Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Active mid-infrared ring resonators
Active mid-infrared ring resonators
Multifunctional active mid-infrared ring resonators and directional couplers with quantum cascade laser cores allow electrical control of resonant frequency and quality factors, tunable filtering and frequency comb generation.
- Dmitry Kazakov
- , Theodore P. Letsou
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access A mid-infrared lab-on-a-chip for dynamic reaction monitoring
A mid-infrared lab-on-a-chip for dynamic reaction monitoring
Rapid investigation of chemical reactions is a challenge in bio-medical analysis. Here, the authors demonstrate sensitive in-situ real-time reaction-monitoring of conformational changes in protein solution, based on a fingertip-sized mid-IR lab-on-a-chip.
- Borislav Hinkov
- , Florian Pilat
- & Gottfried Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-low threshold lasing through phase front engineering via a metallic circular aperture
Ultra-low threshold lasing through phase front engineering via a metallic circular aperture
Low threshold lasing is widely required, especially for portable systems. Here the authors design a circular subwavelength metallic aperture in a QCL to shape its phase front and control diffraction losses, which in turn allows a lower threshold dissipation power, enabling the fabrication of shorter cavities.
- Zhixin Wang
- , Filippos Kapsalidis
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Article
| Open Access Millimeter wave photonics with terahertz semiconductor lasers
Millimeter wave photonics with terahertz semiconductor lasers
Photonic solutions for generating free space millimeter radiation is a fast developing field that combines optoelectronics and RF domains but has many challenges. Here the authors present a quantum cascade laser (QCL) based solution for THz laser emission and millimeter wave generation in a single device.
- Valentino Pistore
- , Hanond Nong
- & Sukhdeep S. Dhillon
-
Article
| Open Access Fast amplitude modulation up to 1.5 GHz of mid-IR free-space beams at room-temperature
Fast amplitude modulation up to 1.5 GHz of mid-IR free-space beams at room-temperature
Broadband integrated electrical modulators are key components for photonic systems. Here, the authors present a room temperature mid-IR free-space amplitude modulator based on a semiconductor heterostructure that exploits the change in reflectance occurring at the change between weak and strong coupling.
- Stefano Pirotta
- , Ngoc-Linh Tran
- & Raffaele Colombelli
-
Article
| Open Access Mode-locked short pulses from an 8 μm wavelength semiconductor laser
Mode-locked short pulses from an 8 μm wavelength semiconductor laser
Producing pulses in the mid-IR often requires bulky sources and has been inaccessible with compact and versatile quantum cascade lasers (QCLs). Here, the authors demonstrate actively mode-locked, mid-IR QCL operation at room temperature.
- Johannes Hillbrand
- , Nikola Opačak
- & Benedikt Schwarz
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical adaptive control of quantum cascade random lasers
All-optical adaptive control of quantum cascade random lasers
Tunable quantum cascade lasers can enable applications in multiple areas. Here, the authors demonstrate the adaptive control of the modes and emission spectra of quantum cascade random lasers through a spatially-tailored optical modulation of the active region.
- S. Schönhuber
- , N. Bachelard
- & K. Unterrainer
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast terahertz saturable absorbers using tailored intersubband polaritons
Ultrafast terahertz saturable absorbers using tailored intersubband polaritons
Structures that can enhance the capabilities of quantum cascade lasers are highly sought after to improve their practicality for a range of applications. Here the authors demonstrate such a structure in a saturable absorber that takes advantage of intersubband polaritons in the terahertz range and study coherent nonlinear dynamics in the system.
- Jürgen Raab
- , Francesco P. Mezzapesa
- & Miriam S. Vitiello
-
Article
| Open Access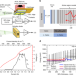 High-speed modulation of a terahertz quantum cascade laser by coherent acoustic phonon pulses
High-speed modulation of a terahertz quantum cascade laser by coherent acoustic phonon pulses
The typical electronic modulation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers is fundamentally limited at fast timescales by device properties. Here the authors propose and study an alternative, acoustic mechanism for modulating such THz QCLs at high speed.
- Aniela Dunn
- , Caroline Poyser
- & Anthony Kent
-
Article
| Open Access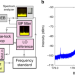 Fully phase-stabilized quantum cascade laser frequency comb
Fully phase-stabilized quantum cascade laser frequency comb
Here, the authors demonstrate full stabilization and control of the two key parameters of a four-wavemixing-based quantum cascade laser comb with metrological precision. These fully-controlled, frequency scalable comb emitters will allow an increasing number of mid- and far-IR applications.
- Luigi Consolino
- , Malik Nafa
- & Saverio Bartalini
-
Article
| Open Access Room temperature terahertz semiconductor frequency comb
Room temperature terahertz semiconductor frequency comb
Terahertz frequency combs are highly desired for applications in precision measurements, sensing, spectroscopy and metrology. Here the authors demonstrate the room-temperature chip-based THz frequency comb using nonlinear frequency generation from a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser comb.
- Quanyong Lu
- , Feihu Wang
- & Manijeh Razeghi
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast switch-on dynamics of frequency-tuneable semiconductor lasers
Ultrafast switch-on dynamics of frequency-tuneable semiconductor lasers
Single-mode, tuneable monolithic semiconductor lasers are important light sources for integrated photonics. Here, Kundu et al. observe the switch-on dynamics and mode competition of a terahertz quantum cascade laser and explain the behaviour with a carrier and photon transport model.
- Iman Kundu
- , Feihu Wang
- & A. Giles Davies
-
Article
| Open Access High power surface emitting terahertz laser with hybrid second- and fourth-order Bragg gratings
High power surface emitting terahertz laser with hybrid second- and fourth-order Bragg gratings
Proper design of the gratings can enhance the efficiency of distributed-feedback and quantum cascade lasers. Here, Jin et al. use a hybrid grating system that superposes second- and fourth-order Bragg gratings and achieve high radiative efficiency and a single-lobe radiation pattern.
- Yuan Jin
- , Liang Gao
- & Sushil Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous-wave highly-efficient low-divergence terahertz wire lasers
Continuous-wave highly-efficient low-divergence terahertz wire lasers
Quantum cascade lasers are compact sources, but simultaneously achieving cw operation, low divergence and single-mode emission has proven difficult. Here, Biasco et al. use a combination of distributed feedback and outcoupling via hole arrays, improving the performance of such a terahertz laser.
- Simone Biasco
- , Katia Garrasi
- & Miriam S. Vitiello
-
Article
| Open Access Active mode locking of quantum cascade lasers in an external ring cavity
Active mode locking of quantum cascade lasers in an external ring cavity
Compact, integrated mode-locked lasers can produce ultrashort pulses of light in the visible and near infrared, but are more difficult to achieve in the mid-infrared. Here, the authors demonstrate active mode locking of an external-cavity quantum cascade laser emitting at 5.2 micrometres at room temperature.
- D. G. Revin
- , M. Hemingway
- & A. Belyanin
-
Article |
 Dual-comb spectroscopy based on quantum-cascade-laser frequency combs
Dual-comb spectroscopy based on quantum-cascade-laser frequency combs
The fundamental vibrational bands of many molecules lie on the mid-infrared, so generating all solid-state, compact frequency combs in that region is important for molecular spectroscopy. Here, Villares et al.use quantum-cascade-laser frequency combs to demonstrate a high resolution, broadband dual-comb spectrometer.
- Gustavo Villares
- , Andreas Hugi
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Article |
 Broadly tunable monolithic room-temperature terahertz quantum cascade laser sources
Broadly tunable monolithic room-temperature terahertz quantum cascade laser sources
The development of terahertz applications, such as sensing and spectroscopy, is limited by the lack of mass-producible tunable radiation sources. Jung et al. report a monolithic electrically pumped room-temperature terahertz source that can be tuned over the widest frequency range yet demonstrated.
- Seungyong Jung
- , Aiting Jiang
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-
Article
| Open Access Reversing the pump dependence of a laser at an exceptional point
Reversing the pump dependence of a laser at an exceptional point
Exceptional points are singularities that occur when two resonant modes coalesce both in their frequency and width, giving rise to counterintuitive behaviour. Brandstetter et al. demonstrate how to induce such an exceptional point in a coupled pair of lasers, causing a reversal in their pump characteristics.
- M. Brandstetter
- , M. Liertzer
- & S. Rotter
-
Article
| Open Access Monolithically integrated mid-infrared lab-on-a-chip using plasmonics and quantum cascade structures
Monolithically integrated mid-infrared lab-on-a-chip using plasmonics and quantum cascade structures
Quantum cascade lasers and detectors enable photonic integration of semiconductor devices across a broad spectral range. Here, Schwarz et al.present a bi-functional laser and detector structure, monolithically integrated with plasmonic waveguides for mid-infrared chemical sensors on a chip.
- Benedikt Schwarz
- , Peter Reininger
- & Gottfried Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of a vertical cavity quantum cascade phonon laser structure
Dynamics of a vertical cavity quantum cascade phonon laser structure
Phonon lasers are the acoustic equivalent to optical lasers. Here Maryam and colleagues study the dynamics of semiconductor phonon lasers operating in the terahertz frequency regime, and show that these dynamics are similar to that of comparable optical lasers.
- W. Maryam
- , A. V. Akimov
- & A. J. Kent
-
Article |
 Broadly tunable terahertz generation in mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers
Broadly tunable terahertz generation in mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers
Compact, tunable terahertz sources are highly desired for sensing and imaging applications. Here Vijayraghavan et al. demonstrate room-temperature quantum cascade laser sources based on the non-linear optical conversion of mid-infrared light that provide a tunable output over a 3.5-THz bandwidth.
- Karun Vijayraghavan
- , Yifan Jiang
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-
Article |
 Observing chaos for quantum-dot microlasers with external feedback
Observing chaos for quantum-dot microlasers with external feedback
Optoelectronic devices such as conventional semiconductor lasers are used to study the chaotic behaviour of nonlinear systems. Here chaos is observed for quantum-dot microlasers operating close to the quantum limit with potential for new directions in the study of chaos in quantum systems.
- Ferdinand Albert
- , Caspar Hopfmann
- & Ido Kanter
-
Article
| Open Access Phase seeding of a terahertz quantum cascade laser
Phase seeding of a terahertz quantum cascade laser
The phase of a laser pulse is usually random, which prevents its use for phase-resolved measurements. Here, the authors seed a quantum cascade laser with coherent terahertz pulses, forcing laser action to start on a fixed phase. This kind of laser could be used as a source in time-domain spectroscopy.
- Dimitri Oustinov
- , Nathan Jukam
- & Sukhdeep Dhillon

 High-power electrically pumped terahertz topological laser based on a surface metallic Dirac-vortex cavity
High-power electrically pumped terahertz topological laser based on a surface metallic Dirac-vortex cavity