Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access In situ X-ray and acoustic observations of deep seismic faulting upon phase transitions in olivine
In situ X-ray and acoustic observations of deep seismic faulting upon phase transitions in olivine
This paper shows that formation of thin weak layers filled with nanocrystalline olivine/wadsleyite, upon the pressure-induced phase transition of olivine, is the major cause of deep-focus earthquakes on the metastable olivine wedge in deep slabs.
- Tomohiro Ohuchi
- , Yuji Higo
- & Tetsuo Irifune
-
Article
| Open Access Juno spacecraft gravity measurements provide evidence for normal modes of Jupiter
Juno spacecraft gravity measurements provide evidence for normal modes of Jupiter
Juno spacecraft experienced unknown accelerations near the closest approach to Jupiter. Here, the authors show that Jupiter’s axially symmetric, north-south asymmetric gravity field measured by Juno is perturbed by a time-variable component, associated to internal oscillations.
- Daniele Durante
- , Tristan Guillot
- & Scott J. Bolton
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the spatiotemporal complexity of the magnitude distribution and b-value during an earthquake sequence
Revealing the spatiotemporal complexity of the magnitude distribution and b-value during an earthquake sequence
The authors introduce a new perspective to study the spatiotemporal behavior of the magnitude–frequency distribution: spatially isolating seismogenic zones to provide an appropriate scale to resolve the b-value. Among those zones, the b-value behaved remarkably throughout the 2016 central Italy sequence.
- Marcus Herrmann
- , Ester Piegari
- & Warner Marzocchi
-
Article
| Open Access Intracontinental deformation of the Tianshan Orogen in response to India-Asia collision
Intracontinental deformation of the Tianshan Orogen in response to India-Asia collision
This study presents seismic images across the central Tianshan. The results show that Tianshan’s crust was extensively deformed according to its inherited properties, but was limitedly underthrusted by surrounding blocks
- Wei Li
- , Yun Chen
- & Brian F. Windley
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Multiple induced seismicity mechanisms at Castor underground gas storage illustrate the need for thorough monitoring
Multiple induced seismicity mechanisms at Castor underground gas storage illustrate the need for thorough monitoring
- Víctor Vilarrasa
- , Silvia De Simone
- & Antonio Villaseñor
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: Multiple induced seismicity mechanisms at Castor underground gas storage illustrate the need for thorough monitoring
Reply to: Multiple induced seismicity mechanisms at Castor underground gas storage illustrate the need for thorough monitoring
- Simone Cesca
- , Daniel Stich
- & William L. Ellsworth
-
Article
| Open Access Low-degree mantle melting controls the deep seismicity and explosive volcanism of the Gakkel Ridge
Low-degree mantle melting controls the deep seismicity and explosive volcanism of the Gakkel Ridge
Joint implementation of seismic tomography and numerical thermo-mechanical modeling sheds light to the causes of explosive submarine volcanic eruptions on the Gakkel Ridge and deeply penetrating seismicity down to 25 km depth.
- Ivan Koulakov
- , Vera Schlindwein
- & Aleksey Ivanov
-
Article
| Open Access Kilometer-scale structure on the core–mantle boundary near Hawaii
Kilometer-scale structure on the core–mantle boundary near Hawaii
A new paper constrains a high-resolution ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZ) structure at the base of the Hawaiian mantle. The authors further propose this to be a chemically distinct ULVZ with increasing iron content towards the core mantle boundary.
- Zhi Li
- , Kuangdai Leng
- & Sanne Cottaar
-
Article
| Open Access Seismic precursors to the Whakaari 2019 phreatic eruption are transferable to other eruptions and volcanoes
Seismic precursors to the Whakaari 2019 phreatic eruption are transferable to other eruptions and volcanoes
Volcanic eruptions that occur without warning can be deadly in touristic and populated areas. Using a machine learning approach, the authors here discover distinctive patterns hidden in the seismic signals of a number of New Zealand and Alaskan volcanoes, that occur before most of the eruptions studied.
- Alberto Ardid
- , David Dempsey
- & Shane Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation avalanches are like earthquakes on the micron scale
Dislocation avalanches are like earthquakes on the micron scale
Metallic microsamples deform in a sequence of abrupt strain bursts. Here, the authors demonstrate by analysing the elastic waves emitted by these bursts that this intermittent process resembles earthquakes in several aspects, although on completely different spatial and temporal scales.
- Péter Dusán Ispánovity
- , Dávid Ugi
- & István Groma
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the seismic cycle timing with coseismic twisting of subduction margins
Probing the seismic cycle timing with coseismic twisting of subduction margins
Satellite geodesy and downscaled laboratory experiments reveal that great subduction earthquakes trigger step changes in kinematics of neighboring segments. This signal is potentially informative of the timing of the seismic cycle.
- F. Corbi
- , J. Bedford
- & Z. Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Repetitive marsquakes in Martian upper mantle
Repetitive marsquakes in Martian upper mantle
The authors detect 47 hitherto unreported low-frequency marsquakes originating from Cerberus Fossae at all times of the Martian day. The matched filter technique confirms repetitive events implying that the Martian mantle is dynamically active.
- Weijia Sun
- & Hrvoje Tkalčić
-
Article
| Open Access Slab control on the mega-sized North Pacific ultra-low velocity zone
Slab control on the mega-sized North Pacific ultra-low velocity zone
Ultra-low velocity zones (ULVZs) are localized small-scale patches with extreme physical properties at the core-mantle boundary. Here, the authors discover a mega-sized ULVZ (1,500 × 900 km) at the northern edge of the Pacific Large Low Velocity Province.
- Jiewen Li
- , Daoyuan Sun
- & Dan J. Bower
-
Article
| Open Access Earthquake breakdown energy scaling despite constant fracture energy
Earthquake breakdown energy scaling despite constant fracture energy
Earthquake breakdown energy is commonly interpreted as a proxy for fracture energy but is observed to scale with magnitude. Here the authors show that a scale-independent stress overshoot, as seen in the 3D dynamic earthquake rupture simulations, leads to comparable scaling despite constant fault fracture energy.
- Chun-Yu Ke
- , Gregory C. McLaskey
- & David S. Kammer
-
Article
| Open Access Investigating the potential effectiveness of earthquake early warning across Europe
Investigating the potential effectiveness of earthquake early warning across Europe
The viability of earthquake early warning (EEW) in Europe is highly dependent on the magnitude of the ongoing earthquake and the ground-shaking threshold for alert issuance. The potential effectiveness of EEW is highest for Turkey, Italy, and Greece.
- Gemma Cremen
- , Carmine Galasso
- & Elisa Zuccolo
-
Article
| Open Access Fault rock heterogeneity can produce fault weakness and reduce fault stability
Fault rock heterogeneity can produce fault weakness and reduce fault stability
This paper shows that faults comprised of heterogeneously distributed materials, as is typical for tectonic faults in nature, are weaker and more unstable than equivalent faults where the materials are homogeneously mixed together.
- John D. Bedford
- , Daniel R. Faulkner
- & Nadia Lapusta
-
Article
| Open Access Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Precision measurement plays an important role in frequency metrology and optical communications. Here the authors compare two geographically separate ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability over a 2220 km optical fibre link and these measurements can be useful for dissemination of ultrastable light to distant optical clocks.
- M. Schioppo
- , J. Kronjäger
- & G. Grosche
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of episodic slow slip on seismicity and stress near a subduction-zone megathrust
Effects of episodic slow slip on seismicity and stress near a subduction-zone megathrust
Large slow slip earthquakes and tremor occur in subduction zones near the locked megathrust. Combined analysis of changes in slab seismicity and stress field near the times of such slow slip events highlights the role of fluid in promoting slow slip.
- Saeko Kita
- , Heidi Houston
- & Naoki Suda
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting fault slip via transfer learning
Predicting fault slip via transfer learning
By teaching machine learning models with earthquake fault numerical simulations laboratory fault slip is predictable. Training the model further with a snippet of laboratory data improves predictions suggesting an approach to probing faults in Earth.
- Kun Wang
- , Christopher W. Johnson
- & Paul A. Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access Uppermost crustal structure regulates the flow of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Uppermost crustal structure regulates the flow of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Anomalously slow seismic velocities in the upper Greenlandic crust reveal soft sedimentary substrates beneath major outlet glaciers. This, together with elevated geothermal heat flux observed at the onset of fast ice flow, has major implications for ice-sheet dynamics.
- G. A. Jones
- , A. M. G. Ferreira
- & A. Morelli
-
Article
| Open Access Fluid-injection-induced earthquakes characterized by hybrid-frequency waveforms manifest the transition from aseismic to seismic slip
Fluid-injection-induced earthquakes characterized by hybrid-frequency waveforms manifest the transition from aseismic to seismic slip
Yu et al. report a new type of induced earthquake signal characterized by hybrid-frequency waveforms (EHW). The low-frequency source features of the EHWs suggest they may represent slow ruptures transitioning from aseismic to seismic slip.
- Hongyu Yu
- , Rebecca M. Harrington
- & Bei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access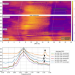 The shallow structure of Mars at the InSight landing site from inversion of ambient vibrations
The shallow structure of Mars at the InSight landing site from inversion of ambient vibrations
We invert Rayleigh wave ellipticity curves extracted from ambient seismic vibrations at the InSight landing site to resolve, for the first time on Mars, the shallow subsurface to around 200 m depth. While our seismic velocity model is largely consistent with the expected stacks of lava flows, we find a seismic low velocity zone at about 30 to 75 m depth that we interpret as a sedimentary layer sandwiched between layers of basalt flows.
- M. Hobiger
- , M. Hallo
- & W. B. Banerdt
-
Article
| Open Access Fluid migrations and volcanic earthquakes from depolarized ambient noise
Fluid migrations and volcanic earthquakes from depolarized ambient noise
Deep fluids inside volcanoes disrupt the oscillations of signals produced by wind and sea. Imaging this disruption through space and time allows tracking hazardous fluid migrations leading to earthquakes before they reach the surface.
- S. Petrosino
- & L. De Siena
-
Article
| Open Access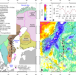 Long-lived Paleoproterozoic eclogitic lower crust
Long-lived Paleoproterozoic eclogitic lower crust
The nature of the lower crust and the crust-mantle transition is fundamental to Earth Sciences. Here, the authors provide evidence for long-lasting presence of lower crustal eclogite below the seismic Moho, challenging conventional models.
- Sebastian Buntin
- , Irina M. Artemieva
- & Stefan Buske
-
Article
| Open Access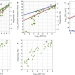 Magnitude and nucleation time of the 2017 Pohang Earthquake point to its predictable artificial triggering
Magnitude and nucleation time of the 2017 Pohang Earthquake point to its predictable artificial triggering
Here, authors find scaling of maximum magnitudes of earthquakes triggered by underground fluid injections with logarithmic event-occurrence times. This also applies to the Pohang Earthquake, the high probability of which was predictable using an approach based on monitoring of the Seismogenic Index.
- Serge A. Shapiro
- , Kwang-Hee Kim
- & Jin-Han Ree
-
Article
| Open Access Seismological expression of the iron spin crossover in ferropericlase in the Earth’s lower mantle
Seismological expression of the iron spin crossover in ferropericlase in the Earth’s lower mantle
This study identifies the predicted seismic expression of the high-to-low iron spin crossover in the deep Earth mineral ferropericlase. A depth-dependent signal is detected in the fastest and slowest regions, related to lateral temperature variations, of several global seismic tomography models.
- Grace E. Shephard
- , Christine Houser
- & Renata M. Wentzcovitch
-
Article
| Open Access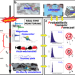 Probabilistic tsunami forecasting for early warning
Probabilistic tsunami forecasting for early warning
Probabilistic tsunami forecasting (PTF) defines an approach to tsunami early warning based on uncertainty quantification, enhancing forecast accuracy and enabling rational decision making. PTF is here developed for near-source tsunami warning, and tested in hindcasting mode over a wide range of past earthquakes.
- J. Selva
- , S. Lorito
- & A. Amato
-
Article
| Open Access Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano
Episodic transport of discrete magma batches beneath Aso volcano
Repetitive shallow resonances provide a pathway to unravelling episodic magma transport deep in the magma plumbing system. Episodic deformation of ~1 nanoradian over ~100 s beneath Aso volcano potentially provides a link between long-term volcanic output and short-term eruption dynamics.
- Jieming Niu
- & Teh-Ru Alex Song
-
Article
| Open Access The slow self-arresting nature of low-frequency earthquakes
The slow self-arresting nature of low-frequency earthquakes
Low-frequency earthquakes are a series of small earthquakes with lower dominant frequencies than ordinary earthquakes. By comparing the simulated earthquakes with the real data, we find that low-frequency earthquakes represent an earthquake rupture process that arrests spontaneously.
- Xueting Wei
- , Jiankuan Xu
- & Xiaofei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Seismicity at the Castor gas reservoir driven by pore pressure diffusion and asperities loading
Seismicity at the Castor gas reservoir driven by pore pressure diffusion and asperities loading
The 2013 Castor seismic sequence, offshore Spain, is a rare example of seismicity induced by gas storage operations. Here we show that early seismicity marked the progressive failure of a fault in response to pore pressure diffusion, while later larger earthquakes resulted by the failure of loaded asperities.
- Simone Cesca
- , Daniel Stich
- & William L. Ellsworth
-
Comment
| Open Access Machine learning and earthquake forecasting—next steps
Machine learning and earthquake forecasting—next steps
A new generation of earthquake catalogs developed through supervised machine-learning illuminates earthquake activity with unprecedented detail. Application of unsupervised machine learning to analyze the more complete expression of seismicity in these catalogs may be the fastest route to improving earthquake forecasting.
- Gregory C. Beroza
- , Margarita Segou
- & S. Mostafa Mousavi
-
Article
| Open Access Two end-member earthquake preparations illuminated by foreshock activity on a meter-scale laboratory fault
Two end-member earthquake preparations illuminated by foreshock activity on a meter-scale laboratory fault
By tuning fault surface heterogeneity, the authors report earthquake preparation processes respectively driven by preslip and cascade-up on a meter-scale laboratory fault. The findings suggest that foreshock activity can be useful for predicting when and how the impending mainshock will occur.
- Futoshi Yamashita
- , Eiichi Fukuyama
- & Shigeru Takizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Subduction history of the Caribbean from upper-mantle seismic imaging and plate reconstruction
Subduction history of the Caribbean from upper-mantle seismic imaging and plate reconstruction
Seismic imaging of subducted plates offers a way to improve plate tectonic reconstructions. Here, Braszus et al. use new ocean-bottom seismometer data from the Lesser Antilles to locate subducted spreading centres and faults thus providing a new understanding of the evolution of the Caribbean plate.
- Benedikt Braszus
- , Saskia Goes
- & Marjorie Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow slow earthquakes to decipher future catastrophic earthquakes in the Guerrero seismic gap
Shallow slow earthquakes to decipher future catastrophic earthquakes in the Guerrero seismic gap
New offshore observations in the Guerrero seismic gap discovered shallow slow earthquakes, which suggest that a portion of the plate interface undergoes stable slip. This may explain the long return period of large earthquakes and why have previous large earthquakes not propagated into the gap.
- R. Plata-Martinez
- , S. Ide
- & Y. Ito
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean-bottom and surface seismometers reveal continuous glacial tremor and slip
Ocean-bottom and surface seismometers reveal continuous glacial tremor and slip
Anomalously slow earthquakes play a critical role in the earthquake cycle and fault sliding. Here, the authors detect continuous seismic radiation from a glacier sliding over its bed and show persistent coastal shaking to represent an addition to the family of slow earthquakes.
- Evgeny A. Podolskiy
- , Yoshio Murai
- & Shin Sugiyama
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation interactions in olivine control postseismic creep of the upper mantle
Dislocation interactions in olivine control postseismic creep of the upper mantle
Models of the viscosity evolution of mantle rocks are central to analyses of postseismic deformation but constraints on underlying physical processes are lacking. Here, the authors present measurements of microscale stress heterogeneity in olivine suggesting that long-range dislocation interactions contribute to viscosity evolution.
- David Wallis
- , Lars N. Hansen
- & Ricardo A. Lebensohn
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional singularities and energy balance in frictional rupture
Unconventional singularities and energy balance in frictional rupture
Ordinary cracks in bulk materials feature square root singular deformation fields near their edge. Here, the authors show that rupture fronts propagating along frictional interfaces, while resembling ordinary cracks in some respects, feature edge sigularity that differs from the conventional square root one.
- Efim A. Brener
- & Eran Bouchbinder
-
Article
| Open Access Segregated oceanic crust trapped at the bottom mantle transition zone revealed from ambient noise interferometry
Segregated oceanic crust trapped at the bottom mantle transition zone revealed from ambient noise interferometry
By combining ambient noise interferometry with mineral physics modeling, this work sheds new light on mantle transition zone physics. Their findings provide new evidence of segregated oceanic crust subducted and trapped within the mantle transition zone, implying complex mantle circulation modes.
- Jikun Feng
- , Huajian Yao
- & Zhu Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Fluid pressurisation and earthquake propagation in the Hikurangi subduction zone
Fluid pressurisation and earthquake propagation in the Hikurangi subduction zone
Laboratory experiments reproducing earthquake slip in non cohesive fault rocks under fluid pressurised conditions are challenging. Thanks to these experiments, the authors show that earthquake slip occurring in tsunamigenic subduction zone faults is controlled by dilatancy and pressurisation processes.
- S. Aretusini
- , F. Meneghini
- & G. Di Toro
-
Article
| Open Access How deep ocean-land coupling controls the generation of secondary microseism Love waves
How deep ocean-land coupling controls the generation of secondary microseism Love waves
The authors here study the origin of seismic Love waves induced by ocean waves. The study finds Love waves to originate along steep bathymetry and underlying geological interfaces, particularly sedimentary basins, yielding spatio-temporal information about ocean-land coupling in deep water.
- Florian Le Pape
- , David Craig
- & Christopher J. Bean
-
Article
| Open Access Early forecasting of tsunami inundation from tsunami and geodetic observation data with convolutional neural networks
Early forecasting of tsunami inundation from tsunami and geodetic observation data with convolutional neural networks
Rapid and accurate hazard prediction is important for prompt evacuation and casualty reduction during natural disasters. Here, the authors present an AI-enabled tsunami forecasting approach, which provided rapid and accurate early warnings.
- Fumiyasu Makinoshima
- , Yusuke Oishi
- & Fumihiko Imamura
-
Article
| Open Access Short-term interaction between silent and devastating earthquakes in Mexico
Short-term interaction between silent and devastating earthquakes in Mexico
This study shows how seismic and aseismic events are related in Mexico between 2017 and 2019. Based on a series of observations and models, the study suggests that the Mw 8.2 intraslab earthquake of 8 September 2017 severely altered the mechanical properties of the plate interface, facilitating the interaction between the events and disrupting the slow slip cycles at a regional scale.
- V. M. Cruz-Atienza
- , J. Tago
- & E. Kazachkina
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-phase seismic source imprint of tropical cyclones
Multi-phase seismic source imprint of tropical cyclones
The authors locate the maximum seismic energy imprint and lateral extent of the seismic sources generated by Typhoon Ioke. Based on this data set, they present a new tool to shed light on the generation mechanism of secondary microseisms body waves.
- Lise Retailleau
- & Lucia Gualtieri
-
Article
| Open Access Fault zone heterogeneities explain depth-dependent pattern and evolution of slow earthquakes in Cascadia
Fault zone heterogeneities explain depth-dependent pattern and evolution of slow earthquakes in Cascadia
Here, the authors combine the geological and seismological constraints of the Cascadia Subduction Zone and develop a 3D rate and state friction model. By considering depth-dependent variations of differential pore pressure following a simple linear profile, the model reproduces the full spectrum of the observed ETS complexity.
- Yingdi Luo
- & Zhen Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of large low shear velocity provinces through the decomposition of oxidized mantle
Formation of large low shear velocity provinces through the decomposition of oxidized mantle
Dense Fe3+-rich bridgmanite can explain the seismic features of Large Low Shear Velocity Provinces, as it can form large-scale thermochemical piles in the deep mantle that remain stable throughout Earth’s history.
- Wenzhong Wang
- , Jiachao Liu
- & Zhongqing Wu
-
Article
| Open Access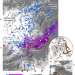 The Hindu Kush slab break-off as revealed by deep structure and crustal deformation
The Hindu Kush slab break-off as revealed by deep structure and crustal deformation
Here, the authors document active slab break-off and the crustal response during continental collision under the Hindu Kush, a rarely observed process since it happens over geologically short time spans.
- Sofia-Katerina Kufner
- , Najibullah Kakar
- & Bernd Schurr
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time determination of earthquake focal mechanism via deep learning
Real-time determination of earthquake focal mechanism via deep learning
The authors here present a deep learning method to determine the source focal mechanism of earthquakes in realtime. They trained their network with approximately 800k synthetic samples and managed to successfully estimate the focal mechanism of four 2019 Ridgecrest earthquakes with magnitudes larger than Mw 5.4.
- Wenhuan Kuang
- , Congcong Yuan
- & Jie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access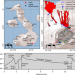 Caldera resurgence during the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra volcano, Galápagos Islands
Caldera resurgence during the 2018 eruption of Sierra Negra volcano, Galápagos Islands
The authors here present geodetic and seismic data for a complete eruptive cycle (2005-2018) for Sierra Negra volcano, Galapagos Island. The data shows the largest pre-eruptive inflation (6.5 m) and rates of seismicity ever observed before a basaltic eruption and provides a rare illustration of caldera resurgence mechanisms.
- Andrew F. Bell
- , Peter C. La Femina
- & Michael J. Stock
-
Article
| Open Access Near-surface softening and healing in eastern Honshu associated with the 2011 magnitude-9 Tohoku-Oki Earthquake
Near-surface softening and healing in eastern Honshu associated with the 2011 magnitude-9 Tohoku-Oki Earthquake
The authors here investigate the stiffness reduction of solid geomaterials during earthquakes via combining field, experimental and numerical data. The study shows multiple metastable contacts at small surface separations below a few diameters of a water molecule due to the oscillatory hydration interaction.
- Su-Yang Wang
- , Hai-Yang Zhuang
- & Yu Miao

 Machine learning-based tsunami inundation prediction derived from offshore observations
Machine learning-based tsunami inundation prediction derived from offshore observations