Featured
-
-
Article |
 MXenes with ordered triatomic-layer borate polyanion terminations
MXenes with ordered triatomic-layer borate polyanion terminations
MXenes with borate polyanion terminations are synthesized using a flux-assisted eutectic molten etching approach. These triatomic-layer terminations empower MXenes with considerably improved charge transport and charge storage capabilities.
- Dongqi Li
- , Wenhao Zheng
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Research Briefing |
 Perovskite solar cells that withstand photolysis and are stable under reverse bias
Perovskite solar cells that withstand photolysis and are stable under reverse bias
Photolysis and ion migration under electrical bias cause intrinsic instability in halide perovskite solar cells. By harnessing materials that both capture and confine iodide and polyiodide ions at the perovskite surface, the stability of devices under ultraviolet irradiation, thermal–light conditions or reverse bias can be greatly increased.
-
News & Views |
 Etch A Sketch-like liquid-crystal phase patterning
Etch A Sketch-like liquid-crystal phase patterning
Precision laser irradiation of liquid-crystal polymer networks with dynamic bonds enables reversible phase patterning to create multi-stimuli responsive materials towards wearable devices and information encryption.
- Elizabeth A. Recker
- , Joy Zhou
- & Zachariah A. Page
-
Article |
 Evidence for electron–hole crystals in a Mott insulator
Evidence for electron–hole crystals in a Mott insulator
Scanning tunnelling microscopy of doped RuCl3 shows distinct charge orderings at the lower and upper Hubbard bands, which can be attributed to a correlation-driven honeycomb hole crystal composed of hole-rich Ru sites and a rotational-symmetry-breaking paired electron crystal composed of electron-rich Ru–Ru bonds.
- Zhizhan Qiu
- , Yixuan Han
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article |
 Enabling three-dimensional real-space analysis of ionic colloidal crystallization
Enabling three-dimensional real-space analysis of ionic colloidal crystallization
Index-matched fluorescent particles provide a system that directly visualizes ionic crystallization using confocal microscopy, and offers insight into the structure, nucleation and growth of ionic solids.
- Shihao Zang
- , Adam W. Hauser
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Article |
 Clamping enables enhanced electromechanical responses in antiferroelectric thin films
Clamping enables enhanced electromechanical responses in antiferroelectric thin films
Here, the authors observe that in thin films of antiferroelectric PbZrO3, substrate clamping enhances the electromechanical response, with expansion purely in the out-of-plane direction, achieving 1.7% strain for 100-nm-thick films.
- Hao Pan
- , Menglin Zhu
- & Lane W. Martin
-
Article |
 Elucidating chirality transfer in liquid crystals of viruses
Elucidating chirality transfer in liquid crystals of viruses
The authors investigate the origins of chirality transfer across length scales, quantitatively demonstrating how chirality propagates from the molecular to liquid crystal level in filamentous virus systems.
- Eric Grelet
- & Maxime M. C. Tortora
-
Article
| Open Access A programmable topological photonic chip
A programmable topological photonic chip
The authors demonstrate a programmable topological photonic chip with large-scale integration of silicon photonic nanocircuits and microresonators that can be rapidly reprogrammed to implement diverse multifunctionalities.
- Tianxiang Dai
- , Anqi Ma
- & Jianwei Wang
-
Article |
 Correlated electron–nuclear dynamics of photoinduced water dissociation on rutile TiO2
Correlated electron–nuclear dynamics of photoinduced water dissociation on rutile TiO2
Understanding the origin of photoinduced water splitting on TiO2 is crucial to control photocatalytic surface reactions. A photoexcited-hole-transfer-driven mechanism now shows that water dissociation is strongly coupled with dynamic lattice distortion (photoexcited phonons) on TiO2 surfaces.
- Peiwei You
- , Daqiang Chen
- & Sheng Meng
-
Article
| Open Access A quantum coherent spin in hexagonal boron nitride at ambient conditions
A quantum coherent spin in hexagonal boron nitride at ambient conditions
Quantum coherent control of single-photon-emitting defect spins have been reported in hexagonal boron nitride, revealing that spin coherence is mainly governed by coupling to a few proximal nuclei and can be prolonged by decoupling protocols.
- Hannah L. Stern
- , Carmem M. Gilardoni
- & Mete Atatüre
-
Article |
 Metal bond strength regulation enables large-scale synthesis of intermetallic nanocrystals for practical fuel cells
Metal bond strength regulation enables large-scale synthesis of intermetallic nanocrystals for practical fuel cells
Although structurally ordered intermetallic nanocrystals are promising electrocatalysts for fuel cells, their high-temperature large-scale preparation has proved challenging. A low-melting-point-metal-induced bond strength weakening strategy to promote alloy catalyst ordering is now proposed.
- Jiashun Liang
- , Yangyang Wan
- & Qing Li
-
News & Views |
 A gentle nerve wrapper
A gentle nerve wrapper
Integrating electrochemically actuated soft robotics with ultra-flexible microelectrodes enables reversible and gentle wrapping around nerves for high-quality recordings.
- Klas Tybrandt
-
Article
| Open Access Sweet-spot operation of a germanium hole spin qubit with highly anisotropic noise sensitivity
Sweet-spot operation of a germanium hole spin qubit with highly anisotropic noise sensitivity
The authors report the sweet-spot operation of germanium hole spin qubits, exploring the optimization of the external magnetic field orientation, the g-tensor and its electric tunability, and hyperfine interactions.
- N. W. Hendrickx
- , L. Massai
- & A. Fuhrer
-
Article |
 Exciton polaron formation and hot-carrier relaxation in rigid Dion–Jacobson-type two-dimensional perovskites
Exciton polaron formation and hot-carrier relaxation in rigid Dion–Jacobson-type two-dimensional perovskites
The detailed interplay between electronic and lattice dynamics in two-dimensional perovskite materials remains elusive. Here the authors establish the room-temperature polaronic nature of the excitons in two-dimensional Dion–Jacobson-type perovskites.
- Somnath Biswas
- , Ruyan Zhao
- & Gregory D. Scholes
-
News & Views |
Sensitive proton-radiation detectors
Halide perovskite nanocrystal scintillators detect high-energy protons with sensitivity suitable for clinical applications.
- Matthew C. Beard
-
Letter |
 Exceptional electronic transport and quantum oscillations in thin bismuth crystals grown inside van der Waals materials
Exceptional electronic transport and quantum oscillations in thin bismuth crystals grown inside van der Waals materials
Ultrathin and flat crystals of bismuth are grown between the atomically flat layers of a van der Waals material. These crystals exhibit outstanding electronic properties, including gate-tunable quantum oscillations of the magnetoresistance.
- Laisi Chen
- , Amy X. Wu
- & Javier D. Sanchez-Yamagishi
-
Article
| Open Access Phase segregation and nanoconfined fluid O2 in a lithium-rich oxide cathode
Phase segregation and nanoconfined fluid O2 in a lithium-rich oxide cathode
Lithium-rich oxygen-redox cathodes demonstrate high capacities, but lose energy density when cycled, showing cation disordering and formation of nanovoids and bulk molecular O2. These structural changes are shown to be a consequence of a kinetically viable and thermodynamically favoured local phase segregation mechanism.
- Kit McColl
- , Samuel W. Coles
- & M. Saiful Islam
-
Article |
 Accelerating ionizable lipid discovery for mRNA delivery using machine learning and combinatorial chemistry
Accelerating ionizable lipid discovery for mRNA delivery using machine learning and combinatorial chemistry
An approach combining machine learning and combinatorial chemistry enables the creation and evaluation of ionizable lipid libraries for lipid nanoparticle formulation to effectively deliver messenger RNA to several cells and tissues.
- Bowen Li
- , Idris O. Raji
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Article |
 Electric-field-induced multiferroic topological solitons
Electric-field-induced multiferroic topological solitons
Control over topological antiferromagnetic entities is achieved at room temperature in multiferroic nanodevices using an electric field that induces magnetoelectric coupling to ferroelectric centre states.
- Arthur Chaudron
- , Zixin Li
- & Vincent Garcia
-
News & Views |
 Slow on, fast off
Slow on, fast off
The slow turn-on speed in accumulation-mode organic electrochemical transistors is explained by asymmetric ion transport in switching kinetics.
- Hang Yu
- & Jenny Nelson
-
Editorial |
 Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors progress at pace
Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors progress at pace
A synthesis method for large-scale conjugated polymers as well as studies under operational conditions show that research on organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors continues to progress.
-
News & Views |
 Turning powders into fibre via cellulose
Turning powders into fibre via cellulose
A wide range of zero-dimensional powders can be converted into versatile, high-performance one-dimensional micro-/nanofibres by using two-dimensional cellulose sheets as a mediator, preserving the particles’ nanostructural features and acting as building blocks for complex geometric shapes to satisfy application requirements.
- Xizheng Wang
- & Liangbing Hu
-
News & Views |
 Rescuing magnetic oscillations by microwave shocks
Rescuing magnetic oscillations by microwave shocks
‘Two colour’ pump–probe experiments on yttrium iron garnet discs demonstrate how to harness dissipation of magnetic oscillations. This may have important implications for the use of magnetic materials for information processing.
- Takis Kontos
-
News & Views |
 Forming denser glasses on soft substrates
Forming denser glasses on soft substrates
Physical vapour deposition of small-molecule glass formers onto soft substrates enhances the local dynamics at the top free surface, leading to the formation of denser glasses and providing access to states deeper in the potential energy landscape.
- Connie B. Roth
-
News & Views |
 Bulk van der Waals materials by low-temperature moulding
Bulk van der Waals materials by low-temperature moulding
Strong bulk van der Waals materials can be created from water-mediated densification of two-dimensional nanosheets by near-room-temperature moulding, establishing a pathway for the energy-efficient fabrication of a wide range of bulk van der Waals materials and even composites for various applications.
- Tom Lawson
- & Liming Dai
-
News & Views |
 Driving organic electronics to new heights
Driving organic electronics to new heights
Modified Suzuki–Miyaura polymerization procedures provide a scalable and reproducible route to regioregular conjugated polymers.
- Mario Leclerc
- & Serge Beaupré
-
Article |
 Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults
Electrochemomechanical failure in layered oxide cathodes caused by rotational stacking faults
Degradation is one of the most common causes of capacity deterioration in high-energy-density cathodes. Rotational stacking faults in layered lithium transition-metal oxides are shown to play a critical role in determining their structural and electrochemical stabilities.
- Donggun Eum
- , Sung-O Park
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article |
 Giant electron-mediated phononic nonlinearity in semiconductor–piezoelectric heterostructures
Giant electron-mediated phononic nonlinearity in semiconductor–piezoelectric heterostructures
Efficient phononic nonlinear processes are demonstrated in an acoustoelectric heterostructure combining a high-mobility semiconductor indium gallium arsenide film heterogeneously integrated onto a lithium niobate thin film.
- Lisa Hackett
- , Matthew Koppa
- & Matt Eichenfield
-
Article |
 Investigating chiral morphogenesis of gold using generative cellular automata
Investigating chiral morphogenesis of gold using generative cellular automata
The emergence of chiral morphologies from achiral building blocks is not well understood. Deep learning-based interpretation provides representative models for the process of symmetry breaking and chiral development during the growth of gold nanoparticles.
- Sang Won Im
- , Dongsu Zhang
- & Ki Tae Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Non-thermal phonon dynamics and a quenched exciton condensate probed by surface-sensitive electron diffraction
Non-thermal phonon dynamics and a quenched exciton condensate probed by surface-sensitive electron diffraction
The thermalization of acoustic phonons after photoexcitation is traced by electron pulses in TiSe2, and the excitonic contribution to the structural order parameter of the material’s charge density wave phase is quantified.
- Felix Kurtz
- , Tim N. Dauwe
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
 Mobile iodides capture for highly photolysis- and reverse-bias-stable perovskite solar cells
Mobile iodides capture for highly photolysis- and reverse-bias-stable perovskite solar cells
Iodide-related defects pose serious challenges to the irradiation, thermal, light or reverse-bias stabilities of perovskite solar cells. Here, the authors find that by using the iodide/polyiodide capture and confine effects of perfluorodecyl iodide interfacing with perovskites, inverted perovskite solar cells achieve much improved stabilities.
- Xiaoxue Ren
- , Jifei Wang
- & Yongbo Yuan
-
News & Views |
 Nano-oxides boost aluminium heat resistance
Nano-oxides boost aluminium heat resistance
Adding homogeneously dispersed oxide nanoparticles to aluminium pushes its high-temperature strength up to 500 °C.
- Alexis Deschamps
-
News & Views |
 Injectable and retrievable soft electronics
Injectable and retrievable soft electronics
Liquid bioelectronics based on a permanent fluidic magnet made from three-dimensional assembled magnetic colloidal particles can be injected into the surface of the heart for cardiovascular monitoring and subsequently retrieved after use.
- Jiahong Li
- , Yadong Xu
- & Wei Gao
-
Research Briefing |
 Synergistic work hardening by rapid multiplication of dislocations in a multi-principal-element alloy
Synergistic work hardening by rapid multiplication of dislocations in a multi-principal-element alloy
In a multi-principal-element VCoNi alloy, premature necking during Lüders banding has been harnessed to produce rapid dislocation multiplication, leading to both forest hardening and hardening induced by regions of local chemical order. The result is ductility of 20% and a yield strength of 2 GPa, during room-temperature and cryogenic deformation.
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemically actuated microelectrodes for minimally invasive peripheral nerve interfaces
Electrochemically actuated microelectrodes for minimally invasive peripheral nerve interfaces
Electrode arrays for neurological diagnosis and treatment carry a risk of nerve injury. Nerve cuffs with tiny voltage-controlled shape-reconfigurable electrode arrays have been reported, allowing active wrapping around delicate nerves.
- Chaoqun Dong
- , Alejandro Carnicer-Lombarte
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article |
 Plutonium oxide melt structure and covalency
Plutonium oxide melt structure and covalency
The molten structure of plutonium oxide—a component of mixed oxide nuclear fuels—is measured, showing some degree of covalent bonding. Its atomic structure is similar to that of cerium oxide, which could be a non-radioactive structural surrogate.
- Stephen K. Wilke
- , Chris J. Benmore
- & Richard Weber
-
Article |
 Permanent fluidic magnets for liquid bioelectronics
Permanent fluidic magnets for liquid bioelectronics
The magnetism-mediated assembly of non-Brownian magnetic colloidal particles into a three-dimensional oriented and ramified magnetic network yields permanent fluidic magnets that are used in a self-powered, liquid-based wireless cardiovascular sensor.
- Xun Zhao
- , Yihao Zhou
- & Jun Chen
-
Article |
 Heat-resistant super-dispersed oxide strengthened aluminium alloys
Heat-resistant super-dispersed oxide strengthened aluminium alloys
An interface modification strategy has been developed to uniformly distribute high-density sub-10 nm coherent MgO particles in an Al matrix, resulting in high strength and creep resistance at temperatures up to 500 °C.
- Xiangren Bai
- , Haonan Xie
- & Chunnian He
-
Article |
 On-device phase engineering
On-device phase engineering
A strategy of on-device phase engineering of two-dimensional materials is proposed, allowing the in situ realization of various lattice phases with distinct stoichiometries and versatile functions.
- Xiaowei Liu
- , Junjie Shan
- & Feng Miao
-
Article |
 Evolution of the flat band and the role of lattice relaxations in twisted bilayer graphene
Evolution of the flat band and the role of lattice relaxations in twisted bilayer graphene
By combining nano-spot angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy, the authors resolve the fine electronic structure of the flat band and remote bands of twisted bilayer graphene as the twist angle varies, revealing a spectral weight transfer between remote bands that is attributed to lattice relaxations.
- Qian Li
- , Hongyun Zhang
- & Shuyun Zhou
-
Article |
 Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride
Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride
Combining resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and photoluminescence spectroscopy, an elementary excitation in hexagonal-boron-nitride-based single-photon emitters has been demonstrated, giving rise to multiple regular harmonics that can explain the wide frequency range of these emitters.
- Jonathan Pelliciari
- , Enrique Mejia
- & Gabriele Grosso
-
Article |
 Observation of giant non-reciprocal charge transport from quantum Hall states in a topological insulator
Observation of giant non-reciprocal charge transport from quantum Hall states in a topological insulator
The authors report diode-like resistance in a non-magnetic topological insulator in the quantum Hall regime.
- Chunfeng Li
- , Rui Wang
- & Fengqi Song
-
Article |
 Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
The turn-off time is generally faster than the turn-on time in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs), but the mechanism is less understood. Here the authors find different transient behaviours of turn-on and turn-off in accumulation mode OECTs, and ion transport is the limiting factor of device kinetics.
- Jiajie Guo
- , Shinya E. Chen
- & David S. Ginger
-
Article |
 Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Uncovering the predictive pathways of lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides
Ion exchange is a powerful method to access metastable materials for energy storage, but identifying lithium and sodium interchange in layered oxides remains challenging. Using such model materials, vacancy level and corresponding lithium preference are shown to be crucial for ion exchange pathway accessibility.
- Yu Han
- , Weihang Xie
- & Chong Liu
-
Article |
 Manipulating chiral spin transport with ferroelectric polarization
Manipulating chiral spin transport with ferroelectric polarization
The authors report a modulation of the magnon spin current by electric polarization reversal.
- Xiaoxi Huang
- , Xianzhe Chen
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Article |
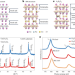 A correlated ferromagnetic polar metal by design
A correlated ferromagnetic polar metal by design
The authors report coexisting ferromagnetism, polar distortion and metallicity in quasi-two-dimensional Ca3Co3O8, providing a platform to exploit magnetoelectric coupling in a metallic system.
- Jianbing Zhang
- , Shengchun Shen
- & Pu Yu
-
Article |
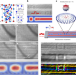 Experimental observation of current-driven antiskyrmion sliding in stripe domains
Experimental observation of current-driven antiskyrmion sliding in stripe domains
Electric current pulses are used to move antiskyrmions, by coupling them with a helical track.
- Zhidong He
- , Zhuolin Li
- & Baogen Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing instability for work hardening in multi-principal element alloys
Harnessing premature necking produces a rapid multiplication of dislocations to interact with local chemical orders for work hardening in VCoNi alloy, achieving ductility of 20% and yield strength of 2 GPa during room-temperature and cryogenic deformation.
- Bowen Xu
- , Huichao Duan
- & Xiaolei Wu
-
Research Briefing |
 Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Drift-free iontronic sensing enabled by a creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer
Soft pressure sensors drift under prolonged high stress because of the creep of soft materials, which causes inaccurate measurements. Now, through molecular-level design, a leakage-free and creep-free polyelectrolyte elastomer is synthesized, and an iontronic sensor using the polyelectrolyte elastomer shows very low signal drift under a high static pressure.

 Stretchable ionic–electronic bilayer hydrogel electronics enable in situ detection of solid-state epidermal biomarkers
Stretchable ionic–electronic bilayer hydrogel electronics enable in situ detection of solid-state epidermal biomarkers