Featured
-
-
Article |
 A submicron plasmonic dichroic splitter
A submicron plasmonic dichroic splitter
The miniaturization of optical devices is crucial for their on-chip integration with a variety of technological applications. Here, Liuet al. present an ultracompact beam splitter to control the direction of light through the generation of surface plasmon polaritons.
- John S.Q. Liu
- , Ragip A. Pala
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article |
 Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers
Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers
Plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials can augment the performance of photovoltaic and thermophotovoltaic cells by enhancing their absorption properties. Aydinet al. demonstrate a broadband, ultrathin plasmonic super absorber using crossed trapezoids as part of a metal–insulator–metal stack.
- Koray Aydin
- , Vivian E. Ferry
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article |
 Field-effect reconfigurable nanofluidic ionic diodes
Field-effect reconfigurable nanofluidic ionic diodes
Nanofluidic diodes are utilized for the rectification of ionic transport, but their rectifying properties cannot be altered after the devices are made. Here, a field-effect reconfigurable nanofluidic diode is reported in which the forward direction and the degree of rectification can be modulated by a gate voltage.
- Weihua Guan
- , Rong Fan
- & Mark A. Reed
-
Article |
 Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule–metal contacts
Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule–metal contacts
The ability to control the charge and spin of single molecules at metal interfaces underpins the concept of molecular electronics. Mugarzaet al. examine these properties using scanning tunnelling microscopy, and uncover their influence on the magnetism and transport properties of the molecule/metal systems.
- Aitor Mugarza
- , Cornelius Krull
- & Pietro Gambardella
-
Article
| Open Access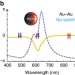 A bimetallic nanoantenna for directional colour routing
A bimetallic nanoantenna for directional colour routing
Plasmon resonances occur as collective excitations of surface electrons in noble metal nanoparticles. This study presents a new way of manipulating their behaviour by creating bimetallic dimers which, as a result of their asymmetric composition, give rise to unusual optical properties.
- Timur Shegai
- , Si Chen
- & Mikael Käll
-
Article |
 Plasmonic substrates for multiplexed protein microarrays with femtomolar sensitivity and broad dynamic range
Plasmonic substrates for multiplexed protein microarrays with femtomolar sensitivity and broad dynamic range
Protein microarrays are useful both in basic research and also in disease monitoring and diagnosis, but their dynamic range is limited. By using plasmonic gold substrates with near-infrared fluorescent enhancement, Tabakman et al. demonstrate a multiplexed protein array with improved detection limits and dynamic range.
- Scott M. Tabakman
- , Lana Lau
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Cascaded logic gates in nanophotonic plasmon networks
Cascaded logic gates in nanophotonic plasmon networks
Optical computing, involving on-chip integrated logic units, could provide improved performance over semiconductor-based computing. Here, a binary NOR gate is developed from cascaded OR and NOT gates in four-terminal plasmonic nanowire networks; the work could lead to new optical computing technologies.
- Hong Wei
- , Zhuoxian Wang
- & Hongxing Xu
-
Article |
 Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales
Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales
Metal-based nanostructures offer a solution to scale down photonics to the nanoscale. Sorgeret al. directly demonstrate waveguiding of ultra-small propagating waves at visible and near-infrared frequencies using NSOM imaging, with the potential for nanoscale photonic applications such as bio-sensing.
- Volker J. Sorger
- , Ziliang Ye
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the molecular structure of single-molecule junctions in different conductance states by fishing-mode tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Revealing the molecular structure of single-molecule junctions in different conductance states by fishing-mode tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The conductance of single-molecule junctions is affected by the structure of the molecule and how it is bound to the electrodes, which may be examined using Raman spectroscopy. Liuet al. have developed 'fishing-mode' tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, which allows the simultaneous determination of conductance and Raman spectra.
- Zheng Liu
- , Song-Yuan Ding
- & Zhong-Qun Tian
-
Article |
 A monolithically integrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera
A monolithically integrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera
Infrared cameras are used for night vision and in medical diagnostics, but currently only present monochrome images. Krishnaet al. demonstrate a monolithically intergrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera as a step towards coloured infrared imaging.
- Sang Jun Lee
- , Zahyun Ku
- & Sam Kyu Noh
-
Article |
 A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
Single-molecule force spectroscopy is used to study single molecule interactions, but probing short-lived events is difficult. Here, a nanomechanical interface is developed, which allows the study of microsecond timescale interactions.
- Mingdong Dong
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access A fast and low-power microelectromechanical system-based non-volatile memory device
A fast and low-power microelectromechanical system-based non-volatile memory device
New memory devices are being developed to overcome the limitations of conventional silicon-based flash memory. Here, a non-volatile memory design is reported that uses a micromechanical cantilever to charge and discharge a floating gate, which controls charge transport through a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor.
- Sang Wook Lee
- , Seung Joo Park
- & Yung Woo Park
-
Article
| Open Access Observation and electric current control of a local spin in a single-molecule magnet
Observation and electric current control of a local spin in a single-molecule magnet
In molecular spintronics, the spin state of a molecule may be switched by changing the molecular structure. Here, the spin of a single-molecule magnet is switched by applying an electric current using a scanning tunnelling microscope, which may aid in information coding at the single-molecule level.
- Tadahiro Komeda
- , Hironari Isshiki
- & Masahiro Yamashita
-
Article
| Open Access Transport spectroscopy of non-equilibrium many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots
Transport spectroscopy of non-equilibrium many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots
All-electrical quantum state manipulation is highly desirable for quantum information technologies. In this study, the authors demonstrate the preparation and detection of excited many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots at 4 K, using only electrical means.
- B. Marquardt
- , M. Geller
- & A. Lorke
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule identification via electric current noise
Single-molecule identification via electric current noise
Molecular fluctuations are a source of noise that can impede single-molecule identification. Here, quantum-fluctuation-induced inelastic noise is observed as current fluctuations in individual molecules, suggesting that inelastic noise could be used as a molecular signature.
- Makusu Tsutsui
- , Masateru Taniguchi
- & Tomoji Kawai

 High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature
High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature