Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Time-domain classification of charge-density-wave insulators
Time-domain classification of charge-density-wave insulators
Insulators can be classified according to the kind of electronic interactions they are dominated by. Hellmannet al. used time- and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy to determine the dominant interactions in a series of transition metal dichalcogenides.
- S. Hellmann
- , T. Rohwer
- & K. Rossnagel
-
Article |
 Disruption of a proto-planetary disc by the black hole at the milky way centre
Disruption of a proto-planetary disc by the black hole at the milky way centre
Recent observations have uncovered a cloud of ionized gas falling into the supermassive black hole at the centre of our galaxy. Murray-Clay and Loeb present a model that may explain these observations, in which the cloud is produced from the proto-planetary disc around a low-mass star orbiting the black hole.
- Ruth A. Murray-Clay
- & Abraham Loeb
-
Article |
 Fabrication of flexible and freestanding zinc chalcogenide single layers
Fabrication of flexible and freestanding zinc chalcogenide single layers
Ultrathin inorganic materials hold promise for a variety of applications, including flexible electronics. This work presents a fabrication method that permits the synthesis of large and flexible freestanding layers of zinc selenide that display a high-photocurrent density.
- Yongfu Sun
- , Zhihu Sun
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
 Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocrystalline boron carbide by nanoporosity and interface phases
Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocrystalline boron carbide by nanoporosity and interface phases
The mechanical properties of structural ceramics are characterized by a high degree of fragility and brittleness. This study demonstrates that, contrary to expectation, their brittleness can be reduced substantially by introducing nanopores together with weak grain boundary phases.
- K. Madhav Reddy
- , J.J. Guo
- & M.W. Chen
-
Article |
 The spin Hall effect as a probe of nonlinear spin fluctuations
The spin Hall effect as a probe of nonlinear spin fluctuations
The spin Hall effect and its inverse allow conversion between charge and spin currents in both magnetic and nonmagnetic materials. Weiet al.observe an anomaly in the temperature dependence of the inverse spin Hall effect, which suggests that it can also be used as a sensor for very small magnetic moments.
- D.H. Wei
- , Y. Niimi
- & Y. Otani
-
Article |
 A non-syn-gas catalytic route to methanol production
A non-syn-gas catalytic route to methanol production
Methanol is an important industrial chemical and liquid fuel, and is usually produced by the syn-gas route from natural gas. Wuet al. develop a new catalytic process that directly converts ethylene glycol, derived from biomass or fossil fuels, to methanol in hydrogen using a Pd/Fe2O3co-precipitated catalyst.
- Cheng-Tar Wu
- , Kai Man Kerry Yu
- & Shik Chi Edman Tsang
-
Article |
 Proximity-induced high-temperature superconductivity in the topological insulators Bi2Se3 and Bi2Te3
Proximity-induced high-temperature superconductivity in the topological insulators Bi2Se3 and Bi2Te3
Inducing superconductivity in topological insulators by proximity to superconductors is a promising strategy for quantum computing. Here the authors induce high-temperature superconductivity in the topological insulators Bi2Se3 and Bi2Te3by placing them in contact with a cuprate superconductor.
- Parisa Zareapour
- , Alex Hayat
- & Kenneth S. Burch
-
Article |
 Phase-locking to a free-space terahertz comb for metrological-grade terahertz lasers
Phase-locking to a free-space terahertz comb for metrological-grade terahertz lasers
Frequency comb synthesizers are important for metrology, but they have been difficult to use as frequency rulers in the terahertz region due to their low power. Consolinoet al. phase-lock a quantum cascade laser to a free-space-propagating terahertz comb, demonstrating that they can overcome this limitation.
- L. Consolino
- , A. Taschin
- & P. De Natale
-
Article
| Open Access Blind topological measurement-based quantum computation
Blind topological measurement-based quantum computation
Blind quantum computation is a protocol that permits an algorithm, its input and output to be kept secret from the owner of the computational resource doing the calculation. Morimae and Fujii propose a strategy for topologically protected fault-tolerant blind quantum computation that is robust to environmental noise.
- Tomoyuki Morimae
- & Keisuke Fujii
-
Article
| Open Access Hard magnetic ferrite with a gigantic coercivity and high frequency millimetre wave rotation
Hard magnetic ferrite with a gigantic coercivity and high frequency millimetre wave rotation
Permanent magnets based on magnetic ferrites such as Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 are used in a wide range of applications. This study demonstrates that introducing rhodium into nanoparticles consisting of the ε phase of Fe2O3gives rise to a very high coercivity.
- Asuka Namai
- , Marie Yoshikiyo
- & Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
-
Article |
 Ultrafast magnetization enhancement in metallic multilayers driven by superdiffusive spin current
Ultrafast magnetization enhancement in metallic multilayers driven by superdiffusive spin current
Spin dynamics in magnetic materials can be driven by ultrafast light pulses, resulting in transient magnetization changes on femtosecond timescales. Rudolphet al. find that in magnetic trilayers the magnetization of one layer can be enhanced by superdiffusive spin currents from adjacent layers.
- Dennis Rudolf
- , Chan La-O-Vorakiat
- & Peter M. Oppeneer
-
Article |
 Naphthol radical couplings determine structural features and enantiomeric excess of dalesconols in Daldinia eschscholzii
Naphthol radical couplings determine structural features and enantiomeric excess of dalesconols in Daldinia eschscholzii
The dalesconol natural products are biosynthesised in an enantiomeric excess of 67%, rather than as a single enantiomer or a racemate. Tanet al. report that this unusual enantioselectivity is a result of the dominance of particular conformers of naphthol dimer intermediates.
- Wei Fang
- , Shen Ji
- & Ren Xiang Tan
-
Article |
 Spin-enhanced organic bulk heterojunction photovoltaic solar cells
Spin-enhanced organic bulk heterojunction photovoltaic solar cells
One of the obstacles to improving the efficiency of organic photovoltaic solar cells is the recombination of polaron pairs at the interface between donor and acceptor molecules. By doping cells with galvinoxyl radicals, Zhanget al. demonstrate a mechanism that overcomes this problem via a spin-flip process.
- Ye Zhang
- , Tek P. Basel
- & Z. Valy Vardeny
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable multimode quantum networks
Programmable multimode quantum networks
Multi-partite entanglement is essential not only to understand large quantum ensembles but also to build useful quantum technologies. Armstronget al. demonstrate multimode entanglement of up to eight modes using programmable virtual networks based on linear optics that can be switched in real time.
- Seiji Armstrong
- , Jean-François Morizur
- & Hans-A. Bachor
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging
Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging
Fibre-based technologies provide miniaturization, flexibility and the capability to access hard to reach areas. Čižmár and Dholakia exploit disorder in multimode fibres to enable a variety of imaging modalities, including bright- and dark-field microscopy and fluorescent imaging, using a single waveguide.
- Tomáš Čižmár
- & Kishan Dholakia
-
Article |
 Charge stripe order near the surface of 12-percent doped La2−xSrxCuO4
Charge stripe order near the surface of 12-percent doped La2−xSrxCuO4
Charge stripe order has been predicted to be the ground state for the parent compounds of copper oxide superconductors. Using resonant X-ray diffraction, Schüßler-Lagenheineet al. probe the surface region of 12 percent doped La2−xSrxCuO4, and observe charge-stripe order.
- H.-H. Wu
- , M. Buchholz
- & C. Schüßler-Langeheine
-
Article
| Open Access Optical detection of a single rare-earth ion in a crystal
Optical detection of a single rare-earth ion in a crystal
The optical transitions that occur in rare-earth-doped crystals offer promise for quantum information storage and processing. Kolesovet al.report the optical detection of a single praseodymium ion residing in a crystal host by using an excited-state absorption process to enhance its fluorescence yield.
- R. Kolesov
- , K. Xia
- & J. Wrachtrup
-
Article |
 Direct dynamic imaging of non-adiabatic spin torque effects
Direct dynamic imaging of non-adiabatic spin torque effects
The torque contributions exerted by spin-polarized currents on magnetic structures are not fully understood due to the difficulty in discerning their relative weight. Pollardet al. propose a novel method to directly determine the value of the competing spin transfer torques by in-situLorentz microscopy.
- S.D. Pollard
- , L. Huang
- & Y. Zhu
-
Article |
 Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation
Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation
Membrane-based technologies to separate oil–water mixtures are energy-intensive, suffer from fouling or cannot separate a wide range of mixtures. Now, a new membrane is reported that is superhydrophilic and superoleophobic, and can separate a range of oil–water mixtures with high efficiency, without an external energy source.
- Arun K. Kota
- , Gibum Kwon
- & Anish Tuteja
-
Article |
 Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
Optical separation of mechanical strain from charge doping in graphene
The spectral position of Raman peaks is a useful diagnostic for determining the degree of strain and excess electronic charges present in graphene. This study demonstrates that these two contributions can be separated from each other and therefore be obtained at the same time.
- Ji Eun Lee
- , Gwanghyun Ahn
- & Sunmin Ryu
-
Article |
 Imaging enzyme-triggered self-assembly of small molecules inside live cells
Imaging enzyme-triggered self-assembly of small molecules inside live cells
Supramolecular interactions allow some small molecules to self-assemble into nanofibres and hydrogels in aqueous environments. Gaoet al.report a hydrogelator that forms fluorescent nanofibres within cells, leading to the visualization of their self-assembly at the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Yuan Gao
- , Junfeng Shi
- & Bing Xu
-
Article |
 Flexible and transparent all-graphene circuits for quaternary digital modulations
Flexible and transparent all-graphene circuits for quaternary digital modulations
Signal modulation is a mechanism which embeds an information-carrying signal into a carrier wave to broadcast information and is essential for high-speed communication. Zhonget al. report a flexible, transparent all-graphene modulator circuit performing quaternary modulation schemes with only two transistors.
- Seunghyun Lee
- , Kyunghoon Lee
- & Zhaohui Zhong
-
Article |
 High-mobility and low-power thin-film transistors based on multilayer MoS2 crystals
High-mobility and low-power thin-film transistors based on multilayer MoS2 crystals
Molybdenum disulphide offers some tantalizing advantages over graphene as a material with which to fabricate field-effect transistors. Kimet al. present a comprehensive study of field-effect transistors made from multilayer samples of MoS2and find that they can achieve high carrier mobilities.
- Sunkook Kim
- , Aniruddha Konar
- & Kinam Kim
-
Article |
 In situ measurement of exciton energy in hybrid singlet-fission solar cells
In situ measurement of exciton energy in hybrid singlet-fission solar cells
Singlet fission converts single singlet excitons into pairs of triplet excitons, and it has been proposed to give additional photocurrent to solar cells. Ehrleret al. use lead selenide nanocrystals of varying sizes to measure the triplet energy in pentacene photovoltaic cells, and achieve efficiencies approaching 5%.
- Bruno Ehrler
- , Brian J. Walker
- & Neil C. Greenham
-
Article |
 Antenna electrodes for controlling electroluminescence
Antenna electrodes for controlling electroluminescence
Metallic nanoantennas can be used to enhance and tailor the photoluminescence effects in small-scale devices. Huanget al.design combined nanoantenna electrodes for quantum well nanoscale light-emitting diodes, to both inject charge and control the electroluminescence properties.
- Kevin C.Y. Huang
- , Min-Kyo Seo
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article |
 Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network
Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network
Understanding ultrafast demagnetisation is key to manipulating magnetic structures on fast timescales, yet laser sources limit the attainable spatial resolution. Here, a soft X-ray high harmonic source enables a high temporal and spatial resolution study of domain demagnetisation in [Co/Pt]30multilayer films.
- Boris Vodungbo
- , Julien Gautier
- & Jan Lüning
-
Article |
 Composite pulses for robust universal control of singlet–triplet qubits
Composite pulses for robust universal control of singlet–triplet qubits
Precise qubit manipulation is essential in quantum computation; however errors can occur from fluctuations in the magnetic field. Wanget al. propose a robust scheme for universal control of qubits in a semiconductor double quantum dot, cancelling leading orders of error in field gradient variation.
- Xin Wang
- , Lev S. Bishop
- & S. Das Sarma
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient fabrication of flexible and large-area organic light-emitting devices using slot-die coating
Ambient fabrication of flexible and large-area organic light-emitting devices using slot-die coating
Light-emitting electrochromic cells are a promising alternative to organic light-emitting diodes, as their performance is less sensitive to fabrication conditions. Here, a roll-to-roll compatible fabrication of such devices is presented, demonstrating large-area continuous production in ambient conditions.
- Andreas Sandström
- , Henrik F. Dam
- & Ludvig Edman
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam
Three-dimensional orientation-unlimited polarization encryption by a single optically configured vectorial beam
Generating arbitrary orientation of light polarization has been an elusive goal, yet it is important to light interactions with nano-objects. By combining azimuthally and radially polarized beams, Liet al. overcome this obstacle and demonstrate its use for polarization-based encryption with gold nanorods.
- Xiangping Li
- , Tzu-Hsiang Lan
- & Min Gu
-
Article |
 Stirring competes with chemical induction in chiral selection of soft matter aggregates
Stirring competes with chemical induction in chiral selection of soft matter aggregates
Chirality can be induced both by physical forces and by chemical induction processes. Here, a self-assembled system is reported in which chiral selection is controlled by the combined action of a chiral dopant and vortical stirring, which can act either constructively or destructively.
- Núria Petit-Garrido
- , Josep Claret
- & Francesc Sagués
-
Article
| Open Access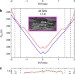 Observation of resistively detected hole spin resonance and zero-field pseudo-spin splitting in epitaxial graphene
Observation of resistively detected hole spin resonance and zero-field pseudo-spin splitting in epitaxial graphene
Along with its electronic characteristics, the spin properties of graphene have recently received increasing attention in the context of spintronic applications. Using microwave radiation, Maniet al. identify resistively detected spin resonance in monolayer and trilayer graphene sheets and extract the value for the Landé g-factor.
- Ramesh G. Mani
- , John Hankinson
- & Walter A. de Heer
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging high-dimensional spatial entanglement with a camera
Imaging high-dimensional spatial entanglement with a camera
Measuring the entanglement between down-converted photons is central to many quantum optical experiments, and is normally performed by scanning detectors stepwise across a plane. Edgaret al. use a CCD camera to measure the entire entangled light field, finding strong correlations in position and momentum.
- M.P. Edgar
- , D.S. Tasca
- & M.J. Padgett
-
Article
| Open Access Multimode circuit optomechanics near the quantum limit
Multimode circuit optomechanics near the quantum limit
Optomechanical systems allow for the exploration of macroscopic behaviour at or near the quantum limit. Masselet al. use micromechanical resonators to study the hybridisation of one photonic and two phononic modes with phonon numbers down to 1.8, showing a coupling between all three degrees of freedom.
- Francesco Massel
- , Sung Un Cho
- & Mika A. Sillanpää
-
Article |
 Skyrmion flow near room temperature in an ultralow current density
Skyrmion flow near room temperature in an ultralow current density
Current-induced motion of magnetic nanostructures, such as skyrmions or domain walls, is envisioned as a promising scalable technology for information storage. Yuet al.demonstrate near-room-temperature motion of skyrmions with current densities orders of magnitude lower than previously reported in domain walls.
- X.Z. Yu
- , N. Kanazawa
- & Y. Tokura
-
Article |
 High-resolution three-dimensional partially coherent diffraction imaging
High-resolution three-dimensional partially coherent diffraction imaging
Coherent diffractive imaging exploits coherent X-ray sources to image objects from their diffraction patterns, but fails for decreasing coherence. Using partially coherent diffraction patterns, Clarket al. obtain three dimensional reconstructions of nanocrystals and determine the wavefield coherence.
- J.N. Clark
- , X. Huang
- & I.K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vortex-beam illumination
Light-induced spiral mass transport in azo-polymer films under vortex-beam illumination
Non-uniform light beams can create patterns in azo-polymer films by inducing mass transport, yet the process is not well understood. Using optical vortex beams, Ambrosioet al. observe the formation of spiral patterns that are surprisingly sensitive to the optical phase, which they explain with a new model.
- Antonio Ambrosio
- , Lorenzo Marrucci
- & Pasqualino Maddalena
-
Article
| Open Access Higgs transition from a magnetic Coulomb liquid to a ferromagnet in Yb2Ti2O7
Higgs transition from a magnetic Coulomb liquid to a ferromagnet in Yb2Ti2O7
Quantum spin ice is a magnetic state of matter which can play host to monopole excitations. Using polarized neutron scattering, Changet al. show that the quantum spin ice material ytterbium titanate undergoes a Higgs transition of emergent magnetic monopoles from a Coulomb liquid to a ferromagnetic phase.
- Lieh-Jeng Chang
- , Shigeki Onoda
- & Martin Richard Lees
-
Article |
 Symmetry breaking in the formation of magnetic vortex states in a permalloy nanodisk
Symmetry breaking in the formation of magnetic vortex states in a permalloy nanodisk
Vortex states in magnetic nanoislands are characterized by a curling of the magnetization in the plane of the disk. This study demonstrates experimentally that vortices tend to form with a preferred handedness that is dictated by the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction.
- Mi-Young Im
- , Peter Fischer
- & Teruo Ono
-
Article |
 Topological crystalline insulators in the SnTe material class
Topological crystalline insulators in the SnTe material class
Topologically protected states of matter are receiving widespread attention owing to their unusual electronic properties. Using numerical simulations, this study predicts that tin telluride is a physical realization of a new class of materials termed topological crystalline insulators.
- Timothy H. Hsieh
- , Hsin Lin
- & Liang Fu
-
Article |
 Solderable and electroplatable flexible electronic circuit on a porous stretchable elastomer
Solderable and electroplatable flexible electronic circuit on a porous stretchable elastomer
The integration of flexible electronics with conventional devices has been hampered by the lack of suitable soldering techniques able to withstand stretching. Jeonget al. use a porous substrate to fabricate biocompatible, stretchable electronics that can be interfaced with commercial components.
- Gi Seok Jeong
- , Dong-Hyun Baek
- & Sang-Hoon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access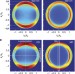 Quantifying the magnetic nature of light emission
Quantifying the magnetic nature of light emission
Light-matter interactions are generally dominated by electric fields and electric-dipole transitions. This study, however, quantifies magnetic contributions to light emission and so exploits the strong natural magnetic-dipole transitions in lanthanide ions to measure optical-frequency magnetic fields.
- Tim H. Taminiau
- , Sinan Karaveli
- & Rashid Zia
-
Article |
 An orbital-selective spin liquid in a frustrated heavy fermion spinel LiV2O4
An orbital-selective spin liquid in a frustrated heavy fermion spinel LiV2O4
The Kondo coupling causes electron mass enhancement in rare earth materials, but not in otherd electron systems. Shimizu et al. report on the combination of frustrated spin liquid and strong Hund's coupling in a vanadium spinel as a mechanism for the microscopic origin of heavy dfermions in transition metals.
- Yasuhiro Shimizu
- , Hikaru Takeda
- & Hidenori Takagi
-
Article
| Open Access Structural correlations in the generation of polaron pairs in low-bandgap polymers for photovoltaics
Structural correlations in the generation of polaron pairs in low-bandgap polymers for photovoltaics
The electronic and optical properties of polymer semiconductors are largely dictated by their chemical structure. This study examines the nature of the photoexcited states generated in donor–acceptor polymers, and uncovers the dynamics of polaron pairs generation and recombination.
- Raphael Tautz
- , Enrico Da Como
- & Ullrich Scherf
-
Article |
 Biomimetic layer-by-layer assembly of artificial nacre
Biomimetic layer-by-layer assembly of artificial nacre
Nacre is an organic–inorganic composite biomaterial, which consists of an ordered multilayer structure of crystalline calcium carbonate platelets separated by porous organic layers. Finnemoreet al. present a route to artificial nacre which mimics the natural layer-by-layer biosynthesis.
- Alexander Finnemore
- , Pedro Cunha
- & Ullrich Steiner
-
Article
| Open Access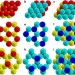 Patterning symmetry in the rational design of colloidal crystals
Patterning symmetry in the rational design of colloidal crystals
Patchy colloids are colloidal particles with chemically or physically patterned surfaces that result in complex interactions arising between them. By means of numerical simulations, Romano and Sciortino show that suitably tailored patches can induce the crystallization of patchy colloids into specific crystal structures.
- Flavio Romano
- & Francesco Sciortino
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Crystallization of noble metal atoms usually leads to the thermodynamically stable face-centred cubic phase. Sunet al. show that internal strain in silver nanoparticles leads to lattice distortion and a stable body-centred tetragonal phase.
- Yugang Sun
- , Yang Ren
- & Dean J. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic black gold by adiabatic nanofocusing and absorption of light in ultra-sharp convex grooves
Plasmonic black gold by adiabatic nanofocusing and absorption of light in ultra-sharp convex grooves
Plasmonic effects can turn reflective metals into strong absorbers, although this is usually realized within narrow wavelength ranges near resonances. Using arrays of ultra-sharp convex grooves, Søndergaardet al. show that nonresonant absorption can lead to effective broadband light absorption.
- Thomas Søndergaard
- , Sergey M. Novikov
- & Sergey I. Bozhevolnyi
-
Article
| Open Access Roles of icosahedral and crystal-like order in the hard spheres glass transition
Roles of icosahedral and crystal-like order in the hard spheres glass transition
The dynamics and structure of the glass transition in liquids is still debated. Using particle-level confocal microscopy, Leocmach and Tanaka investigate supercooled colloidal liquids and distinguish different scenarios for glassy slow dynamics, suggesting that local ordering may only play a minor role.
- Mathieu Leocmach
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article |
 Real-space observation of spin-split molecular orbitals of adsorbed single-molecule magnets
Real-space observation of spin-split molecular orbitals of adsorbed single-molecule magnets
Controlling the behaviour of single molecules on electrode interfaces is crucial for the development of molecular spintronics. This study reports spin-polarized scanning tunnelling microscopy data of the spin-split molecular orbitals of a single-molecule magnet adsorbed on a cobalt surface.
- Jörg Schwöbel
- , Yingshuang Fu
- & Roland Wiesendanger

 The elusive Heisenberg limit in quantum-enhanced metrology
The elusive Heisenberg limit in quantum-enhanced metrology