng Yu
- , Yi Pan
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access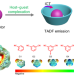 A general supramolecular strategy for fabricating full-color-tunable thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials
A general supramolecular strategy for fabricating full-color-tunable thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials
Thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials with full-colour tunability are desirable but challenging to prepare. Here, the authors report a method for preparing such materials through the design of host-guest cocrystals with through-space charge transfer.
- Nan Xue
- , He-Ye Zhou
- & Chuan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access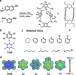 Separation of benzene and toluene associated with vapochromic behaviors by hybrid[4]arene-based co-crystals
Separation of benzene and toluene associated with vapochromic behaviors by hybrid[4]arene-based co-crystals
Cocrystal engineering combined with macrocycle chemistry has allowed the development of materials with vapochromic characteristics. Here, the authors report the development of a macrocycle cocrystal for the separation of trace solvents.
- Jingyu Chen
- , Wenjie Zhang
- & Jiong Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access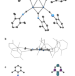 A zero-valent palladium cluster-organic framework
A zero-valent palladium cluster-organic framework
Ultrasmall metallic clusters receive great attention for atom-efficient catalysts. Here a metallic cluster–organic framework is synthesized and characterized; authors demonstrate its stability and catalytic proficiency, paving the way for molecular-scale metal nanoparticle interlocking.
- Xiyue Liu
- , James N. McPherson
- & Kasper S. Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Artificial ion channels have potential in a range of applications, but achieving performance comparable to biological channels has been challenging. Here, the authors report an artificial, light-driven chloride pump, inspired by halorhodopsin, with a helical porphyrin channel array.
- Chao Li
- , Yi Zhai
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-propelled assembly of nanoparticles with self-catalytic regulation for tumour-specific imaging and therapy
Self-propelled assembly of nanoparticles with self-catalytic regulation for tumour-specific imaging and therapy
In vivo manipulation of the dynamics of nanoparticles’ is essential for disease-specific imaging and therapy, but tends to involve complex design processes. Here, the authors report a strategy for manipulating the assembly of nanoparticles in vivo through a self-catalysis-instructed dimerization of tyrosine, offering convenient fabrication, high reaction specificity and biocompatibility.
- Mengmeng Xia
- , Qiyue Wang
- & Daishun Ling
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly of clusters and copolymers towards programmed mesoporous metal oxides
Solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly of clusters and copolymers towards programmed mesoporous metal oxides
A solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly method is developed to achieve a general and programmable synthesis of mesoporous metal oxides via the association of POMs with block copolymers through indirect interaction.
- Wenhe Xie
- , Yuan Ren
- & Yonghui Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Roll-to-plate 0.1-second shear-rolling process at elevated temperature for highly aligned nanopatterns
Roll-to-plate 0.1-second shear-rolling process at elevated temperature for highly aligned nanopatterns
In this work, authors demonstrate a 0.1-second shear rolling process capable of shearing without peeling up to 280 °C. This enables roll-to-plate fabrication of highly and unidirectionally aligned sub−10 nm block copolymer patterns over large wafer areas.
- Junghyun Cho
- , Jinwoo Oh
- & Jeong Gon Son
-
Article
| Open Access Fragment-based drug nanoaggregation reveals drivers of self-assembly
Fragment-based drug nanoaggregation reveals drivers of self-assembly
Drug nanoaggregates could be used to improve drug pharmacokinetics when developed for drug delivery, however, the structural features of molecules that drive nanoaggregate formation remain elusive. Here, the authors investigate nanoaggregate self-assembly mechanisms using small molecule fragments to identify the critical molecular forces that contribute to self-assembly, namely aromatic groups and hydrogen bond acceptors/donors.
- Chen Chen
- , You Wu
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition
Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition
Strategies to construct circularly polarized luminescence (CPL)-active materials with color modulation and handedness of CPL are desirable for the synthesis of chiral photo-responsive devices. Here the authors develop a CPL system based on styrylpyrenes. Benefiting from CH-π interactions between chromophores, the styrylpyrene aggregates show color-dependent CPL property and photo-responsive behavior.
- Wei Yuan
- , Letian Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access DNA T-shaped crossover tiles for 2D tessellation and nanoring reconfiguration
DNA T-shaped crossover tiles for 2D tessellation and nanoring reconfiguration
DNA tiles lay the foundation for programmable self-assembly of diverse DNA nanostructures. Here, the authors present a set of T-shaped crossover DNA tiles for various 2D tessellation and nanoring reconfiguration.
- Qi Yang
- , Xu Chang
- & Fei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying topological corner states in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks
Identifying topological corner states in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks
Two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks (2D MOFs) are ideal platforms to realize exotic theoretical lattice models. Here, the authors experimentally realize second-order topological corner states in the 2D MOF Ni3(HITP)2, which features a star-lattice configuration.
- Tianyi Hu
- , Weiliang Zhong
- & Z. F. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Grinding-induced supramolecular charge-transfer assemblies with switchable vapochromism toward haloalkane isomers
Grinding-induced supramolecular charge-transfer assemblies with switchable vapochromism toward haloalkane isomers
The use of macrocycles to develop charge-transfer complexes in the solid state was recently demonstrated. Here, the authors develop an on-off type vapochromic system toward positional bromoalkane isomers by the reassembly and disassembly of charge-transfer complexes between a pillar[5]arene and electron-deficient aromatic guests in the solid state.
- Jia-Rui Wu
- , Gengxin Wu
- & Ying-Wei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Data-mining unveils structure–property–activity correlation of viral infectivity enhancing self-assembling peptides
Data-mining unveils structure–property–activity correlation of viral infectivity enhancing self-assembling peptides
Certain peptides can boost viral infectivity. However, the requirements for their activity remain unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that peptides are efficient viral enhancers if they form hydrophobic β-sheet-rich, positively charged μm-sized aggregates.
- Kübra Kaygisiz
- , Lena Rauch-Wirth
- & Tanja Weil
-
Article
| Open Access The sharp structural switch of covalent cages mediated by subtle variation of directing groups
The sharp structural switch of covalent cages mediated by subtle variation of directing groups
Controlling the self-assembly on noncovalent components is possible by suppressing entropy loss with templates but this is challenging for covalent components. Here the authors employed directing groups to endow purely covalent molecular building blocks with different conformations which favor the formation of specific self-assembled products.
- Qiong Chen
- , Zhaoyong Li
- & Hao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Active self-assembly of piezoelectric biomolecular films via synergistic nanoconfinement and in-situ poling
Active self-assembly of piezoelectric biomolecular films via synergistic nanoconfinement and in-situ poling
Piezoelectric biomaterials are limited by the challenges in domain orientation alignment and a weak piezoelectric effect. Here, Zhang et. al. present an active self-assembly strategy via nanoconfinement and in-situ poling, to obtain large-scale, high performance piezoelectric β-glycine nanocrystalline films.
- Zhuomin Zhang
- , Xuemu Li
- & Zhengbao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular conformation of polyelectrolytes inside Layer-by-Layer assembled films
Molecular conformation of polyelectrolytes inside Layer-by-Layer assembled films
’Layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly is currently one of the most widely used techniques for the fabrication of multicomponent architectures with nanometer scale control but achieving control over the 3D structure, and thus the ability to predict and understand the device performance, is challenging. Here, the authors use neutron scattering to determine the average conformation of individual deuterated polyelectrolyte chains inside LbL assembled films.
- Philipp Gutfreund
- , Christophe Higy
- & Gero Decher
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating the prediction and discovery of peptide hydrogels with human-in-the-loop
Accelerating the prediction and discovery of peptide hydrogels with human-in-the-loop
Accurate prediction of peptidic hydrogels could prove useful for diverse biomedical applications. Here, the authors develop a “human-in-the-loop” approach that integrates coarse-grained molecular dynamics, machine learning, and experimentation to design natural peptide hydrogels.
- Tengyan Xu
- , Jiaqi Wang
- & Huaimin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Upper critical solution temperature polymer assemblies via variable temperature liquid phase transmission electron microscopy and liquid resonant soft X-ray scattering
Upper critical solution temperature polymer assemblies via variable temperature liquid phase transmission electron microscopy and liquid resonant soft X-ray scattering
The inclusion of an upper critical solution temperature (UCST) block in multiblock copolymer amphiphiles can enable temperature triggered nanoscale morphological transitions, but there are limited studies probing the actual UCST transition. Here, the authors couple variable temperature liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy and variable temperature liquid resonant soft X-ray scattering to study UCST polymeric nanostructures.
- Joanna Korpanty
- , Cheng Wang
- & Nathan C. Gianneschi
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-chiral materials comprising metallosupramolecular and covalent helical polymers containing five axial motifs within a helix
Multi-chiral materials comprising metallosupramolecular and covalent helical polymers containing five axial motifs within a helix
The axial helical structure of supramolecular and covalent polymers provides communication mechanisms among monomer repeating units. Here, the authors present multi-helical materials comprising five axial motifs that combine information from both metallosupramolecular and covalent helical polymers
- Francisco Rey- Tarrío
- , Emilio Quiñoá
- & Félix Freire
-
Article
| Open Access Pore partition in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks
Pore partition in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks
The development of ultramicroporous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) remains a daunting challenge. Here, the authors report a pore partition strategy, which allows for the segmentation of mesopores of COFs into multiple uniform ultramicroporous domains.
- Xiaoyi Xu
- , Xinyu Wu
- & Ning Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic control of self-assembly and disassembly in organic materials
Magnetic control of self-assembly and disassembly in organic materials
Organic molecules and materials are generally insensitive or weakly sensitive to magnetic fields due to their small diamagnetic force. Here, the authors show a strategy to amplify the magnetic responsiveness of self-assembled peptide nanostructures by synergistically combining the concepts of perfect α-helix and rod-coil supramolecular building blocks
- You-jin Jung
- , Hyoseok Kim
- & Yong-beom Lim
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic polymerization of enantiomeric L−3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into films with enhanced rigidity and stability
Enzymatic polymerization of enantiomeric L−3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into films with enhanced rigidity and stability
L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine plays an important role in living system. Here, the authors investigated the effect of the molecular chirality of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine on the improved structural and thermal stability of self-assembled films by tyrosinase-induced oxidative polymerization.
- Yuhe Shen
- , Rongxin Su
- & Wei Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Shape control in 2D molecular nanosheets by tuning anisotropic intermolecular interactions and assembly kinetics
Shape control in 2D molecular nanosheets by tuning anisotropic intermolecular interactions and assembly kinetics
Structuring organic films is of scientific and technological interest. Here, the authors use partially fluorinated organic molecules exhibiting strong intermolecular interactions to form extended 2D molecular nanosheets and control their shape through growth and desorption kinetics.
- Maximilian Dreher
- , Pierre Martin Dombrowski
- & Gregor Witte
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneous intercalated metal-organic framework active materials for fast-charging non-aqueous Li-ion capacitors
Heterogeneous intercalated metal-organic framework active materials for fast-charging non-aqueous Li-ion capacitors
Ideal anode materials for Li-ion capacitors must demonstrate safety and fast-charging properties. Here, the authors propose intercalated metal-organic frameworks for fast-charging Li-ion capacitors using a combined machine learning design and spray-dry synthesis.
- Nobuhiro Ogihara
- , Masaki Hasegawa
- & Naoyuki Nagasako
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid molecular graphene transistor as an operando and optoelectronic platform
Hybrid molecular graphene transistor as an operando and optoelectronic platform
Molecular electronics represents an avenue to enrich conventional electronics, but its reproducibility and scalability are still challenging. Here, the authors report the realization of multifunctional hybrid molecular graphene field effect transistors enabling operando spectroscopy and the implementation of optoelectronic logic gates.
- Jorge Trasobares
- , Juan Carlos Martín-Romano
- & Daniel Granados
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired crowding directs supramolecular polymerisation
Bioinspired crowding directs supramolecular polymerisation
Crowding effects have long been established as powerful guiding forces in natural assembly processes. Here the authors report a bioinspired approach translating this phenomenon to artificial supramolecular polymers.
- Nils Bäumer
- , Eduardo Castellanos
- & Gustavo Fernández
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular framework membrane for precise sieving of small molecules, nanoparticles and proteins
Supramolecular framework membrane for precise sieving of small molecules, nanoparticles and proteins
Synthetic framework materials are appealing candidates for the fabrication of separation membranes but realizing precise control of aperture distribution and separation threshold remains challenging. Here, the authors show a two-dimensional processible supramolecular framework which can be used in the fabrication of separation membranes by integrating directional organic host-guest motifs and inorganic functional polyanionic clusters.
- Guohua Zhang
- , Xinyue Li
- & Lixin Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies
Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies
Self-healing materials hold great promise for applications in wearable electronics, artificial muscles and soft robots but selfhealing at subzero temperatures remains a great challenge. Here, the authors present a robust subzero healable glassy polymer by incorporating polyphenol nano-assemblies with a large number of end groups into polymerizable deep eutectic solvent elastomers.
- Nan Wang
- , Xin Yang
- & Xinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access New insights in polydopamine formation via surface adsorption
New insights in polydopamine formation via surface adsorption
Polydopamine is a biomimetic self-adherent polymer, which can be easily deposited on a wide variety of materials but the polymerization mechanism and the key intermediate species formed during the deposition process are still controversial. Here, the authors report a systematic investigation of polydopamine formation on halloysite nanotubes.
- Hamoon Hemmatpour
- , Oreste De Luca
- & Petra Rudolf
-
Article
| Open Access Priming self-assembly pathways by stacking block copolymers
Priming self-assembly pathways by stacking block copolymers
Self-assembly of block-copolymers yields nanoscale structures in a facile way, but the diversity of structures is limited. Here, the authors demonstrate how block copolymer layering can be used to access new non-equilibrium morphologies.
- Sebastian T. Russell
- , Suwon Bae
- & Kevin G. Yager
-
Article
| Open Access Encapsulated CdSe/CdS nanorods in double-shelled porous nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction
Encapsulated CdSe/CdS nanorods in double-shelled porous nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction
The authors design double shelled hollow superstructures from self-assembled CdSe/CdS nanorods in covalent organic frameworks for CO2 photo-reduction at a gas/solid interface.
- Hui Li
- , Caikun Cheng
- & Jingjing Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Field-induced orientational switching produces vertically aligned Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets
Field-induced orientational switching produces vertically aligned Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets
In this work, authors demonstrate reversible vertical alignment of Ti3C2Tx MXene sheets induced by an applied in-plane electric field. Further modulation of the field can achieve programmed patterns onto various electrode substrates.
- Changjae Lee
- , Soon Mo Park
- & Dong Ki Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Co-assembled perylene/graphene oxide photosensitive heterobilayer for efficient neuromorphics
Co-assembled perylene/graphene oxide photosensitive heterobilayer for efficient neuromorphics
Layered heterostructures are promising photosensitive materials for advanced optoelectronics. Here, the authors introduce an interfacial coassembly method to construct large-scale perylene/grahene oxide (GO) heterobilayer for broadband photoreception and efficient neuromorphics.
- He-Shan Zhang
- , Xue-Mei Dong
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Control cell migration by engineering integrin ligand assembly
Control cell migration by engineering integrin ligand assembly
Engineering peptide assembly that controls integrin ligand presentation on the molecular level possesses by far the highest ligand density, expanding the perspective of ligand-density-dependent modulation.
- Xunwu Hu
- , Sona Rani Roy
- & Ye Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous formation of a self-healing carbon nanoskin at the liquid–liquid interface
Spontaneous formation of a self-healing carbon nanoskin at the liquid–liquid interface
Biological membranes exhibit the ability to self-repair and dynamically change their shape while remaining impermeable but these defining features are difficult to reconcile with mechanical robustness. Here, the authors report on the spontaneous formation of a carbon nanoskin at the oil-water interface that uniquely combines self-healing attributes with high stiffness.
- Enzo Bomal
- , Paul Grandgeorge
- & Holger Frauenrath
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically stable and amplified circularly polarized excimer emission regulated by solvation of chiral co-assembly process
Dynamically stable and amplified circularly polarized excimer emission regulated by solvation of chiral co-assembly process
Chiral supramolecular assembly is an important strategy for the development of excellent circularly polarized luminescent (CPL)-active materials, but often they suffer from low quantum yield and luminescence dissymmetry factor. Herein, the authors we report a chiral coassembly process of achiral pyrene-based dyes leading to chiral excimers emitting with a high dissymmetry factor.
- Yuxia Zhang
- , Hang Li
- & Yixiang Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access CNT-molecule-CNT (1D-0D-1D) van der Waals integration ferroelectric memory with 1-nm2 junction area
CNT-molecule-CNT (1D-0D-1D) van der Waals integration ferroelectric memory with 1-nm2 junction area
The van der Waals integration of molecular layer (0D) with 2D or 3D electrodes is limited at microscale junction. Here, the authors introduce 1D-0D-1D vdWI memory with 1 nm2 junction achieved by cross-stacking t-CNT on molecularly assembled b-CNT.
- Thanh Luan Phan
- , Sohyeon Seo
- & Woo Jong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsically fluorescent polyureas toward conformation-assisted metamorphosis, discoloration and intracellular drug delivery
Intrinsically fluorescent polyureas toward conformation-assisted metamorphosis, discoloration and intracellular drug delivery
Biomimetic materials are of interest but can often suffer from limitations caused by the non-native linkages used. Here, the authors report on the creation of amino acid constructed polyureas which can self-assemble into vesicles and nanotubes with aggregation induced fluorescence and the potential for drug delivery applications.
- Yeqiang Zhou
- , Fan Fan
- & Mingming Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale organization of two-dimensional multimeric pMHC reagents with DNA origami for CD8+ T cell detection
Nanoscale organization of two-dimensional multimeric pMHC reagents with DNA origami for CD8+ T cell detection
MHC-peptide multimers are important reagents for detecting antigen specific T cells. Here the authors show that DNA scaffolds can be used to make MHC-peptide multimers and the avidity controlled so that low abundance or T cells with low affinity TCR can be detected using these reagents.
- Yueyang Sun
- , Lu Yan
- & Hao Pei
-
Article
| Open Access Highly luminescent scintillating hetero-ligand MOF nanocrystals with engineered Stokes shift for photonic applications
Highly luminescent scintillating hetero-ligand MOF nanocrystals with engineered Stokes shift for photonic applications
The development of highly luminescent materials such as large Stokes shift fast emitters is desirable for their potential application in photonics. Here the authors engineer hetero-ligand metal-organic frameworks nanoparticles to achieve high emission yield, large Stokes shift and realize a prototypal fast scintillator.
- J. Perego
- , Charl X. Bezuidenhout
- & A. Monguzzi
-
Article
| Open Access Bis-Schiff base linkage-triggered highly bright luminescence of gold nanoclusters in aqueous solution at the single-cluster level
Bis-Schiff base linkage-triggered highly bright luminescence of gold nanoclusters in aqueous solution at the single-cluster level
Boosting the luminescence of atomically precise metal clusters is a main goal in view of applications. Here, the authors describe a strategy to increase the photoluminescence quantum yield of water-soluble gold clusters at the single-cluster level via formation of bis-Schiff base linkages, providing detailed insight into the mechanism.
- Haohua Deng
- , Kaiyuan Huang
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancement of electrocatalytic oxygen evolution by chiral molecular functionalization of hybrid 2D electrodes
Enhancement of electrocatalytic oxygen evolution by chiral molecular functionalization of hybrid 2D electrodes
While solar-to-fuel catalysis requires the careful transfer of electrons, there are still challenges understanding how electron spin contributes to reactivity. Here, authors employ chiral fused thiadiazole-helicenes to control spin polarization in oxygen evolution electrocatalysts.
- Yunchang Liang
- , Karla Banjac
- & Magalí Lingenfelder
-
Article
| Open Access Light-activated photodeformable supramolecular dissipative self-assemblies
Light-activated photodeformable supramolecular dissipative self-assemblies
Dissipative self-assembly can serve as a controllable platform to exhibit temporal processes for various non-stimulus responsive properties but construction of light-fueled dissipative self-assembly structures with transformable morphology to modulate non-photoresponsive properties remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a light-activated photodeformable dissipative self-assembly system in aqueous solution as metastable fluorescent platform.
- Xu-Man Chen
- , Wei-Jie Feng
- & Quan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid crystals of neat boron nitride nanotubes and their assembly into ordered macroscopic materials
Liquid crystals of neat boron nitride nanotubes and their assembly into ordered macroscopic materials
Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTS) have only been shown to dissolve in chlorosulfonic acid (CSA) at low concentrations. Here the authors successfully demonstrate the formation of liquid crystals of BNNTs in CSA that can be used to produce macroscopically aligned neat fibers of BNNTs.
- Cedric J. Simonsen Ginestra
- , Cecilia Martínez-Jiménez
- & Matteo Pasquali
-
Article
| Open Access Highly stable and tunable peptoid/hemin enzymatic mimetics with natural peroxidase-like activities
Highly stable and tunable peptoid/hemin enzymatic mimetics with natural peroxidase-like activities
Peroxidase mimics are currently being investigated as catalysts for lignin depolymerisation. In this article, the authors investigate a class of self-assembled and highly stable peptoid/hemin nanomaterials as peroxidase mimics that are highly stable and tuneable for the depolymerisation of a biorefinery lignin.
- Tengyue Jian
- , Yicheng Zhou
- & Chun-Long Chen

 Synthetic molecular switches driven by DNA-modifying enzymes
Synthetic molecular switches driven by DNA-modifying enzymes