Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access All-natural 2D nanofluidics as highly-efficient osmotic energy generators
All-natural 2D nanofluidics as highly-efficient osmotic energy generators
Researchers report a sustainable nanofluidic osmotic energy harvester made from natural montmorillonite clay nanosheets and recycled cellulose. Scaled-up films of 700 cm2 show power output of 8 W m−2 with stability over 30 days
- Jiadong Tang
- , Yun Wang
- & Tieyong Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access Sweat permeable and ultrahigh strength 3D PVDF piezoelectric nanoyarn fabric strain sensor
Sweat permeable and ultrahigh strength 3D PVDF piezoelectric nanoyarn fabric strain sensor
Electronic packaging causes piezoelectric sensors to be airtight, resulting in poor wearing comfort. To address this issue, the authors develop a 3D all-fiber piezoelectric sensor with sweat permeable using the advanced 3D textile technology.
- Wei Fan
- , Ruixin Lei
- & Shengbo Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Double-walled Al-based MOF with large microporous specific surface area for trace benzene adsorption
Double-walled Al-based MOF with large microporous specific surface area for trace benzene adsorption
Trace benzene poses a risk to the health and safety of humans, resulting in a challenging task. Here authors synthesise double-walled Al-based MOF ZJU-520(Al) with trace benzene adsorption (5.98 mmol g–1) and excellent benzene/cyclohexane separation ability.
- Laigang Hu
- , Wenhao Wu
- & Kun Yang
-
Article
| Open Access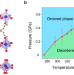 Two-dimensional lead halide perovskite lateral homojunctions enabled by phase pinning
Two-dimensional lead halide perovskite lateral homojunctions enabled by phase pinning
Hong et al. report 2D perovskite lateral homojunction consists of ordered and disordered phases, achieved by organic cation doping induced phase pinning, built upon which they develop tuneable optical properties under external stimuli and directional exciton diffusion in the homojunctions.
- Huilong Hong
- , Songhao Guo
- & Yongping Fu
-
Article
| Open Access A Janus carbaporphyrin pseudo-dimer
A Janus carbaporphyrin pseudo-dimer
Carbaporphyrin dimers, known for their interesting photophysical properties and application in metal-organic chemistry, generally contain two identical subunits. Here, the authors highlight the benefits that can accrue from breaking the inherent symmetry of carbaporphyrin dimers and details a new approach to creating heterobimetallic complexes.
- Haodan He
- , Jiyeon Lee
- & Xian-Sheng Ke
-
Article
| Open Access Crosslinking-induced patterning of MOFs by direct photo- and electron-beam lithography
Crosslinking-induced patterning of MOFs by direct photo- and electron-beam lithography
Precise and scalable patterning is essential for the use of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in solid-state electronics and photonics. Here, the authors report on resistance-free, direct photo- and electron-beam lithography of MOF films using crosslinking chemistry.
- Xiaoli Tian
- , Fu Li
- & Jinghong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Intragrain impurity annihilation for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
Intragrain impurity annihilation for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
The detrimental effects of intragrain impurity nanoclusters on the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells remain unexplored. Here, the authors study the intragrain impurity annihilation by in situ scanning transmission electron microscopy and adopt a laser stimulus to heal such impurity.
- Songhua Cai
- , Zhipeng Li
- & Yuanyuan Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access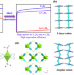 Molecular sieving of iso-butene from C4 olefins with simultaneous high 1,3-butadiene and n-butene uptakes
Molecular sieving of iso-butene from C4 olefins with simultaneous high 1,3-butadiene and n-butene uptakes
The efficient separation of iso-butene, an important raw material in chemical industry, remains challenging due to similar molecular properties of C4 olefins. Here, the authors report a sulfate-pillared adsorbent for the molecular sieving of iso-C4H8 from C4H6 and n-C4H8 with good benchmark uptake ratios and Henry’s selectivities.
- Junhui Liu
- , Hanting Xiong
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Complete separation of benzene-cyclohexene-cyclohexane mixtures via temperature-dependent molecular sieving by a flexible chain-like coordination polymer
Complete separation of benzene-cyclohexene-cyclohexane mixtures via temperature-dependent molecular sieving by a flexible chain-like coordination polymer
The separation and purification of C6 cyclic hydrocarbons by thermal distillation is an energy intensive process which may be replaced by alternative energy-efficient adsorptive techniques. Here, the authors report a chain-like coordination polymer which facilitates complete separation of benzene, cyclohexene, and cyclohexane via an ideal molecular sieving mechanism.
- Feng Xie
- , Lihang Chen
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
By virtue of the rotational motions of interlocked macrocycles, the authors describe a chameleon-like catenane host that can adjust its co-conformation for selective binding to copper(I) or sulfate ion. While the cationic copper(I) complex is achiral, the interlocked rings in the catenane host rotate and re-orient into a chiral co-conformation upon forming the anionic sulfate complex.
- Yueliang Yao
- , Yuen Cheong Tse
- & Ho Yu Au-Yeung
-
Article
| Open Access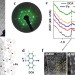 Ferromagnetism on an atom-thick & extended 2D metal-organic coordination network
Ferromagnetism on an atom-thick & extended 2D metal-organic coordination network
Despite having all the ingredients required for the formation of two-dimensional ferromagnetism, achieving such a magnetic state in atomically thin metal-organic coordination networks has proved to be a persistent challenge. Here, Lobo-Checa et al demonstrate 2Dferromagnetism in a self-assembled network, exhibiting coercive fields over 2 Tesla and a Curie temperature of 35K.
- Jorge Lobo-Checa
- , Leyre Hernández-López
- & Fernando Bartolomé
-
Article
| Open Access Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Crack formation typically results in random patterns and material failure. Inspired by plant phototropism, the authors use plasmonic absorbers to control crack propagation in colloidal films with light, showcasing a robust, programmable self-assembly process.
- Fanny Thorimbert
- , Mateusz Odziomek
- & Marco Faustini
-
Article
| Open Access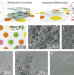 Unusual flexibility of transparent poly(methylsilsesquioxane) aerogels by surfactant-induced mesoscopic fiber-like assembly
Unusual flexibility of transparent poly(methylsilsesquioxane) aerogels by surfactant-induced mesoscopic fiber-like assembly
Aerogels are mechanically friable despite their attractive properties such as visible-light transparency and low thermal conductivity. Here the authors show mechanically flexible, highly transparent aerogels based on fiber-like pore skeletons.
- Ryota Ueoka
- , Yosuke Hara
- & Kazuyoshi Kanamori
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Assembly is an interesting strategy to build chiral hierarchies with premade properties and functionalities. Here, the authors present assembled chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks with dynamical chiroptical activities and employ them as powerful and recoverable platforms for enantioselective recognition of chiral aliphatic substrates.
- Jun Guo
- , Yulong Duan
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly of clusters and copolymers towards programmed mesoporous metal oxides
Solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly of clusters and copolymers towards programmed mesoporous metal oxides
A solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly method is developed to achieve a general and programmable synthesis of mesoporous metal oxides via the association of POMs with block copolymers through indirect interaction.
- Wenhe Xie
- , Yuan Ren
- & Yonghui Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired mechanical mineralization of organogels
Bioinspired mechanical mineralization of organogels
Mineralization is common in biological materials for selective strengthening, but similar toughening in polymer composites is challenging. Here, the authors report a mechanically-mediated reaction for formation of mineralized microrods within a synthetic material.
- Jorge Ayarza
- , Jun Wang
- & Aaron P. Esser-Kahn
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon mediated coherent population oscillations in molecular aggregates
Plasmon mediated coherent population oscillations in molecular aggregates
The authors uncover a coherent, long-range transport of excitons in organic semiconductors that are strongly coupled to spatially structured plasmon fields by tracing ultrafast Rabi oscillations using two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy.
- Daniel Timmer
- , Moritz Gittinger
- & Christoph Lienau
-
Article
| Open Access Sharp zero-phonon lines of single organic molecules on a hexagonal boron-nitride surface
Sharp zero-phonon lines of single organic molecules on a hexagonal boron-nitride surface
Low-temperature spectroscopy of single fluorescent molecules can be of use to study dynamics in the nano-environment around them. Here, Smit et al. show that the fluorescence wavelength of molecules on the surface of hexagonal boron-nitride is particularly sensitive to how clean this surface is.
- Robert Smit
- , Arash Tebyani
- & Michel Orrit
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchically manufactured chiral plasmonic nanostructures with gigantic chirality for polarized emission and information encryption
Hierarchically manufactured chiral plasmonic nanostructures with gigantic chirality for polarized emission and information encryption
The application of chiral metamaterials is limited by the fabrication of large-area chiral plasmonic structures with high dissymmetry factors. Here, the authors overcome this limitation imparting extrinsic chirality to hierarchical nanostructured polymer substrates with application in quantum and security enhanced optical communications.
- Yoon Ho Lee
- , Yousang Won
- & Joon Hak Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of aligned dipoles and angular chromism of exciplexes in organic molecular heterostructures
Observation of aligned dipoles and angular chromism of exciplexes in organic molecular heterostructures
The directional features of dipole moments of Frenkel excitons and exciplexes are important for optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors study photo- and electro-luminescence emissions of organic heterostructures and observe angular chromism of exciplexes, indicating possible delocalization.
- Sang-hun Lee
- , Taek Joon Kim
- & Jinsoo Joo
-
Article
| Open Access Thin lamellar films with enhanced mechanical properties for durable radiative cooling
Thin lamellar films with enhanced mechanical properties for durable radiative cooling
Practical application of radiative cooling technology in harsh outdoor conditions remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a lamellar ANFs/Mica@TiO2 composite via a “solvent exchange-reprotonation” process enabling durable outdoor cooling.
- Lianhu Xiong
- , Yun Wei
- & Hua Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling bilayer interfacial features and their effects in polar polymer nanocomposites
Unraveling bilayer interfacial features and their effects in polar polymer nanocomposites
The nanoparticle-polymer interface plays a key role in nanoparticle-polymer composites but understanding the structures and properties of the interfacial region remains challenging. Here, the authors directly observe the presence of two interfacial polymer layers around a nanoparticle in polar polymers with different polar molecular conformations from the bulk polymer leading to an enhancement in polarity-related properties of polymer nanocomposites
- Xinhui Li
- , Shan He
- & Ce-Wen Nan
-
Article
| Open Access A nanoscale MOF-based heterogeneous catalytic system for the polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides enables direct routes toward both polypeptides and related hybrid materials
A nanoscale MOF-based heterogeneous catalytic system for the polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides enables direct routes toward both polypeptides and related hybrid materials
Metal-based heterogeneous catalysts are widely employed in ring-opening polymerization (ROP) but up to now the exploration of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) as catalysts in ROP remains underdeveloped. Here, the authors report a MOF heterogeneous catalytic system for fast, controllable, air- and moisture-insensitive ring-opening polymerization of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides, and its seamless integration with hybrid material preparation.
- Ying Liu
- , Zhongwu Ren
- & Yugang Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating adsorption performance of zeolites by pre-activation in electric fields
Regulating adsorption performance of zeolites by pre-activation in electric fields
The gas adsorption capacity and selectivity in zeolite molecular sieves can be regulated by an external electric field through the electric field-induced cation relocation and framework expansion.
- Kaifei Chen
- , Zhi Yu
- & Gang Kevin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic flexibility and rigidification in a TPE-based Zr-MOFs with scu topology
Anisotropic flexibility and rigidification in a TPE-based Zr-MOFs with scu topology
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with adjustable porosity and tunable functionality have attracted considerable attention, but the directional control of intermolecular and intramolecular motion of TPE-based ligands in the non-interpenetrated flexible MOFs has not yet been studied. Here, the authors report a non-interpenetrated tetraphenylethylene-based MOF with anisotropic flexibility.
- Sha-Sha Meng
- , Ming Xu
- & Zhi-Yuan Gu
-
Article
| Open Access A route to metalloligands consolidated silver nanoclusters by grafting thiacalix[4]arene onto polyoxovanadates
A route to metalloligands consolidated silver nanoclusters by grafting thiacalix[4]arene onto polyoxovanadates
Metalloligands provide a potent strategy for manipulating the surface metal arrangements of metal nanoclusters (NCs), but their synthesis and subsequent installation onto metal NCs remains a significant challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate the synthesis of two atomically precise silver NCs by controlling reaction temperature and demonstrate thermal induced structure transformation between the clusters during a temperature-dependent assembly process.
- Zhi Wang
- , Yan-Jie Zhu
- & Di Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of structural chirality, electron spin and topological orbital in chiral molecular spin valves
Interplay of structural chirality, electron spin and topological orbital in chiral molecular spin valves
Chirality induced spin selectivity is a process whereby a chiral molecule induces a spin-polarization to a current passing along the chiral molecule. The exact physical origin of the effect is still debated despite extensive experimental result. Here, Adhikari et al provide evidence for the important role of spin-orbit coupling in the normal metals that connect to the chiral molecule in CISS experiments.
- Yuwaraj Adhikari
- , Tianhan Liu
- & Peng Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Design of mechanical-robust phosphorescence materials through covalent click reaction
Design of mechanical-robust phosphorescence materials through covalent click reaction
Materials with room temperature phosphorescence that are mechanically robust are desirable, but can be challenging to obtain. Here, the authors report the combination of poly(vinyl alcohol) and chromophore molecules with layered double hydroxides for room temperature phosphorescent materials.
- Rui Tian
- , Shuo Gao
- & Chao Lu
-
Article
| Open Access An approach to MOFaxanes by threading ultralong polymers through metal–organic framework microcrystals
An approach to MOFaxanes by threading ultralong polymers through metal–organic framework microcrystals
Mechanically interlocked architectures inspired the fabrication of numerous molecular systems, but the topological design of such architectures has not been fully explored from the nano- to the macroscopic scale. Here, the authors propose a MOFaxane, comprised of long chain molecules penetrating a microcrystal of metal– organic framework.
- Tomoya Iizuka
- , Hiroyuki Sano
- & Takashi Uemura
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic binding sites in a metal-organic framework for the optical sensing of nitrogen dioxide
Synergistic binding sites in a metal-organic framework for the optical sensing of nitrogen dioxide
Luminescent metal-organic frameworks are an emerging class of optical sensors capable to capture and detect toxic gases. Here, the authors report the incorporation of synergistic binding sites in MOF-808 through post-synthetic modification with copper for optical sensing of NO2 at remarkably low concentrations.
- Isabel del Castillo-Velilla
- , Ahmad Sousaraei
- & Ana E. Platero-Prats
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-derived defects suppress adsorption in MOF-74
Solvent-derived defects suppress adsorption in MOF-74
Defects in metal-organic frameworks impact their structure and properties. Here authors uncover formate defects in MOF-74 that originate from decomposed DMF solvent. NMR shows that the defects partially eliminate open metal sites and lead to a decrease of gas adsorption; the adsorption mechanism of CO2 in defective MOF is also elucidated.
- Yao Fu
- , Yifeng Yao
- & Xueqian Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid magnonics in hybrid perovskite antiferromagnets
Hybrid magnonics in hybrid perovskite antiferromagnets
Recently there has been interest in exploring the coupling between magnons for use in information processing, however, this is hampered by the fact that such coupling is forbidden due to the different parity of the acoustic and optical magnons. Here, Comstock et al show that the interlayer Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya-Interaction in a layered hybrid antiferromagnet can allow for strong coupling between the acoustic and optical magnons, offering a pathway for magnon coherent information processing.
- Andrew H. Comstock
- , Chung-Tao Chou
- & Dali Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting membrane carbon capture via multifaceted polyphenol-mediated soldering
Boosting membrane carbon capture via multifaceted polyphenol-mediated soldering
The development of mixed-matrix membranes is especially challenging when highly permeable materials are used. Here the authors present a molecular soldering strategy featuring multifunctional polyphenols in tailored polymer chains, well-designed hollow MOF structures, and defect-free interfaces to break the permeability-selectivity trade-off limit.
- Bin Zhu
- , Shanshan He
- & Lu Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially confined protein assembly in hierarchical mesoporous metal-organic framework
Spatially confined protein assembly in hierarchical mesoporous metal-organic framework
Immobilization of biomolecules into porous materials could lead to enhanced performance in terms of stability and easier separation for their reuse. Here authors gain insights into the spatial arrangement of green fluorescent protein entrapped in a mesoporous MOF by situ small-angle neutron scattering.
- Xiaoliang Wang
- , Lilin He
- & Shengqian Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Construction of angstrom-scale ion channels with versatile pore configurations and sizes by metal-organic frameworks
Construction of angstrom-scale ion channels with versatile pore configurations and sizes by metal-organic frameworks
The fabrication of synthetic nanochannels for ion separation is challenging. Here, the authors synthesize angstrom-scale ion channels featuring one-dimensional to three-dimensional pore configurations by growing metal‒organic frameworks into nanochannels; the structure of the pore influences the ion transport performance.
- Xingya Li
- , Gengping Jiang
- & Huacheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A self-standing three-dimensional covalent organic framework film
A self-standing three-dimensional covalent organic framework film
Fabrication of 3D covalent organic framework thin films is challenging. Here the authors report on a liquid-liquid interfacial approach based on physical-organic considerations to synthesize an ultrathin covalent crystal film.
- Yizhou Yang
- , Yanyan Chen
- & Karl Börjesson
-
Article
| Open Access Primary radiation damage in bone evolves via collagen destruction by photoelectrons and secondary emission self-absorption
Primary radiation damage in bone evolves via collagen destruction by photoelectrons and secondary emission self-absorption
X-rays are used for imaging and sterilisation of bone but cause damage due to ionising radiation. Here, the authors study the degradation of collagen caused by photon-electron excitations and show that damage is initiated from onset which has implications for X-ray imaging and the levels of safe exposure.
- Katrein Sauer
- , Ivo Zizak
- & Paul Zaslansky
-
Article
| Open Access Silicone engineered anisotropic lithography for ultrahigh-density OLEDs
Silicone engineered anisotropic lithography for ultrahigh-density OLEDs
Ultrahigh-resolution patterning with high-throughput and high-fidelity is highly in demand for expanding the potential of OLEDs. Here, the authors report that silicone-incorporated organic light-emitting semiconductors can achieve anisotropic lithography via reactive ion etching-coupled photolithography, for ultrahigh-density RGB OLED arrays.
- Hyukmin Kweon
- , Keun-Yeong Choi
- & Do Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A bioinspired flexible neuromuscular system based thermal-annealing-free perovskite with passivation
A bioinspired flexible neuromuscular system based thermal-annealing-free perovskite with passivation
Designing efficient brain-inspired electronics remains a challenge. Here, Liu et al. develop a flexible perovskite-based artificial synapse with low energy consumption and fast response frequency and realize an artificial neuromuscular system with muscular-fatigue warning.
- Jiaqi Liu
- , Jiangdong Gong
- & Wentao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access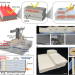 Scalable anisotropic cooling aerogels by additive freeze-casting
Scalable anisotropic cooling aerogels by additive freeze-casting
Scaling up anisotropic freeze-casting processes can be challenging due to the temperature gradient farther from the cold source. Here, authors report an additive freeze-casting technique able to produce large-scale aerogel panels and demonstrate it towards practical passive cooling applications.
- Kit-Ying Chan
- , Xi Shen
- & Jang-Kyo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Microspectroscopic visualization of how biochar lifts the soil organic carbon ceiling
Microspectroscopic visualization of how biochar lifts the soil organic carbon ceiling
A decadal-scale field trial revealed 1.01 Mg of rhizodeposit and necromass C was stored in soil microaggregate and mineral fractions per Mg biochar-C applied. Microspectroscopic analyses visualize mechanisms for this elevated soil C storage ceiling.
- Zhe (Han) Weng
- , Lukas Van Zwieten
- & Annette Cowie
-
Article
| Open Access Environmentally adaptive MOF-based device enables continuous self-optimizing atmospheric water harvesting
Environmentally adaptive MOF-based device enables continuous self-optimizing atmospheric water harvesting
Atmospheric water harvesting by MOF-based devices is critically dependent on weather conditions. Here, the authors report a MOF-based adaptive water harvesting system capable of adapting its cycles to temperature and relative humidity fluctuations throughout the day, continuously optimizing water production.
- Husam A. Almassad
- , Rada I. Abaza
- & Kyle E. Cordova
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional electron ptychography of organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures
Three-dimensional electron ptychography of organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures
The authors demonstrate electron ptychographic computed tomography by simultaneously recording high contrast data from both the organic- and inorganic components in a 3D DNA-origami framework hybrid nanostructure.
- Zhiyuan Ding
- , Si Gao
- & Peng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Strong, tough, ionic conductive, and freezing-tolerant all-natural hydrogel enabled by cellulose-bentonite coordination interactions
Strong, tough, ionic conductive, and freezing-tolerant all-natural hydrogel enabled by cellulose-bentonite coordination interactions
Cellulose based ion conductive hydrogels are emerging materials for application in flexible electronics but achieving simultaneously high conductivity and good mechanical properties remains challenging. Here, the authors propose a supramolecular engineering strategy to strengthen cellulosic hydrogel and to improve simultaneously its ionic conductivity and freezing tolerance.
- Siheng Wang
- , Le Yu
- & Chaoji Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Highly luminescent scintillating hetero-ligand MOF nanocrystals with engineered Stokes shift for photonic applications
Highly luminescent scintillating hetero-ligand MOF nanocrystals with engineered Stokes shift for photonic applications
The development of highly luminescent materials such as large Stokes shift fast emitters is desirable for their potential application in photonics. Here the authors engineer hetero-ligand metal-organic frameworks nanoparticles to achieve high emission yield, large Stokes shift and realize a prototypal fast scintillator.
- J. Perego
- , Charl X. Bezuidenhout
- & A. Monguzzi
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic non-classical crystallization drives hierarchical structuring of efficient circularly polarized phosphors
Biomimetic non-classical crystallization drives hierarchical structuring of efficient circularly polarized phosphors
Chiral emitters with high photoluminescence quantum yield are desirable for use in circularly polarized LEDs. The authors demonstrate the transfer of chirality from nanoscale copper iodide clusters to microscale chiral luminescent polycrystals by non-classical crystallization.
- Li-Zhe Feng
- , Jing-Jing Wang
- & Hong-Bin Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Gigahertz free-space electro-optic modulators based on Mie resonances
Gigahertz free-space electro-optic modulators based on Mie resonances
Active photonics in free space is important in computing, imaging and sensing. Here, hybrid silicon-organic nanoscale structures change the intensity of a free-space light beam by applied microwave signals at gigahertz speeds with a high efficiency.
- Ileana-Cristina Benea-Chelmus
- , Sydney Mason
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic magnetic field alignment and polarized emission of semiconductor nanoplatelets in a liquid crystal polymer
Dynamic magnetic field alignment and polarized emission of semiconductor nanoplatelets in a liquid crystal polymer
Liquid crystals (LC) are promising materials for the fabrication of reconfigurable arrays of 2D nanomaterials but it remains difficult to achieve stable dispersions of nanomaterials. Here, the authors report on good dispersions of pristine CdSe nanoplatelets (NPLs) in LCs, and reversible, rapid control of their alignment and associated anisotropic photoluminescence using a magnetic field.
- Dahin Kim
- , Dennis Ndaya
- & Chinedum O. Osuji
-
Article
| Open Access Type II porous ionic liquid based on metal-organic cages that enables l-tryptophan identification
Type II porous ionic liquid based on metal-organic cages that enables l-tryptophan identification
Porous liquids are potentially useful materials for the identification and separation of non-gaseous compounds. Herein, the authors report a type II porous ionic liquid with permanent porosity and high selectivity towards l-tryptophan (l-Trp) over other aromatic amino acids.
- Zhuxiu Zhang
- , Baolin Yang
- & Xu Qiao

 Halide Perovskite Inducing Anomalous Nonvolatile Polarization in Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based Flexible Nanocomposites
Halide Perovskite Inducing Anomalous Nonvolatile Polarization in Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based Flexible Nanocomposites