Featured
-
-
Article |
 Photon-mediated interaction between distant quantum dot circuits
Photon-mediated interaction between distant quantum dot circuits
Controlling the interaction between distant quantum dots is important if they are to be used in quantum information devices. Delbecq et al. place two quantum dot circuits in a microwave cavity and show that they interact via cavity photons, even though they are separated by 200 times their own size.
- M.R. Delbecq
- , L.E. Bruhat
- & T. Kontos
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling quantum pathways using optical 3D Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Unraveling quantum pathways using optical 3D Fourier-transform spectroscopy
Knowledge of the Hamiltonian of a quantum system is essential for predicting and controlling its behaviour. Li et al.use optical three-dimensional Fourier-transform spectroscopy to separate and study each pathway, gaining quantitative insight into the quantum pathways of an atomic vapour Hamiltonian.
- Hebin Li
- , Alan D. Bristow
- & Steven T. Cundiff
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel photonic information processing at gigabyte per second data rates using transient states
Parallel photonic information processing at gigabyte per second data rates using transient states
Inspired by neural networks, reservoir computing uses nonlinear transient states to perform computations, offering faster parallel information processing. Brunner et al.show a photonic approach to reservoir computing capable of simultaneous spoken digit and speaker recognition at high data rates.
- Daniel Brunner
- , Miguel C. Soriano
- & Ingo Fischer
-
Article |
 Multiphoton quantum interference in a multiport integrated photonic device
Multiphoton quantum interference in a multiport integrated photonic device
For future optical information processing applications, including quantum computing, ever more complex quantum photonic devices are needed. Metcalf et al. present an integrated photonic device capable of three-photon quantum operation, including Hong-Ou-Mandel-type interference between three photons.
- Benjamin J. Metcalf
- , Nicholas Thomas-Peter
- & Ian A. Walmsley
-
Article
| Open Access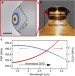 Mid-infrared optical frequency combs at 2.5 μm based on crystalline microresonators
Mid-infrared optical frequency combs at 2.5 μm based on crystalline microresonators
Optical frequency combs are vital tools for precision measurements, and extending them further into the mid-infrared 'molecular fingerprint' range will open new avenues for spectroscopy. Using crystalline microresonators, Wang et al. demonstrate Kerr combs at 2.5 μm as a promising route into the mid-infrared.
- C. Y. Wang
- , T. Herr
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 Growth and optical properties of axial hybrid III–V/silicon nanowires
Growth and optical properties of axial hybrid III–V/silicon nanowires
Nanowires with sharp interfaces between two different semiconducting materials could lead to useful nanoelectronic and nanophotonic structures. Hocevar et al.develop a method to integrate a gallium arsenide section in silicon nanowires with atomically sharp interfaces and no dislocations.
- Moïra Hocevar
- , George Immink
- & Erik Bakkers
-
Article |
 The surface plasmon modes of self-assembled gold nanocrystals
The surface plasmon modes of self-assembled gold nanocrystals
The 3D self-assembly of nanocrystals could generate materials with unique optical and electronic properties. Barrowet al. report the DNA-mediated assembly of symmetrical 3D gold tetrahedra, pentamers and hexamers, and elucidate their plasmon modes.
- Steven J. Barrow
- , Xingzhan Wei
- & Paul Mulvaney
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme sensitivity of graphene photoconductivity to environmental gases
Extreme sensitivity of graphene photoconductivity to environmental gases
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms whose high electron mobility offers potential for cheap, high-speed opto-electronic devices. Docherty et al.show that the terahertz frequency photoconductivity in graphene depends crucially on the type and density of environmental gas adsorbed.
- Callum J. Docherty
- , Cheng-Te Lin
- & Michael B. Johnston
-
Article |
 On-chip transformation optics for multimode waveguide bends
On-chip transformation optics for multimode waveguide bends
Integrated photonic devices rely on single-mode waveguides, as inter-mode coupling prevents multimode waveguides from being efficiently bent for on-chip schemes. Using transformation optics, Gabrielliet al. overcome this limitation and show a multimode waveguide bend with minimal inter-mode coupling.
- Lucas H. Gabrielli
- , David Liu
- & Michal Lipson
-
Article
| Open Access Control of exciton spin statistics through spin polarization in organic optoelectronic devices
Control of exciton spin statistics through spin polarization in organic optoelectronic devices
Control of spin statistics by spin injection from ferromagnetic electrodes has been shown to achieve only weak effects in organic optoelectronic devices. Wang et al.use instead polarization of spins after injection, at high magnetic fields and low temperatures, achieving a 50% change in device characteristics.
- Jianpu Wang
- , Alexei Chepelianskii
- & Neil C. Greenham
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-polarity plasmonic metalens for visible light
Dual-polarity plasmonic metalens for visible light
The wide range of properties encountered in metamaterials make them promising for numerous optical applications. Chenet al. build a plasmonic flat metamaterial lens with an abrupt phase change that functions as a convex lens for one handedness of light and a concave lens for the other.
- Xianzhong Chen
- , Lingling Huang
- & Thomas Zentgraf
-
Review Article |
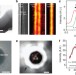 Hyperlenses and metalenses for far-field super-resolution imaging
Hyperlenses and metalenses for far-field super-resolution imaging
The diffraction limit of light constrains the achievable resolution of conventional optical systems, but metamaterials provide numerous avenues to beat it. Lu and Liu review recent advances in super-resolution imaging with hyperlenses and metalenses, and discuss future directions and hurdles for the field.
- Dylan Lu
- & Zhaowei Liu
-
Article |
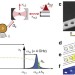 Coherent optical wavelength conversion via cavity optomechanics
Coherent optical wavelength conversion via cavity optomechanics
Coherent conversion of photons from one wavelength to another is promising for future quantum communications technologies. By exploiting coupling between resonances in an optomechanical crystal nanocavity, Hillet al. demonstrate conversion between optical wavelength photons via a mechanical resonance.
- Jeff T. Hill
- , Amir H. Safavi-Naeini
- & Oskar Painter
-
Article
| Open Access Carrier multiplication in semiconductor nanocrystals detected by energy transfer to organic dye molecules
Carrier multiplication in semiconductor nanocrystals detected by energy transfer to organic dye molecules
In semiconductors, an absorbed photon can generate multiple electron-hole pairs, but measurements of this carrier multiplication efficiency in nanocrystals need to correctly account for charged excitons. Xiaoet al.meet this need by measuring energy transfer of biexcitons from nanocrystals to acceptor dyes.
- Jun Xiao
- , Ying Wang
- & Min Xiao
-
Article |
 A hybrid CMOS-imager with a solution-processable polymer as photoactive layer
A hybrid CMOS-imager with a solution-processable polymer as photoactive layer
Solution-processed organic semiconductor devices present a low-cost alternative to their silicon counterparts, yet their performance is usually not as strong. By replacing silicon with an organic photoactive layer, Baierlet al. present a solution-processed hybrid CMOS-imager with a 100% pixel fill factor.
- Daniela Baierl
- , Lucio Pancheri
- & Paolo Lugli
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-contact electrically driven microdisk lasers
Graphene-contact electrically driven microdisk lasers
Microdisk lasers are useful for compact wavelength-scale photonic devices and circuits, but their operation by electrical injection can hamper their optical properties. Kimet al. show that a graphene-contact electrode provides efficient electrical injection while minimising optical losses.
- Yoon-Ho Kim
- , Soon-Hong Kwon
- & Hong-Gyu Park
-
Article |
 Single-shot ultrafast tomographic imaging by spectral multiplexing
Single-shot ultrafast tomographic imaging by spectral multiplexing
Computed tomography relies on scanning to measure an object from many angles, which fails for shot-to-shot changes and ultrafast phenomena. Matliset al. demonstrate an approach based on spectral multiplexing for single-shot tomographic imaging and use it to measure femtosecond plasma filaments.
- N.H. Matlis
- , A. Axley
- & W.P. Leemans
-
Article |
 Probing the tunnelling site of electrons in strong field enhanced ionization of molecules
Probing the tunnelling site of electrons in strong field enhanced ionization of molecules
Molecules in intense laser fields have enhanced multiple ionization rates, caused by the ionic core and laser fields acting on the part of the molecule in the up-field. Here, direct proof of this model is presented by studying the instantaneous effect of the field direction during double ionization in ArXe.
- J. Wu
- , M. Meckel
- & R. Dörner
-
Article
| Open Access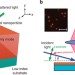 Hybrid nanoparticle–microcavity-based plasmonic nanosensors with improved detection resolution and extended remote-sensing ability
Hybrid nanoparticle–microcavity-based plasmonic nanosensors with improved detection resolution and extended remote-sensing ability
Plasmonic nanoparticles are useful as optical sensors, but their spectral resolution is hindered by the linewidth of the plasmon resonance. Schmidtet al. find that coupling this resonance to a microcavity creates hybrid modes with enhanced sensing figure-of-merit and improved frequency resolution.
- Markus A. Schmidt
- , Dang Yuan Lei
- & Stefan A. Maier
-
Article |
 Multichannel cavity optomechanics for all-optical amplification of radio frequency signals
Multichannel cavity optomechanics for all-optical amplification of radio frequency signals
Cavity optomechanics can exploit optical forces to achieve all-optical signal processing, but most schemes are limited to a narrow wavelength range. Using a cavity optomechanical design system with two optical channels, Liet al. show broadband readout and all-optical amplification of radio-frequency signals.
- Huan Li
- , Yu Chen
- & Mo Li
-
Article |
 Integrable microwave filter based on a photonic crystal delay line
Integrable microwave filter based on a photonic crystal delay line
The flexibility of microwave photonics provides advantages over electronic circuitry, yet the lack of integrated chip-scale devices limits its practical application. This study presents microwave filters based on photonic crystal waveguides with controllable delays as a step towards intregable circuits.
- Juan Sancho
- , Jerome Bourderionnet
- & Alfredo De Rossi
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging
Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging
Fibre-based technologies provide miniaturization, flexibility and the capability to access hard to reach areas. Čižmár and Dholakia exploit disorder in multimode fibres to enable a variety of imaging modalities, including bright- and dark-field microscopy and fluorescent imaging, using a single waveguide.
- Tomáš Čižmár
- & Kishan Dholakia
-
Article
| Open Access Optical detection of a single rare-earth ion in a crystal
Optical detection of a single rare-earth ion in a crystal
The optical transitions that occur in rare-earth-doped crystals offer promise for quantum information storage and processing. Kolesovet al.report the optical detection of a single praseodymium ion residing in a crystal host by using an excited-state absorption process to enhance its fluorescence yield.
- R. Kolesov
- , K. Xia
- & J. Wrachtrup
-
Article |
 Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
The spectral position of Raman peaks is a useful diagnostic for determining the degree of strain and excess electronic charges present in graphene. This study demonstrates that these two contributions can be separated from each other and therefore be obtained at the same time.
- Ji Eun Lee
- , Gwanghyun Ahn
- & Sunmin Ryu
-
Article |
 In situ measurement of exciton energy in hybrid singlet-fission solar cells
In situ measurement of exciton energy in hybrid singlet-fission solar cells
Singlet fission converts single singlet excitons into pairs of triplet excitons, and it has been proposed to give additional photocurrent to solar cells. Ehrleret al. use lead selenide nanocrystals of varying sizes to measure the triplet energy in pentacene photovoltaic cells, and achieve efficiencies approaching 5%.
- Bruno Ehrler
- , Brian J. Walker
- & Neil C. Greenham
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam
Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam
Generating arbitrary orientation of light polarization has been an elusive goal, yet it is important to light interactions with nano-objects. By combining azimuthally and radially polarized beams, Liet al. overcome this obstacle and demonstrate its use for polarization-based encryption with gold nanorods.
- Xiangping Li
- , Tzu-Hsiang Lan
- & Min Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging high-dimensional spatial entanglement with a camera
Imaging high-dimensional spatial entanglement with a camera
Measuring the entanglement between down-converted photons is central to many quantum optical experiments, and is normally performed by scanning detectors stepwise across a plane. Edgaret al. use a CCD camera to measure the entire entangled light field, finding strong correlations in position and momentum.
- M.P. Edgar
- , D.S. Tasca
- & M.J. Padgett
-
Article |
 High-resolution three-dimensional partially coherent diffraction imaging
High-resolution three-dimensional partially coherent diffraction imaging
Coherent diffractive imaging exploits coherent X-ray sources to image objects from their diffraction patterns, but fails for decreasing coherence. Using partially coherent diffraction patterns, Clarket al. obtain three dimensional reconstructions of nanocrystals and determine the wavefield coherence.
- J.N. Clark
- , X. Huang
- & I.K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vortex-beam illumination
Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vortex-beam illumination
Non-uniform light beams can create patterns in azo-polymer films by inducing mass transport, yet the process is not well understood. Using optical vortex beams, Ambrosioet al. observe the formation of spiral patterns that are surprisingly sensitive to the optical phase, which they explain with a new model.
- Antonio Ambrosio
- , Lorenzo Marrucci
- & Pasqualino Maddalena
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic black gold by adiabatic nanofocusing and absorption of light in ultra-sharp convex grooves
Plasmonic black gold by adiabatic nanofocusing and absorption of light in ultra-sharp convex grooves
Plasmonic effects can turn reflective metals into strong absorbers, although this is usually realized within narrow wavelength ranges near resonances. Using arrays of ultra-sharp convex grooves, Søndergaardet al. show that nonresonant absorption can lead to effective broadband light absorption.
- Thomas Søndergaard
- , Sergey M. Novikov
- & Sergey I. Bozhevolnyi
-
Article |
 Efficient power extraction in surface-emitting semiconductor lasers using graded photonic heterostructures
Efficient power extraction in surface-emitting semiconductor lasers using graded photonic heterostructures
Photonic crystal semiconductor lasers normally operate in a non-radiative mode, characterized by reduced losses but also low surface emission. Using graded photonic heterostructures, Xuet al. boost power extraction by forcing laser emission in a mode with higher radiation efficiency.
- Gangyi Xu
- , Raffaele Colombelli
- & David A. Ritchie
-
Article |
 Exploring the wavefront of hard X-ray free-electron laser radiation
Exploring the wavefront of hard X-ray free-electron laser radiation
X-ray free-electron lasers offer a wealth of possibilities for future diffraction studies, but variations in successive pulses mean the wavefront is not well defined. Rutishauseret al. use grating interferometry to characterize the wavefronts shot to shot, both in situand under operating conditions.
- Simon Rutishauser
- , Liubov Samoylova
- & Christian David
-
Article |
 Absorption imaging of a single atom
Absorption imaging of a single atom
Absorption imaging relies on the capture of photons by an object to create intensity contrasts, allowing for the visualization of small quantum systems. Streedet al. demonstrate the first absorption imaging of an isolated ytterbium ion, with contrast at the limit of semiclassical theory.
- Erik W. Streed
- , Andreas Jechow
- & David Kielpinski
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light
Deep-tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light
Fluorescence imaging is important for biomedical research and applications, but the turbidity of biological material prohibits deep tissue study. By combining ultrasound-encoding with digital time-reversal, Wanget al.perform focussed fluorescence imaging at a tissue depth of 2.5mm.
- Ying Min Wang
- , Benjamin Judkewitz
- & Changhuei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Light–matter interaction in a microcavity-controlled graphene transistor
Light–matter interaction in a microcavity-controlled graphene transistor
Graphene's remarkable properties make it ideal for optoelectronic devices, and its two-dimensional nature enables its integration with photonic structures. By combining a graphene transistor with a planar microcavity, Engelet al. control the spectrum of the photocurrent and the light emitted by the device.
- Michael Engel
- , Mathias Steiner
- & Ralph Krupke
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of prompt pre-thermal laser ion sheath acceleration
Direct observation of prompt pre-thermal laser ion sheath acceleration
High-intensity laser-plasma ion generation is promising as a compact proton source for applications like ion beam therapy. Using a femtosecond table-top laser system, Zeilet al. show that protons efficiently gain energy in the pre-thermal intra-pulse phase of the generation process.
- K. Zeil
- , J. Metzkes
- & U. Schramm
-
Article |
 Twisted optical metamaterials for planarized ultrathin broadband circular polarizers
Twisted optical metamaterials for planarized ultrathin broadband circular polarizers
Three-dimensional optical metamaterials provide a range of exciting features, such as broadband circular dichroism, yet their fabrication is challenging. Here, a broadband optical circular polarizer is presented based on twisted stacks of metasurfaces, avoiding the issues of three-dimensional fabrication.
- Y. Zhao
- , M.A. Belkin
- & A. Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-low-loss optical delay line on a silicon chip
Ultra-low-loss optical delay line on a silicon chip
Fibre-optic waveguides are used to provide timing delays for different sensing and signal processing applications, but their transfer to on-chip platforms is a challenge. Here low-loss delay lines based on whispering-gallery spiral waveguides up to 27 m long are produced, presenting a scalable alternative.
- Hansuek Lee
- , Tong Chen
- & Kerry J. Vahala
-
Article
| Open Access All optical reconfiguration of optomechanical filters
All optical reconfiguration of optomechanical filters
Nanoscale optomechanical systems offer a route to using optical forces for a range of devices based on photonic structures. Deotareet al. present a reconfigurable optical filter based on coupled silicon photonic crystal nanobeam cavities that can overcome thermo-optic effects at high frequencies.
- Parag B. Deotare
- , Irfan Bulu
- & Marko Loncar
-
Article |
 Giant nonlinear optical activity in a plasmonic metamaterial
Giant nonlinear optical activity in a plasmonic metamaterial
Light propagating in a medium can undergo polarization rotation, an effect that depends on light intensity and chiral properties. Renet al. report polarization rotation in a plasmonic metamaterial with million-fold stronger nonlinearity than that found in natural crystals.
- Mengxin Ren
- , Eric Plum
- & Nikolay I. Zheludev
-
Article
| Open Access Bridging quantum and classical plasmonics with a quantum-corrected model
Bridging quantum and classical plasmonics with a quantum-corrected model
As lengthscales in plasmonic structures enter the sub-nanometre regime, quantum effects become increasingly important. Here, a quantum-corrected model is presented that addresses quantum effects in realistic-sized plasmonic structures, a situation not feasible for full-quantum-mechanical simulations.
- Ruben Esteban
- , Andrei G. Borisov
- & Javier Aizpurua
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency stabilization in nonlinear micromechanical oscillators
Frequency stabilization in nonlinear micromechanical oscillators
Micromechanical oscillators present a route to miniaturisation of devices and may be used as frequency references or sensitive sensors, but their small size means that they often behave nonlinearly. Antonioet al. demonstrate frequency stabilisation of nonlinear resonators by coupling two vibrational modes.
- Dario Antonio
- , Damián H. Zanette
- & Daniel López
-
Article |
 Non-polydimethylsiloxane devices for oxygen-free flow lithography
Non-polydimethylsiloxane devices for oxygen-free flow lithography
Flow lithography is used to synthesize microparticles but relies on polydimethylsiloxane microchannels for oxygen to permeate and inhibit polymerization near channel interfaces. Now, non-polydimethylsiloxane devices have been developed, which allow oxygen-free lithography, increasing the capabilities of flow lithography.
- Ki Wan Bong
- , Jingjing Xu
- & Patrick S. Doyle
-
Article |
 Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions
Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions
The terahertz spectral region is desirable for applications such as imaging or spectroscopy, but progress is hampered by a lack of efficient terahertz devices. By exploiting intraband transitions in graphene, Sensale-Rodriguezet al. demonstrate a broadband intensity modulator working at terahertz frequencies.
- Berardi Sensale-Rodriguez
- , Rusen Yan
- & Huili Grace Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity
Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity
Stable, ultrahigh repetition rate optical clocks are critical for applications in high-speed communications, metrology and microchip computing. Pecciantiet al.present a mode-locked laser based on an integrated microcavity, with repetition rate exceeding 200 GHz and narrow linewidth pulses.
- M. Peccianti
- , A. Pasquazi
- & R. Morandotti
-
Article |
 Recovering three-dimensional shape around a corner using ultrafast time-of-flight imaging
Recovering three-dimensional shape around a corner using ultrafast time-of-flight imaging
An important goal in optics is to image objects hidden by turbid media, although line-of-sight techniques fail when the obscuring medium becomes opaque. Veltenet al. use ultrafast imaging techniques to recover three-dimensional shapes of non-line-of-sight objects after reflection from diffuse surfaces.
- Andreas Velten
- , Thomas Willwacher
- & Ramesh Raskar
-
Article
| Open Access Bright single-photon sources in bottom-up tailored nanowires
Bright single-photon sources in bottom-up tailored nanowires
Single-photon sources are important for quantum optical technologies, although achieving efficient light extraction from them with waveguides is limited in top-down approaches. Reimeret al. show a high extraction efficiency using a bottom-up method to grow quantum dots on the axis of nanowire waveguides.
- Michael E. Reimer
- , Gabriele Bulgarini
- & Val Zwiller
-
Article |
 Ultrafast changes in lattice symmetry probed by coherent phonons
Ultrafast changes in lattice symmetry probed by coherent phonons
Ultrafast excitation offers new routes to controlling material properties on short timescales, but probes are needed to better understand the changes. By studying the phonon spectrum of VO2 in the time domain, Wall et al. find a prompt change in lattice potential after a photoinduced structural transition.
- S. Wall
- , D. Wegkamp
- & M. Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Ptychographic electron microscopy using high-angle dark-field scattering for sub-nanometre resolution imaging
Ptychographic electron microscopy using high-angle dark-field scattering for sub-nanometre resolution imaging
Diffractive imaging can deliver wavelength-scale resolution with X-rays, although its use with electrons is hampered by experimental constraints. By applying ptychographic methods to transmission electron microscopy, Humphryet al. demonstrate sub-nanometre resolution using low-energy electrons.
- M.J. Humphry
- , B. Kraus
- & J.M. Rodenburg

 Improved heat dissipation in gallium nitride light-emitting diodes with embedded graphene oxide pattern
Improved heat dissipation in gallium nitride light-emitting diodes with embedded graphene oxide pattern