Featured
-
-
Article |
 Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales
Experimental demonstration of low-loss optical waveguiding at deep sub-wavelength scales
Metal-based nanostructures offer a solution to scale down photonics to the nanoscale. Sorgeret al. directly demonstrate waveguiding of ultra-small propagating waves at visible and near-infrared frequencies using NSOM imaging, with the potential for nanoscale photonic applications such as bio-sensing.
- Volker J. Sorger
- , Ziliang Ye
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoantenna-enhanced ultrafast nonlinear spectroscopy of a single gold nanoparticle
Nanoantenna-enhanced ultrafast nonlinear spectroscopy of a single gold nanoparticle
Optical nanoantennas can be used for spectroscopic investigations at previously unattainable dimensions. Schumacheret al.describe time-resolved antenna-enhanced ultrafast nonlinear optical spectroscopy and determine the transient absorption signal of a single gold nanoparticle.
- Thorsten Schumacher
- , Kai Kratzer
- & Markus Lippitz
-
Article |
 Stabilizing lithium–sulphur cathodes using polysulphide reservoirs
Stabilizing lithium–sulphur cathodes using polysulphide reservoirs
Lithium–sulphur batteries may achieve higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion cells, but the dissolution of sulphur intermediates is a continuing challenge. Here this problem is overcome using a cathode with a mesoporous structure that is able to accommodate intermediate polysulphide anions.
- Xiulei Ji
- , Scott Evers
- & Linda F. Nazar
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the molecular structure of single-molecule junctions in different conductance states by fishing-mode tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Revealing the molecular structure of single-molecule junctions in different conductance states by fishing-mode tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The conductance of single-molecule junctions is affected by the structure of the molecule and how it is bound to the electrodes, which may be examined using Raman spectroscopy. Liuet al. have developed 'fishing-mode' tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, which allows the simultaneous determination of conductance and Raman spectra.
- Zheng Liu
- , Song-Yuan Ding
- & Zhong-Qun Tian
-
Article
| Open Access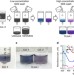 Large-scale single-chirality separation of single-wall carbon nanotubes by simple gel chromatography
Large-scale single-chirality separation of single-wall carbon nanotubes by simple gel chromatography
Large-scale separation of single-wall carbon nanotubes into populations of single chirality is a significant challenge in the practical application of nanotubes. Now, using multicolumn gel chromatography, the large-scale separation of 13 different carbon nanotube species is achieved.
- Huaping Liu
- , Daisuke Nishide
- & Hiromichi Kataura
-
Article
| Open Access Travelling-wave resonant four-wave mixing breaks the limits of cavity-enhanced all-optical wavelength conversion
Travelling-wave resonant four-wave mixing breaks the limits of cavity-enhanced all-optical wavelength conversion
Wave mixing in optical resonators suffers from strong bandwidth constraints, hindering practical implementation. Morichettiet al. report travelling-wave four-wavemixing in coupled ring resonators, which combines the efficiency enhancement of resonant propagation with a wide-band conversion process.
- Francesco Morichetti
- , Antonio Canciamilla
- & Andrea Melloni
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional enzyme diffusion in laterally confined DNA monolayers
Two-dimensional enzyme diffusion in laterally confined DNA monolayers
Little is known about the effects of molecular crowding and confinement on biomolecule function. Castronovoet al. investigate the reactions of restriction enzymes with DNA confined in bushy matrices and find that the enzymes enter at the side of the matrix before diffusing two-dimensionally.
- Matteo Castronovo
- , Agnese Lucesoli
- & Giacinto Scoles
-
Article |
 Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures
Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures
Solid gold is most stable as a face-centred cubic structure, and stable colloidal gold with hexagonal close packing has not been produced. Huanget al.prepare square gold sheets with hexagonal close packing that are stable under ambient conditions.
- Xiao Huang
- , Shaozhou Li
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Plasmonic beaming and active control over fluorescent emission
Plasmonic beaming and active control over fluorescent emission
Nanometallic optical antennas can concentrate light into a deep-subwavelength volume for sensor and photovoltaic applications. Junet al. demonstrate an optical antenna design that achieves a high level of control over fluorescent emission for a wide range of nanoscale optical spectroscopy applications.
- Young Chul Jun
- , Kevin C.Y. Huang
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article |
 A monolithically integrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera
A monolithically integrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera
Infrared cameras are used for night vision and in medical diagnostics, but currently only present monochrome images. Krishnaet al. demonstrate a monolithically intergrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera as a step towards coloured infrared imaging.
- Sang Jun Lee
- , Zahyun Ku
- & Sam Kyu Noh
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-engineered electron–hole exchange interaction controls exciton dynamics in core–shell semiconductor nanocrystals
Nano-engineered electron–hole exchange interaction controls exciton dynamics in core–shell semiconductor nanocrystals
Electron–hole exchange interaction is an intrinsic property of semiconductors, which affects their fine structure. Brovelliet al. demonstrate a nanoengineering-based approach that provides control over the exchange interaction energy at nearly constant emission energy, which cannot be carried out using core-only nanocrystals.
- S. Brovelli
- , R.D. Schaller
- & V.I. Klimov
-
Article
| Open Access The Meissner effect in a strongly underdoped cuprate above its critical temperature
The Meissner effect in a strongly underdoped cuprate above its critical temperature
In the pseudogap state of cuprates, although diamagnetic signals have been detected, a Meissner effect has never been observed. Morenzoni and colleagues probe the local diamagnetic response in the normal state of an underdoped layer showing that a 'barrier' layer exhibits a Meissner effect.
- Elvezio Morenzoni
- , Bastian M. Wojek
- & Ivan Božović
-
Article
| Open Access 3D optical Yagi–Uda nanoantenna array
3D optical Yagi–Uda nanoantenna array
Nanoantennas may be important for future photonic circuits; they combine an emitter or detector with free-space propagation of light. Dregelyet al. fabricate an array of 3D optical Yagi–Uda nanoantennas and show that radiofrequency antenna array concepts applied to the optical regime can provide improved directional properties.
- Daniel Dregely
- , Richard Taubert
- & Harald Giessen
-
Article |
 Tip-enhanced photovoltaic effects in bismuth ferrite
Tip-enhanced photovoltaic effects in bismuth ferrite
Bismuth ferrite has photoelectric properties that make it an attractive alternative for use in photovoltaic devices. Here, using photoelectric atomic force microscopy, the authors show that photogenerated carriers can be collected by the tip and suggest that this can be used in photoelectric applications.
- Marin Alexe
- & Dietrich Hesse
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a universal stress sensor for graphene and carbon fibres
Development of a universal stress sensor for graphene and carbon fibres
Embedding carbon fibres in polymer matrices provides significant gains in strength and stiffness. Here, the Raman G peak of carbon fibre is studied in relation to applied strain and referenced to graphene; the work could facilitate stress measurements of carbon fibre polymer composites.
- Otakar Frank
- , Georgia Tsoukleri
- & Costas Galiotis
-
Article
| Open Access Whispering gallery microresonators for second harmonic light generation from a low number of small molecules
Whispering gallery microresonators for second harmonic light generation from a low number of small molecules
Small molecules can be detected by second harmonic light generation, but sensitive detection usually requires a large number of molecules and a high-power laser source. Here, relatively low numbers of molecules are detected using Q spherical microresonators and low average power.
- J.L. Dominguez-Juarez
- , G. Kozyreff
- & Jordi Martorell
-
Article |
 A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
Single-molecule force spectroscopy is used to study single molecule interactions, but probing short-lived events is difficult. Here, a nanomechanical interface is developed, which allows the study of microsecond timescale interactions.
- Mingdong Dong
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article |
 Coherent electron–phonon coupling in tailored quantum systems
Coherent electron–phonon coupling in tailored quantum systems
Graphene and InAs nanowires are both promising materials for coherent spin manipulation, but coupling between a quantum system and its environment leads to decoherence. Here, the contribution of electron–phonon coupling to decoherence in graphene and InAs nanowire is studied.
- P. Roulleau
- , S. Baer
- & T. Ihn
-
Article |
 Nanofriction in cold ion traps
Nanofriction in cold ion traps
Cold ion traps have not previously been used to study sliding friction between crystal lattices. Here, Benassiet al. use simulations to show that cold ion traps could be used for detailed investigation of atomic scale friction.
- A. Benassi
- , A. Vanossi
- & E. Tosatti
-
Article |
 Optical virtual imaging at 50 nm lateral resolution with a white-light nanoscope
Optical virtual imaging at 50 nm lateral resolution with a white-light nanoscope
Lenses are restricted by diffraction to imaging features roughly the size of visible wavelengths. Wanget al. develop a white-light nanoscope that uses optically transparent spherical silica lenses to virtually image, in the far-field, features down to 50 nm resolution.
- Zengbo Wang
- , Wei Guo
- & Minghui Hong
-
Article
| Open Access A fast and low-power microelectromechanical system-based non-volatile memory device
A fast and low-power microelectromechanical system-based non-volatile memory device
New memory devices are being developed to overcome the limitations of conventional silicon-based flash memory. Here, a non-volatile memory design is reported that uses a micromechanical cantilever to charge and discharge a floating gate, which controls charge transport through a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor.
- Sang Wook Lee
- , Seung Joo Park
- & Yung Woo Park
-
Article
| Open Access Observation and electric current control of a local spin in a single-molecule magnet
Observation and electric current control of a local spin in a single-molecule magnet
In molecular spintronics, the spin state of a molecule may be switched by changing the molecular structure. Here, the spin of a single-molecule magnet is switched by applying an electric current using a scanning tunnelling microscope, which may aid in information coding at the single-molecule level.
- Tadahiro Komeda
- , Hironari Isshiki
- & Masahiro Yamashita
-
Article
| Open Access Transport spectroscopy of non-equilibrium many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots
Transport spectroscopy of non-equilibrium many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots
All-electrical quantum state manipulation is highly desirable for quantum information technologies. In this study, the authors demonstrate the preparation and detection of excited many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots at 4 K, using only electrical means.
- B. Marquardt
- , M. Geller
- & A. Lorke
-
Article |
 Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Water-soluble peptides with stable α-helical conformations are desirable for a range of applications, but incorporating charged residues to improve solubility usually leads to reduced helical stability. Here, polypeptides produced from amino acids with elongated charged side chains are found to be water soluble and exhibit very high helical stability.
- Hua Lu
- , Jing Wang
- & Jianjun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Interconnect-free parallel logic circuits in a single mechanical resonator
Interconnect-free parallel logic circuits in a single mechanical resonator
Eliminating wiring in transistors could lead to high integration densities and low power consumption. Here, multiple logic gates are implemented in a microelectromechanical resonator by parametrically mixing binary information channels corresponding to mechanical oscillations of the resonator at different frequencies.
- I. Mahboob
- , E. Flurin
- & H. Yamaguchi
-
Article |
 Spherical hyperlens for two-dimensional sub-diffractional imaging at visible frequencies
Spherical hyperlens for two-dimensional sub-diffractional imaging at visible frequencies
Although hyperlenses made of metamaterials can image sub-diffraction-limited objects, they are limited to one-dimensional magnification and ultraviolet frequencies. Here, the authors demonstrate a spherical hyperlens for visible light far-field imaging, with a resolution of 160 nm in both lateral dimensions.
- Junsuk Rho
- , Ziliang Ye
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article |
 Atomically flat single-crystalline gold nanostructures for plasmonic nanocircuitry
Atomically flat single-crystalline gold nanostructures for plasmonic nanocircuitry
Polycrystalline substrates are a hindrance to the realization of high-definition plasmonic nanostructures. In this paper the authors chemically grow large and thin gold single crystals, and show that they can be coupled with top-down fabrication methods to produce high-quality nanostructures with good optical properties.
- Jer-Shing Huang
- , Victor Callegari
- & Bert Hecht
-
Article
| Open Access Discrete plasticity in sub-10-nm-sized gold crystals
Discrete plasticity in sub-10-nm-sized gold crystals
Deformations in nanocrystals smaller than 10 nm are not well understood. The authors perform compression high-resolution transmission electron microscopy studies of gold nanoparticles, and determine that the nanoparticles deform through the emission of partial dislocations from free surfaces.
- He Zheng
- , Ajing Cao
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule identification via electric current noise
Single-molecule identification via electric current noise
Molecular fluctuations are a source of noise that can impede single-molecule identification. Here, quantum-fluctuation-induced inelastic noise is observed as current fluctuations in individual molecules, suggesting that inelastic noise could be used as a molecular signature.
- Makusu Tsutsui
- , Masateru Taniguchi
- & Tomoji Kawai
-
Article
| Open Access Field-induced water electrolysis switches an oxide semiconductor from an insulator to a metal
Field-induced water electrolysis switches an oxide semiconductor from an insulator to a metal
Water is composed of the electrochemically active species, H+ and OH−, but has not been used as an active electronic material. In this study, a field-effect transistor is developed that uses water-infiltrated nanoporous glass as the gate insulator; this new application of water may be useful in electronics and energy storage.
- Hiromichi Ohta
- , Yukio Sato
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Article
| Open Access Dimensionality-driven insulator–metal transition in A-site excess non-stoichiometric perovskites
Dimensionality-driven insulator–metal transition in A-site excess non-stoichiometric perovskites
Many technological applications would benefit from new ways of bringing complex materials near the insulator–metal transition region. The authors induce, in a Lantanum Strontium Titanate, a transition from insulating to metallic behaviour by structural intercalation of intrinsically insulating units, opening new avenues to engineer these materials.
- Zhongchang Wang
- , Masaki Okude
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article |
 Piezoelectric-nanowire-enabled power source for driving wireless microelectronics
Piezoelectric-nanowire-enabled power source for driving wireless microelectronics
Energy harvesting through mechanical actions of nanosized components could be useful for powering mobile electronics. Here, the authors grow lead zirconate nanowire arrays at comparatively low temperature and use them to power a macroscopic laser diode.
- Sheng Xu
- , Benjamin J. Hansen
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article |
 One-by-one trap activation in silicon nanowire transistors
One-by-one trap activation in silicon nanowire transistors
Flicker noise in nanoscale field effect transistors deviates from the simple frequency-dependent behaviour of macroscale objects. Here the authors show that Coulomb repulsion between nearby trap sites leads to an order of magnitude reduction in noise in these devices.
- N. Clément
- , K. Nishiguchi
- & D. Vuillaume
-
Article
| Open Access Structural bases for the interaction of frataxin with the central components of iron–sulphur cluster assembly
Structural bases for the interaction of frataxin with the central components of iron–sulphur cluster assembly
Frataxin is an essential protein that has been linked to iron–sulphur cluster assembly, and reduced levels are associated with Friedrich's ataxia. In this study, a combination of techniques is used to probe the interactions of the bacterial frataxin orthologue CyaY with the iron–sulphur cluster assembly machinery.
- Filippo Prischi
- , Petr V. Konarev
- & Annalisa Pastore
-
Article |
 'Quantized' states of the charge-density wave in microcrystals of K0.3MoO3
'Quantized' states of the charge-density wave in microcrystals of K0.3MoO3
In low-temperature one-dimensional metals, electrons condense into collective charge-density wave states. Zybtsevet al. observe conductivity jumps with temperature in a metal bar, as only specific wavelengths are permitted in the bar for the charge-density wave modes.
- S.G. Zybtsev
- , V.Ya. Pokrovskii
- & S.V. Zaitsev-Zotov
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling thermal transitions of polymers in subnanometre pores
Unveiling thermal transitions of polymers in subnanometre pores
Understanding the thermal transitions of confined polymers is important for the design of molecular scale devices. In this study, unusual thermal transitions are observed in polyethylene glycol chains incorporated in nanochannels of porous coordination polymers.
- Takashi Uemura
- , Nobuhiro Yanai
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article |
 A systems approach towards the stoichiometry-controlled hetero-assembly of nanoparticles
A systems approach towards the stoichiometry-controlled hetero-assembly of nanoparticles
The assembly of nanoparticles into stoichiometry-controlled structures could lead to materials with novel properties and functions. Here, reaction systems are developed, which allow the rational assembly of differently functionalized gold nanoparticles (A and B) to give AB, AB2, AB3 and AB4nanoclusters.
- Yong Wang
- , Gang Chen
- & Hongyu Chen
-
Article |
 Enhanced proton transport in nanostructured polymer electrolyte/ionic liquid membranes under water-free conditions
Enhanced proton transport in nanostructured polymer electrolyte/ionic liquid membranes under water-free conditions
One challenge in the development of proton exchange fuel cells is the requirement for durable, high-conductivity electrolytes. The authors show that incorporating ionic liquids into synthetic block co-polymer electrolytes results in nanostructured membranes with much higher conductivities than currently available.
- Sung Yeon Kim
- , Suhan Kim
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article |
 Reduced graphene oxide by chemical graphitization
Reduced graphene oxide by chemical graphitization
The mass production of high-quality reduced graphene oxide could aid the scale-up of graphene-based technologies. Here, a one-pot reduction of graphene oxide using hydriodic acid and acetic acid provides large quantities of highly conductive reduced graphene oxide.
- In Kyu Moon
- , Junghyun Lee
- & Hyoyoung Lee
-
Article |
 Self-assembled aggregates formed by single-molecule magnets on a gold surface
Self-assembled aggregates formed by single-molecule magnets on a gold surface
The spontaneous ordering of molecules into two-dimensional arrays is usually a result of directional intermolecular interactions. Here, it is shown that electrospray-deposited Mn12(acetate)16forms filamentary aggregates driven by anisotropic interactions, which are a consequence of the complex shape of the molecule.
- Alex Saywell
- , Graziano Magnano
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article |
 Nanostructural hierarchy increases the strength of aluminium alloys
Nanostructural hierarchy increases the strength of aluminium alloys
Improving the properties of metallic alloys is important to develop new lightweight materials. In this paper, we show that an aluminium (Al) alloy containing a hierarchy of nanostructures in a solid solution with a high density of dislocations is capable of beating strength records for Al alloys while maintaining good ductility.
- Peter V. Liddicoat
- , Xiao-Zhou Liao
- & Simon P. Ringer
-
Article |
 Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging
Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging
With the miniaturization of integrated optical devices, traditional colour filters are increasingly bulky. To supersede these, the authors devise a plasmonic metal–insulator–metal nanostructured array that can filter colours with high spatial and band resolution.
- Ting Xu
- , Yi-Kuei Wu
- & L. Jay Guo
-
Article |
 Imaging Coulomb islands in a quantum Hall interferometer
Imaging Coulomb islands in a quantum Hall interferometer
The complex electronic motion in the quantum Hall regime in semiconductors has so far eluded analysis of its microscopic structure. Here, the authors use scanning gate microscopy to measure the spatial structure of transport inside a metal in this regime, opening the way for localized manipulation of the electronic states.
- B. Hackens
- , F. Martins
- & V. Bayot
-
Article |
 Multifunctional nanoparticles as coupled contrast agents
Multifunctional nanoparticles as coupled contrast agents
Multifunctional imaging probes are important in bionanotechnology. In this paper, the authors show that nanoparticles with magnetic cores, thin gold shells and an organic spacer layer support a novel magnetomotive photoacoustic imaging mode, and enhance contrast with respect to conventional imaging techniques.
- Yongdong Jin
- , Congxian Jia
- & Xiaohu Gao
-
Article |
 Nanoelectromechanical coupling in fullerene peapods probed by resonant electrical transport experiments
Nanoelectromechanical coupling in fullerene peapods probed by resonant electrical transport experiments
Fullerene peapods are carbon nanotubes encapsulating buckyball molecules. Here the authors show by low-temperature electron transport experiments, that the electronic states of nanotubes couple to the vibrational states of fullerenes, making the peapods a new class of nanoelectromechanical devices.
- Pawel Utko
- , Raffaello Ferone
- & Jesper Nygård
-
Article |
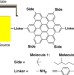 Gate-controlled electron transport in coronenes as a bottom-up approach towards graphene transistors
Gate-controlled electron transport in coronenes as a bottom-up approach towards graphene transistors
Graphene sheets used to build electronic devices have defects that limit performance. As a possible bottom-up route towards better devices, Diez-Perez and co-workers build large polyaromatic molecules with precisely defined structures which show good performance as field-effect transistors.
- Ismael Diez-Perez
- , Zhihai Li
- & Nongjian Tao
-
Article |
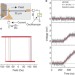 Enhanced stochasticity of domain wall motion in magnetic racetracks due to dynamic pinning
Enhanced stochasticity of domain wall motion in magnetic racetracks due to dynamic pinning
Understanding the details of domain wall motion in nanowires is important for magnetic racetrack memories. Jiang and co-workers show that this motion can become more random by varying the magnetic field, pinning the domains at several local imperfections of the nanowire.
- Xin Jiang
- , Luc Thomas
- & Stuart S.P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Electron-beam-assisted superplastic shaping of nanoscale amorphous silica
Electron-beam-assisted superplastic shaping of nanoscale amorphous silica
At room temperature, glasses are known to be brittle and fracture upon deformation. Zhenget al. show that, by exposing amorphous silica nanostructures to a low-intensity electron beam, it is possible to achieve dramatic shape changes, including a superplastic elongation of 200% for nanowires.
- Kun Zheng
- , Chengcai Wang
- & Evan Ma
-
Article |
 Fluidic supramolecular nano- and microfibres as molecular rails for regulated movement of nanosubstances
Fluidic supramolecular nano- and microfibres as molecular rails for regulated movement of nanosubstances
Microtubules act as molecular tracks for the transport of substances within cells, and have inspired the construction of artificial supramolecular fibres. Here, self-assembled glycol–lipid fibres are shown to be sufficiently fluid to allow directional movement of attached molecules, proteins and nanobeads.
- Shun-ichi Tamaru
- , Masato Ikeda
- & Itaru Hamachi

 Determination of nanoparticle size distribution together with density or molecular weight by 2D analytical ultracentrifugation
Determination of nanoparticle size distribution together with density or molecular weight by 2D analytical ultracentrifugation