Featured
-
-
Comment
| Open Access A global forum on synthetic biology: the need for international engagement
A global forum on synthetic biology: the need for international engagement
A Global Forum on Synthetic Biology is needed to engage policymakers with practitioners across borders at the highest level. The international community needs a global confidence-building measure focused on discussing policy futures for the age of engineering biology.
- Thomas A. Dixon
- , Paul S. Freemont
- & Isak S. Pretorius
-
Comment
| Open AccessCommunity voices: sowing, germinating, flourishing as strategies to support inclusion in STEM
Understanding gaps in academic representation while considering the intersectionality concept is paramount to promoting real progress towards a more inclusive STEM. Here we discuss ways in which STEM careers can be sown and germinated so that inclusivity can flourish.
- Luisa Maria Diele-Viegas
- , Thamara Santos de Almeida
- & Flávia Virginio
-
Comment
| Open Access Crowd-sourcing observations of volcanic eruptions during the 2021 Fagradalsfjall and Cumbre Vieja events
Crowd-sourcing observations of volcanic eruptions during the 2021 Fagradalsfjall and Cumbre Vieja events
This study explores the scientific potential of crowdsourced observations during volcanic eruptions, using the 2021 Fagradalsfjall (Iceland) and Cumbre Vieja (Canary Islands) events as case studies.
- Fabian B. Wadsworth
- , Edward W. Llewellin
- & Alejandro Polo Santabárbara
-
Article
| Open Access The 4D Nucleome Data Portal as a resource for searching and visualizing curated nucleomics data
The 4D Nucleome Data Portal as a resource for searching and visualizing curated nucleomics data
This paper describes the ‘4DN Data Portal’ that hosts data generated by the 4D Nucleome network, including Hi-C and other chromatin conformation capture assays, as well as various sequencing-based and imaging-based assays. Raw data have been uniformly processed to increase comparability and the portal is implemented with visualization tools to browse the data without download.
- Sarah B. Reiff
- , Andrew J. Schroeder
- & Peter J. Park
-
Article
| Open Access An analysis of neuroscience and psychiatry papers published from 2009 and 2019 outlines opportunities for increasing discovery of sex differences
An analysis of neuroscience and psychiatry papers published from 2009 and 2019 outlines opportunities for increasing discovery of sex differences
Sex differences occur in many neurological and psychiatric diseases, and yet research is not always designed optimally to identify these. Here the authors perform a study of how sex was incorporated into the design and analyses of papers published six journals in neuroscience and psychiatry in 2009 compared with 2019.
- Rebecca K. Rechlin
- , Tallinn F. L. Splinter
- & Liisa A. M. Galea
-
Comment
| Open AccessCommunity voices: Achieving real diversity in STEM requires the ability to transform institutions
Resilience is often invoked to address systemic marginalization (e.g. racism) in academia but inadvertently maintains harmful systems. We argue that the ability to transform systems, as opposed to persevering within them, must be prioritized to make real, lasting change.
- Jory C. Lerback
- , Monique M. Holt
- & Stephanie Alvarez
-
Comment
| Open Access Community voices: NIH working toward inclusive excellence by promoting and supporting women in science
Community voices: NIH working toward inclusive excellence by promoting and supporting women in science
The U. S. National Institutes of Health is committed to addressing gender discrimination and fostering inclusive excellence, which is critical for the advancement of creativity and innovation in science. Strategies and processes aimed at achieving these goals are discussed.
- Kelly G. Ten Hagen
- , Carrie Wolinetz
- & Marie A. Bernard
-
Comment
| Open Access Community voices: the importance of diverse networks in academic mentoring
Community voices: the importance of diverse networks in academic mentoring
Mentor relationships are crucial to retention, success, and wellbeing of women and underrepresented minority scientists in academia. A network of diverse mentors may support achieving long-term career goals, advancement, and retention of both mentors and mentees, thus enhancing diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives.
- Rocío Deanna
- , Bethann Garramon Merkle
- & Gabriela Auge
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution population estimation using household survey data and building footprints
High-resolution population estimation using household survey data and building footprints
A lack of up-to-date population figures may hamper effective decision-making. Here, the authors develop a Bayesian model to estimate population data at high resolution in five provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Gianluca Boo
- , Edith Darin
- & Andrew J. Tatem
-
Comment
| Open Access Multilateral benefit-sharing from digital sequence information will support both science and biodiversity conservation
Multilateral benefit-sharing from digital sequence information will support both science and biodiversity conservation
Ensuring international benefit-sharing from sequence data without jeopardising open sharing is a major obstacle for the Convention on Biological Diversity and other UN negotiations. Here, the authors propose a solution to address the concerns of both developing countries and life scientists.
- Amber Hartman Scholz
- , Jens Freitag
- & Jörg Overmann
-
Comment
| Open AccessA Just Digital framework to ensure equitable achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals
While the technological revolution is accelerating, digital poverty is undermining the Sustainable Development Goals. This article introduces a justice-oriented digital framework which considers how fair access to digital capabilities, commodities, infrastructure, and governance can reduce global inequality and advance the SDGs.
- Katriona O’Sullivan
- , Serena Clark
- & Malcolm MacLachlan
-
Comment
| Open Access Impacts of climate change to African indigenous communities and examples of adaptation responses
Impacts of climate change to African indigenous communities and examples of adaptation responses
Climate change negatively impacts the livelihoods of indigenous communities across the world, including those located on the African continent. This Comment reports on how five African indigenous communities have been impacted by climate change and the adopted adaptation mechanisms.
- Walter Leal Filho
- , Newton R. Matandirotya
- & Richard Achia Mbih
-
Article
| Open Access BAMboozle removes genetic variation from human sequence data for open data sharing
BAMboozle removes genetic variation from human sequence data for open data sharing
Transparent data sharing is central to scientific progress, but limited for human sequencing data because of patient privacy concerns. Here, the authors propose an approach that removes certain types of genetic information in sequencing data, without affecting count-based downstream analyses.
- Christoph Ziegenhain
- & Rickard Sandberg
-
Comment
| Open Access Potentially long-lasting effects of the pandemic on scientists
Potentially long-lasting effects of the pandemic on scientists
The pandemic has caused disruption to many aspects of scientific research. In this Comment the authors describe the findings from surveys of scientists between April 2020 and January 2021, which suggests there was a decline in new projects started in that time.
- Jian Gao
- , Yian Yin
- & Dashun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic review and meta-analyses of studies analysing instructions to authors from 1987 to 2017
Systematic review and meta-analyses of studies analysing instructions to authors from 1987 to 2017
Publishers’ policies have the capability to increase transparency in scholarly literature. Malički and colleagues carried out a systematic review of over 150 studies that have examined scholarly journals’ recommendations. They find that requirements in terms of authorship, conflict of interests, data sharing, funding disclosure or ethics approval declaration vary greatly over time, among journals and across disciplines.
- Mario Malički
- , Ana Jerončić
- & Gerben ter Riet
-
Article
| Open Access Scientific prizes and the extraordinary growth of scientific topics
Scientific prizes and the extraordinary growth of scientific topics
Scientific revolutions have famously inspired scientists and innovation but large-scale analyses of scientific revolutions in modern science are rare. Here, the authors investigate one possible factor connected with a topic’s extraordinary growth—scientific prizes.
- Ching Jin
- , Yifang Ma
- & Brian Uzzi
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the onset of hot streaks across artistic, cultural, and scientific careers
Understanding the onset of hot streaks across artistic, cultural, and scientific careers
Despite their ubiquitous nature across a wide range of creative domains, it remains unclear if there is any regularity underlying the beginning of successful periods in a career. Here, the authors develop computational methods to trace the career outputs of artists, film directors, and scientists and explore how they move in their creative space along their career trajectory.
- Lu Liu
- , Nima Dehmamy
- & Dashun Wang
-
Perspective
| Open Access An actionable anti-racism plan for geoscience organizations
An actionable anti-racism plan for geoscience organizations
Racism thrives in geoscience. We present an antiracism plan to support the recruitment, retention and success of Black, Indigenous, and other people of color in geoscience. Our action plan can be adapted by any organization to remove barriers to participation for all marginalized geoscientists.
- Hendratta N. Ali
- , Sarah L. Sheffield
- & Blair Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Two decades of neuroscience publication trends in Africa
Two decades of neuroscience publication trends in Africa
Here, the authors survey neuroscience publications from Africa over the past two decades, highlighting areas of active research, international networks, funding, and techniques used.
- M. B. Maina
- , U. Ahmad
- & T. Baden
-
Article
| Open Access The influence of decision-making in tree ring-based climate reconstructions
The influence of decision-making in tree ring-based climate reconstructions
Tree rings are a crucial archive for Common Era climate reconstructions, but the degree to which methodological decisions influence outcomes is not well known. Here, the authors show how different approaches taken by 15 different groups influence the ensemble temperature reconstruction from the same data.
- Ulf Büntgen
- , Kathy Allen
- & Jan Esper
-
Comment
| Open Access Strengthening the United Nations Secretary-General’s Mechanism to an alleged use of bioweapons through a quality-assured laboratory response
Strengthening the United Nations Secretary-General’s Mechanism to an alleged use of bioweapons through a quality-assured laboratory response
The cascade of innovations in biotechnology opens new pathways for biological warfare. The international laboratory network being developed under the UN Secretary-General’s Mechanism could provide vital evidence in case of an alleged biological attack.
- Sandra Appelt
- , Anna-Maria Rohleder
- & Roland Grunow
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive performance of international COVID-19 mortality forecasting models
Predictive performance of international COVID-19 mortality forecasting models
Forecasts of COVID-19 mortality have been critical inputs into a range of policies, and decision-makers need information about their predictive performance. Here, the authors gather a panel of global epidemiological models and assess their predictive performance across time and space.
- Joseph Friedman
- , Patrick Liu
- & Emmanuela Gakidou
-
Article
| Open Access Sarcoma classification by DNA methylation profiling
Sarcoma classification by DNA methylation profiling
Sarcomas are morphologically heterogeneous tumours rendering their classification challenging. Here the authors developed a classifier using DNA methylation data from several soft tissue and bone sarcoma subtypes, which has the potential to improve classification for research and clinical purposes.
- Christian Koelsche
- , Daniel Schrimpf
- & Andreas von Deimling
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying and addressing the prevalence and bias of study designs in the environmental and social sciences
Quantifying and addressing the prevalence and bias of study designs in the environmental and social sciences
Randomised controlled experiments are the gold standard for scientific inference, but environmental and social scientists often rely on different study designs. Here the authors analyse the use of six common study designs in the fields of biodiversity conservation and social intervention, and quantify the biases in their estimates.
- Alec P. Christie
- , David Abecasis
- & William J. Sutherland
-
Comment
| Open Access Building resilient Arctic science amid the COVID-19 pandemic
Building resilient Arctic science amid the COVID-19 pandemic
Arctic research faces unprecedented disruptions due to COVID-19. This ‘pause’ gives an opportunity to reflect on the current state and the future of Arctic science and move towards a more resilient, thus equitable, coordinated, safe and locally-embedded Arctic research enterprise. Arctic science has been greatly affected by COVID-19. This comment looks forward to how Arctic science could be conducted in the future.
- Andrey N. Petrov
- , Larry D. Hinzman
- & Alona Yefimenko
-
Perspective
| Open AccessThe biosecurity benefits of genetic engineering attribution
A key security challenge with biosecurity threats is determining the responsible actor. In this Perspective, the authors review recent developments in using genetic sequence to assign a lab-of-origin and the potential protection it provides against misuse of synthetic biology.
- Gregory Lewis
- , Jacob L. Jordan
- & Thomas V. Inglesby
-
Article
| Open Access Patient and public perspectives on cell and gene therapies: a systematic review
Patient and public perspectives on cell and gene therapies: a systematic review
Cell and gene therapies offer opportunities for treating disease. Here, the authors conduct a systematic review of the evidence of patient and public perceptions of gene and cell therapies, and highlight the need for appropriate patient and public education, noting that patient perception, alongside evidence of clinical and cost-effectiveness, will be central to uptake and use of these therapies.
- Olalekan Lee Aiyegbusi
- , Karen Macpherson
- & Melanie J. Calvert
-
Article
| Open Access A versatile and customizable low-cost 3D-printed open standard for microscopic imaging
A versatile and customizable low-cost 3D-printed open standard for microscopic imaging
Open standard microscopy is urgently needed to give low-cost solutions to researchers and to overcome the reproducibility crisis in science. Here the authors present a 3D-printed, open-source modular microscopy toolbox UC2 (You. See. Too.) for a few hundred Euros.
- Benedict Diederich
- , René Lachmann
- & Rainer Heintzmann
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE: The association between early career informal mentorship in academic collaborations and junior author performance
RETRACTED ARTICLE: The association between early career informal mentorship in academic collaborations and junior author performance
Here, the authors study mentorship in scientific collaborations, and find that mentorship quality predicts the scientific impact of protégés post mentorship. Moreover, female protégés collaborating with male mentors become more impactful post mentorship than those who collaborate with female mentors.
- Bedoor AlShebli
- , Kinga Makovi
- & Talal Rahwan
-
Comment
| Open Access Using alt text to make science Twitter more accessible for people with visual impairments
Using alt text to make science Twitter more accessible for people with visual impairments
Scientists increasingly post images and photos on social media to share their research activities. However, posting images and photos could potentially exclude people with visual impairments. Here, we outline actions that should be taken to foster accessibility and inclusion in posting scientific images on social media.
- Domenico Chiarella
- , Justin Yarbrough
- & Christopher A.-L. Jackson
-
Perspective
| Open Access The misuse of colour in science communication
The misuse of colour in science communication
The accurate representation of data is essential in science communication, however, colour maps that visually distort data through uneven colour gradients or are unreadable to those with colour vision deficiency remain prevalent. Here, the authors present a simple guide for the scientific use of colour and highlight ways for the scientific community to identify and prevent the misuse of colour in science.
- Fabio Crameri
- , Grace E. Shephard
- & Philip J. Heron
-
Perspective
| Open Access Microplastic regulation should be more precise to incentivize both innovation and environmental safety
Microplastic regulation should be more precise to incentivize both innovation and environmental safety
Plastic pollution is recognized as a global threat, but policy hurdles and a lack of effective plastic substitutes contribute to the problem. In this Perspective, the authors argue that an effective and sustainable path forward must rely on key restrictions and regulations optimized for impact and efficacy.
- Denise M. Mitrano
- & Wendel Wohlleben
-
Article
| Open Access Framework for quality assessment of whole genome cancer sequences
Framework for quality assessment of whole genome cancer sequences
Working with cancer genomes from multiple projects can increase investigative power, but quality of sequences can vary. Here, the authors present a framework for comparing whole genome sequencing quality to help researchers guide downstream analyses and exclude poor quality samples.
- Justin P. Whalley
- , Ivo Buchhalter
- & Ivo G. Gut
-
Comment
| Open Access Three questions to ask before using model outputs for decision support
Three questions to ask before using model outputs for decision support
Decision makers must have sufficient confidence in models if they are to influence their decisions. We propose three screening questions to critically evaluate models with respect to their purpose, organization, and evidence. They enable a more transparent, robust, and secure use of model outputs.
- Volker Grimm
- , Alice S. A. Johnston
- & P. Thorbek
-
Article
| Open Access Retrospective evaluation of whole exome and genome mutation calls in 746 cancer samples
Retrospective evaluation of whole exome and genome mutation calls in 746 cancer samples
With the generation of large pan-cancer whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing projects, a question remains about how comparable these datasets are. Here, using The Cancer Genome Atlas samples analysed as part of the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes project, the authors explore the concordance of mutations called by whole exome sequencing and whole genome sequencing techniques.
- Matthew H. Bailey
- , William U. Meyerson
- & Christian von Mering
-
Article
| Open Access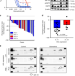 Transient IGF-1R inhibition combined with osimertinib eradicates AXL-low expressing EGFR mutated lung cancer
Transient IGF-1R inhibition combined with osimertinib eradicates AXL-low expressing EGFR mutated lung cancer
Cancer cells develop resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting EGFR. Here, the authors explore the mechanism of resistance to one such inhibitor - osimertinib - and find that resistance is caused by increased expression and activation of the IGF1 receptor and subsequent activation of the donwstream signalling pathway.
- Rong Wang
- , Tadaaki Yamada
- & Seiji Yano
-
Article
| Open Access Different scaling of linear models and deep learning in UKBiobank brain images versus machine-learning datasets
Different scaling of linear models and deep learning in UKBiobank brain images versus machine-learning datasets
Schulz et al. systematically benchmark performance scaling with increasingly sophisticated prediction algorithms and with increasing sample size in reference machine-learning and biomedical datasets. Complicated nonlinear intervariable relationships remain largely inaccessible for predicting key phenotypes from typical brain scans.
- Marc-Andre Schulz
- , B. T. Thomas Yeo
- & Danilo Bzdok
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: Alternative meta-analysis of behavioural interventions to promote action on climate change yields different conclusions
- Claudia F. Nisa
- , Edyta M. Sasin
- & Jocelyn J. Belanger
-
Article
| Open Access Blind spots in global soil biodiversity and ecosystem function research
Blind spots in global soil biodiversity and ecosystem function research
Soil organism biodiversity contributes to ecosystem function, but biodiversity and function have not been equivalently studied across the globe. Here the authors identify locations, environment types, and taxonomic groups for which there is currently a lack of biodiversity and ecosystem function data in the existing literature.
- Carlos A. Guerra
- , Anna Heintz-Buschart
- & Nico Eisenhauer
-
Comment
| Open AccessHigh-altitude populations need special considerations for COVID-19
- Arnar Breevoort
- , Giovanni A. Carosso
- & Mohammed A. Mostajo-Radji
-
Perspective
| Open AccessAI for social good: unlocking the opportunity for positive impact
The AI for Social Good movement aims to apply AI/ML tools to help in delivering on the United Nations’ sustainable development goals (SDGs). Here, the authors identify the challenges and propose guidelines for designing and implementing successful partnerships between AI researchers and application - domain experts.
- Nenad Tomašev
- , Julien Cornebise
- & Claudia Clopath
-
Comment
| Open Access Opportunities for big data in conservation and sustainability
Opportunities for big data in conservation and sustainability
Big data reveals new, stark pictures of the state of our environments. It also reveals ‘bright spots’ amongst the broad pattern of decline and—crucially—the key conditions for these cases. Big data analyses could benefit the planet if tightly coupled with ongoing sustainability efforts.
- Rebecca K. Runting
- , Stuart Phinn
- & James E. M. Watson
-
Article
| Open Access Low replicability can support robust and efficient science
Low replicability can support robust and efficient science
There has been much concern about the “replication crisis” in psychology and other disciplines. Here the authors show that an efficient solution to the crisis would not insist on replication before publication, and would instead encourage publication before replication, with the findings marked as preliminary.
- Stephan Lewandowsky
- & Klaus Oberauer
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule detection on a portable 3D-printed microscope
Single-molecule detection on a portable 3D-printed microscope
Single-molecule in vitro assays require dedicated confocal microscopes equipped with fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) modules. Here the authors present a compact, cheap and open-source 3D-printed confocal microscope for single photon counting and FCS measurements, and use it to detect α-synuclein aggregation.
- James W. P. Brown
- , Arnaud Bauer
- & Yann Gambin
-
Review Article
| Open Access The marine geological imprint of Antarctic ice shelves
The marine geological imprint of Antarctic ice shelves
The recent collapses of ice shelves in Antarctica due to warming make it essential to understand past ice shelf conditions and mechanisms. Here Smith and colleagues review the latest progress in deciphering the geological imprint of Antarctic ice shelves via sediments, landforms and proxy indicators.
- James A. Smith
- , Alastair G. C. Graham
- & Ross D. Powell
-
Article
| Open Access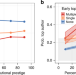 Early coauthorship with top scientists predicts success in academic careers
Early coauthorship with top scientists predicts success in academic careers
By examining publication records of scientists from four disciplines, the authors show that coauthoring a paper with a top-cited scientist early in one's career predicts lasting increases in career success, especially for researchers affiliated with less prestigious institutions.
- Weihua Li
- , Tomaso Aste
- & Giacomo Livan
-
Article
| Open Access Cathode porosity is a missing key parameter to optimize lithium-sulfur battery energy density
Cathode porosity is a missing key parameter to optimize lithium-sulfur battery energy density
For high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries, a dense electrode with low porosity is desired to minimize electrolyte intake, parasitic weight, and cost. Here the authors show the impact of porosity on the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries and reveal the mechanism through analytical modeling.
- Ning Kang
- , Yuxiao Lin
- & Mei Cai
-
Perspective
| Open Access Engaging with research impact assessment for an environmental science case study
Engaging with research impact assessment for an environmental science case study
Existing approaches to research impact assessment fail to include a range of soft impacts. The authors present a 3-part impact mapping approach and apply it to an environmental initiative. They highlight that support for realising research impact is vital, and call on researchers to be open to new ideas and avenues for creating impact from their work.
- Kirstie A. Fryirs
- , Gary J. Brierley
- & Thom Dixon
-
Article
| Open Access Early-career setback and future career impact
Early-career setback and future career impact
Little is known about the long-term effects of early-career setback. Here, the authors compare junior scientists who were awarded a NIH grant to those with similar track records, who were not, and find that individuals with the early setback systematically performed better in the longer term.
- Yang Wang
- , Benjamin F. Jones
- & Dashun Wang
