Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ noncovalent interaction of ammonium ion enabled C–H bond functionalization of polyethylene glycols
In-situ noncovalent interaction of ammonium ion enabled C–H bond functionalization of polyethylene glycols
The noncovalent interaction of ammonium ion with multidentate oxygen-based host serving as a key reacting center in catalytic reactions is rare. In this work, the authors report a noncovalent interaction of ammonium ion enabled reactivity enhancement process, achieving the C–H functionalization of polyethylene glycols with acrylates.
- Zongnan Zhang
- , Xueli Lv
- & Rong Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access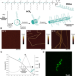 Heat-activated growth of metastable and length-defined DNA fibers expands traditional polymer assembly
Heat-activated growth of metastable and length-defined DNA fibers expands traditional polymer assembly
The combination of dynamic, energy driven folding and growth with structural stiffness and length control is difficult to achieve in synthetic polymer self-assembly. Here the authors show that highly charged, monodisperse DNA oligomers assemble via seeded growth into length-controlled supramolecular fibers during heating.
- Michael D. Dore
- , Muhammad Ghufran Rafique
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
Article
| Open Access Active droplets through enzyme-free, dynamic phosphorylation
Active droplets through enzyme-free, dynamic phosphorylation
Despite the importance of dynamic phosphorylation in biology, enzyme-free, synthetic systems that use dynamic phosphorylation to regulate supramolecular processes are unexplored. Here, the authors report an enzyme-free chemical reaction cycle that can dynamically phosphorylate amino acids and peptides using simple phosphorylating agents and regulate supramolecular functions.
- Simone M. Poprawa
- , Michele Stasi
- & Job Boekhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable supramolecular helices for asymmetric stereodivergent catalysis
Switchable supramolecular helices for asymmetric stereodivergent catalysis
Controlling multiple stereogenic centers in a single molecular scaffold represents a challenge for current switchable asymmetric catalysts. Here, the authors achieve asymmetric stereodivergency by means of a switchable supramolecular helical catalyst allowing all stereoisomers to be obtained with high and similar enantioselectivities.
- Ran Chen
- , Ahmad Hammoud
- & Matthieu Raynal
-
Article
| Open Access Bulk transparent supramolecular glass enabled by host–guest molecular recognition
Bulk transparent supramolecular glass enabled by host–guest molecular recognition
Strategies to produce supramolecular glass and the study of its intrinsic structure and mechanical properties remains largely unexplored. Here, the authors prepare a supramolecular glass via the host–guest recognition between methyl-β-cyclodextrin and para-hydroxybenzoic acid with recyclability, compatibility, and thermal processability.
- Changyong Cai
- , Shuanggen Wu
- & Shengyi Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Noncovalent synthesis of homo and hetero-architectures of supramolecular polymers via secondary nucleation
Noncovalent synthesis of homo and hetero-architectures of supramolecular polymers via secondary nucleation
Synthesis of supramolecular polymers with controlled architecture is desirable but challenging. Here, the authors use a secondary nucleation event to prepare a range of supramolecular polymer architectures.
- Srinu Kotha
- , Rahul Sahu
- & Kotagiri Venkata Rao
-
Article
| Open Access In situ enzymatic control of colloidal phoresis and catalysis through hydrolysis of ATP
In situ enzymatic control of colloidal phoresis and catalysis through hydrolysis of ATP
The design of synthetic systems that can sense chemical gradients and respond with directional motility and chemical activity is of interest. Here, the authors realize and control such behaviors in a synthetic system by tailoring multivalent interactions of adenosine nucleotides with catalytic microbeads.
- Ekta Shandilya
- , Bhargav Rallabandi
- & Subhabrata Maiti
-
Article
| Open Access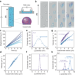 Probing the surface charge of condensates using microelectrophoresis
Probing the surface charge of condensates using microelectrophoresis
The surface charge and ζ-potential of biomolecular condensates is key to their interactions with membranes and proteins. Here, the authors developed a method to determine the ζ-potential of condensates using microelectrophoresis and single-droplet tracking.
- Merlijn H. I. van Haren
- , Brent S. Visser
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting thermoelectric performance of single-walled carbon nanotubes-based films through rational triple treatments
Boosting thermoelectric performance of single-walled carbon nanotubes-based films through rational triple treatments
Authors introduce triple treatments to advance flexible single-walled carbon nanotube films, achieving a power factor of 20.29 µW cm−1 K−2. High structural stability and flexibility enable the fabrication of a high-power-density flexible device.
- Yuan-Meng Liu
- , Xiao-Lei Shi
- & Zhi-Gang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Assembly of short amphiphilic peptoids into nanohelices with controllable supramolecular chirality
Assembly of short amphiphilic peptoids into nanohelices with controllable supramolecular chirality
Helical protein assemblies are an important biological structure, but are challenging to mimic with synthetic materials. Here, the authors report the use of peptoids to form nanohelix structures with controllable supramolecular chirality.
- Renyu Zheng
- , Mingfei Zhao
- & Chun-Long Chen
-
Article
| Open Access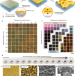 Kinetically controlled metal-elastomer nanophases for environmentally resilient stretchable electronics
Kinetically controlled metal-elastomer nanophases for environmentally resilient stretchable electronics
Metal-elastomer nanophases are critical for stretchable electronics but face mixing challenges. This study introduces a kinetic method for precise mixing, yielding gyrified nanophases with improved durability and strain-invariant conductivity, which holds promise for resilient stretchable devices.
- Soosang Chae
- , Won Jin Choi
- & Tae Il Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Convoluted micellar morphological transitions driven by tailorable mesogenic ordering effect from discotic mesogen-containing block copolymer
Convoluted micellar morphological transitions driven by tailorable mesogenic ordering effect from discotic mesogen-containing block copolymer
Assembly of block copolymers can be controlled to give varying morphologies and functionalities, but there are still aspects of the process that are not well understood. Here, the authors report convoluted self-assembly behaviours of block copolymers with discotic liquid crystalline moieties.
- Huanzhi Yang
- , Yunjun Luo
- & Xiaoyu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial kagome lattices of Shockley surface states patterned by halogen hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks
Artificial kagome lattices of Shockley surface states patterned by halogen hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks
By utilizing the templating effect of a halogen hydrogen-bonded organic framework, the authors show that the Shockley surface states of coinage metals can be patterned into artificial kagome lattices with high tunability.
- Ruoting Yin
- , Xiang Zhu
- & Bing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access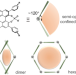 Chiral BINOL-phosphate assembled single hexagonal nanotube in aqueous solution for confined rearrangement acceleration
Chiral BINOL-phosphate assembled single hexagonal nanotube in aqueous solution for confined rearrangement acceleration
Supramolecular confined catalysis aims to mimic the active pocket of an enzyme to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of catalytic reactions. Here, the authors describe the formation of chiral nanotubes stable in aqueous solution employing a chiral BINOL-phosphate which can accelerate the 3-aza-Cope rearrangement by a nanotubular interior confinement effect.
- Kang Li
- , Wei-Min Qin
- & Yue-Peng Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular polynuclear clusters sustained cubic hydrogen bonded frameworks with octahedral cages for reversible photochromism
Supramolecular polynuclear clusters sustained cubic hydrogen bonded frameworks with octahedral cages for reversible photochromism
The development of supramolecular porous crystalline frameworks with architectures from secondary building units remains challenging. Here, the authors report ammonium node-assembled clusters as supramolecular secondary building units to sustain a body centered cubic hydrogenbonded framework with octahedral cages for haloform encapsulation and reversible photochromism.
- Xiaojun Ding
- , Jing Chen
- & Gang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Developing a machine learning model for accurate nucleoside hydrogels prediction based on descriptors
Developing a machine learning model for accurate nucleoside hydrogels prediction based on descriptors
Supramolecular nucleoside-based hydrogels have potential in biomedical applications, but there is no model to predict what nucleoside derivatives will form hydrogels. Here, the authors report a machine learning model to predict the ability of nucleoside derivatives to form hydrogels.
- Weiqi Li
- , Yinghui Wen
- & Hang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Structurally diverse macrocycle co-crystals for solid-state luminescence modulation
Structurally diverse macrocycle co-crystals for solid-state luminescence modulation
Organic co-crystals are useful in the fabrication of functional materials, but it is challenging to achieve structural diversity of co-crystals. Here, the authors report nine sets of macrocycle cocrystals with diverse structures and stoichiometric ratios giving different luminescence properties.
- Bin Li
- , Lingling Liu
- & Chunju Li
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular near-infrared triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion with eigen oxygen immunity
Molecular near-infrared triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion with eigen oxygen immunity
Molecular triplet-triplet upconversion is useful in a wide range of applications, but is limited by significant oxygen quenching. Here the authors report the combination of sensitiser and annihilator that is stable in aerated environments, and suitable for in vivo sensing.
- Xinyu Wang
- , Fangwei Ding
- & Guanying Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular T-pentomino for separating BTEX hydrocarbons
A molecular T-pentomino for separating BTEX hydrocarbons
Globally important BTEX hydrocarbons are separated using a T-shaped host with the shape and crystal tiling characteristics of a pentomino. A strategy based on designing and applying crystalline molecular ominos to perform separations of hydrocarbons and other environmentally-relevant compounds is outlined.
- Christopher J. Hartwick
- , Eric W. Reinheimer
- & Leonard R. MacGillivray
-
Article
| Open Access Abnormal thermally-stimulated dynamic organic phosphorescence
Abnormal thermally-stimulated dynamic organic phosphorescence
In thermally stimulated phosphorescent materials a thermal stimulus inevitably quenches the emission due to intensive non radiative transition. Here, the authors report an abnormal thermally stimulated phosphorescence behavior in organic phosphors and show enhancement of phosphorescence and change of the emission color upon temperature increase.
- He Wang
- , Huili Ma
- & Zhongfu An
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic control of DNA condensation
Dynamic control of DNA condensation
Artificial biomolecular condensates are valuable tools to study the design principles of phase separation. Here, the authors demonstrate and characterize a model system of artificial DNA condensates whose kinetic formation and dissolution depends on DNA inputs that activate or deactivate the phase separating DNA subunits.
- Siddharth Agarwal
- , Dino Osmanovic
- & Elisa Franco
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-catenation between position-isomeric metallacages
Cross-catenation between position-isomeric metallacages
The study of cross-catenated metallacages could provide facile insights into achieving more precise control over low-symmetry/high-complexity hierarchical assembly systems but is currently lacking. Here, the authors report a cross-catenane formed between two position-isomeric Pt(II) metallacages in the solid state.
- Yiliang Wang
- , Taotao Liu
- & Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Separation of benzene and toluene associated with vapochromic behaviors by hybrid[4]arene-based co-crystals
Separation of benzene and toluene associated with vapochromic behaviors by hybrid[4]arene-based co-crystals
Cocrystal engineering combined with macrocycle chemistry has allowed the development of materials with vapochromic characteristics. Here, the authors report the development of a macrocycle cocrystal for the separation of trace solvents.
- Jingyu Chen
- , Wenjie Zhang
- & Jiong Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Water-stable boroxine structure with dynamic covalent bonds
Water-stable boroxine structure with dynamic covalent bonds
Despite the structural significance of boroxines in different classes of materials, their applicability in aqueous media is limited by their hydrolytic instability. Here, the authors discovered a water-stable boroxine structure with excellent pH stability and water-compatible dynamic covalent bonds.
- Xiaopei Li
- , Yongjie Zhang
- & Guangyan Qing
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable droplet networks
Reconfigurable droplet networks
Earlier methods for droplet network stabilization require extremely precise control and manipulation with considerable energy consumption, making them difficult to implement. Here, the authors present 2D interfacial networks, formed by irreversible interfacial interactions between polymer chains dissolved in one liquid and ligands dissolved in a second immiscible liquid at random points along the chains.
- Shuyi Sun
- , Shuailong Li
- & Shaowei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Multifunctional composite hydrogels are promising candidates to develop smart and recyclable electronic components. Here, the authors report a reversible on-demand liquefication and solidification conductive gel formed by the self-assembly of photoresponsive host-guest complexes and MXene nanosheets which can be integrated into traditional solid-state circuits.
- Yu-Liang Lin
- , Sheng Zheng
- & Jiun-Tai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired polymeric supramolecular columns as efficient yet controllable artificial light-harvesting platform
Bioinspired polymeric supramolecular columns as efficient yet controllable artificial light-harvesting platform
The formation of artificial light-harvesting systems with high donor/acceptor ratios for efficient energy transfer remains challenging. Here, the authors describe a polymeric supramolecular column-based light-harvesting system by modular columnar assembly of donor/acceptor chromophores, enabling superior light-harvesting efficiency and dynamic full-color tunable emission.
- Bin Mu
- , Xiangnan Hao
- & Wei Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering supramolecular chirality codes for the design of tunable biomaterials
Uncovering supramolecular chirality codes for the design of tunable biomaterials
Assembly of amyloids is important in neurodegenerative diseases, but there is limited understanding of how supramolecular chirality is controlled. Here, the authors report the design of peptide derivatives that allow chirality inversion at biologically relevant temperatures.
- Stephen J. Klawa
- , Michelle Lee
- & Ronit Freeman
-
Article
| Open Access Self-similar chiral organic molecular cages
Self-similar chiral organic molecular cages
To enhance the utility of organic molecular cages (OMCs), the evolution of OMCs into higher-level chiral OMCs with self-similar superstructures is meaningful yet challenging. Here, the authors report a pair of higher-level 3D tri-bladed chiral helical molecular cages, displaying self-similarity in a discrete self-similar superstructure at different levels.
- Zhen Wang
- , Qing-Pu Zhang
- & Chuan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access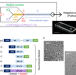 Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Native spider silk has desirable mechanical properties, but these are challenging to replicate in an artificial material. Here, the authors report the use of a microfluidic system to create continuous fibers based on recombinant spidroin.
- Jianming Chen
- , Arata Tsuchida
- & Keiji Numata
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled dendrimer polyamide nanofilms with enhanced effective pore area for ion separation
Self-assembled dendrimer polyamide nanofilms with enhanced effective pore area for ion separation
Membrane technology using well-defined pore structure enables high ion purity and recovery but achieving uniform pore structure and effective pore area is challenging. Here the authors introduce dendrimers that self-assemble, facilitating the formation of polyamide nanofilms with well-defined effective pore ranges and uniform pore structures.
- Bingbing Yuan
- , Yuhang Zhang
- & Q. Jason Niu
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Electro-active ionic soft actuators generally present slow responses and poor durability when are applied as artificial muscles. Here, the authors describe a polyelectrolyte membrane based on the assembly of Nafion molecules into micelles with efficient ionic conducting pathways for electro-ionic soft actuators and soft robotics with fast responses and long durability.
- Van Hiep Nguyen
- , Saewoong Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Multistate structures in a hydrogen-bonded polycatenation non-covalent organic framework with diverse resistive switching behaviors
Multistate structures in a hydrogen-bonded polycatenation non-covalent organic framework with diverse resistive switching behaviors
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks as stimuli responsive multistate structures show potential in the field of resistive switching. Here, the authors report a 0D+1D hydrogen-bonded polycatenation non-covalent organic framework showing reversible transformation of multistate-structures triggered by electrical field and temperature, enabling reversibly switchable resistive random-access memory and write-once-read-many-times memory behavior.
- Shimin Chen
- , Yan Ju
- & Zhangjing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access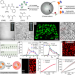 Dipeptide coacervates as artificial membraneless organelles for bioorthogonal catalysis
Dipeptide coacervates as artificial membraneless organelles for bioorthogonal catalysis
Coacervate droplets have potential as components for cell-like materials, but are limited by complex molecular structure and control of the internal microenvironment. Here, the authors report stable dipeptide-based coacervates with a microenvironment for the encapsulation of hydrophobic species.
- Shoupeng Cao
- , Tsvetomir Ivanov
- & Lucas Caire da Silva
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Assembly is an interesting strategy to build chiral hierarchies with premade properties and functionalities. Here, the authors present assembled chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks with dynamical chiroptical activities and employ them as powerful and recoverable platforms for enantioselective recognition of chiral aliphatic substrates.
- Jun Guo
- , Yulong Duan
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Stoichiometry validation of supramolecular complexes with a hydrocarbon cage host by van ’t Hoff analyses
Stoichiometry validation of supramolecular complexes with a hydrocarbon cage host by van ’t Hoff analyses
“van ’t Hoff, the first Nobel laureate, invented a double-arrow formalism to define equilibria in 1884. Here, the authors apply his accompanying method, the van ’t Hoff plot, to a modern problem to decide the stoichiometry of supramolecular complexes.”
- Toshiya M. Fukunaga
- , Yuzuka Onaka
- & Hiroyuki Isobe
-
Article
| Open Access Janus particles with tunable patch symmetry and their assembly into chiral colloidal clusters
Janus particles with tunable patch symmetry and their assembly into chiral colloidal clusters
Janus particles commonly exhibit a high-symmetry patch, constraining the range of possible assemblies. Here, the authors devise a synthetic approach to fine-tune the patch symmetry in Janus particles and showcase the assembly of these particles into chiral colloidal clusters.
- Tianran Zhang
- , Dengping Lyu
- & Yufeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Selective amide bond formation in redox-active coacervate protocells
Selective amide bond formation in redox-active coacervate protocells
Coacervate droplets are promising protocells that sequester nutrients, but how new peptides could be synthesized inside coacervates remains a mystery. Here, the authors develop redox-active coacervates that facilitate the formation of new peptide bonds.
- Jiahua Wang
- , Manzar Abbas
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly of clusters and copolymers towards programmed mesoporous metal oxides
Solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly of clusters and copolymers towards programmed mesoporous metal oxides
A solvent-pair surfactants enabled assembly method is developed to achieve a general and programmable synthesis of mesoporous metal oxides via the association of POMs with block copolymers through indirect interaction.
- Wenhe Xie
- , Yuan Ren
- & Yonghui Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Site-selective chemical reactions by on-water surface sequential assembly
Site-selective chemical reactions by on-water surface sequential assembly
Controlling site-selectivity and reactivity in chemical reactions continues to be a key challenge in modern synthetic chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate the assembly of amino-substituted porphyrins on a water surface into J-aggregate structures in the presence of charged surfactants.
- Anupam Prasoon
- , Xiaoqing Yu
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Thermally-induced atropisomerism promotes metal-organic cage construction
Thermally-induced atropisomerism promotes metal-organic cage construction
While heat modification is ubiquitous in biologic systems, it remains a significant challenge in artificial systems. Here the authors demonstrate thermal regulation of conversion between different rigid macrocycle atropisomers and related self-assemblies.
- Jiaqi Liang
- , Shuai Lu
- & Han-Yuan Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-Kasha triplet energy transfer and excitation wavelength dependent persistent luminescence from host-guest doping systems
Anti-Kasha triplet energy transfer and excitation wavelength dependent persistent luminescence from host-guest doping systems
Anti-Kasha processes have potential in organic luminogens, but design of materials with these characteristics is challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a host-guest system with anti-Kasha behaviour and triplet energy transfer.
- Weiwei Xie
- , Wenbin Huang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access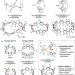 A dodecamethoxy[6]cycloparaphenylene consisting entirely of hydroquinone ethers: unveiling in-plane aromaticity through a rotaxane structure
A dodecamethoxy[6]cycloparaphenylene consisting entirely of hydroquinone ethers: unveiling in-plane aromaticity through a rotaxane structure
“Cycloparaphenylenes consisting of are cyclic π-conjugated structures presetting interesting physical properties upon functionalization. However, the ring strain and steric hindrance of the substituents hamper the functionalization of small sized cycloparaphenylenes. Here, the authors describe a [6]cycloparaphenylene with twelve methoxy units employed to form a rotaxane with in-plane aromaticity upon oxidation.”
- Naoki Narita
- , Yusuke Kurita
- & Yoshitaka Tsuchido
-
Article
| Open Access Electrosynthesis of buckyballs with fused-ring systems from PCBM and its analogue
Electrosynthesis of buckyballs with fused-ring systems from PCBM and its analogue
[6,6]-Phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM), a star molecule in the fullerene field, has found wide applications in materials science. Here, the authors demonstrate the synthesis of buckyballs with fused-ring systems via electrosynthesis through radical α-C−H functionalization of the side-chain ester for both PCBM and its analogue.
- Wei-Feng Wang
- , Kai-Qing Liu
- & Guan-Wu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition
Cooperative supramolecular polymerization of styrylpyrenes for color-dependent circularly polarized luminescence and photocycloaddition
Strategies to construct circularly polarized luminescence (CPL)-active materials with color modulation and handedness of CPL are desirable for the synthesis of chiral photo-responsive devices. Here the authors develop a CPL system based on styrylpyrenes. Benefiting from CH-π interactions between chromophores, the styrylpyrene aggregates show color-dependent CPL property and photo-responsive behavior.
- Wei Yuan
- , Letian Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A colloidal viewpoint on the sausage catastrophe and the finite sphere packing problem
A colloidal viewpoint on the sausage catastrophe and the finite sphere packing problem
Packing a finite number of spheres in a compact cluster does not always result in the densest packing. Here, the authors provide a physical realization of the finite sphere packing problem by enclosing colloids in a flaccid lipid vesicle and mapping out a state diagram that displays linear, planar, and cluster conformations of spheres, as well as bistable states that alternate between cluster-plate and plate-linear conformations.
- Susana Marín-Aguilar
- , Fabrizio Camerin
- & Marjolein Dijkstra
-
Article
| Open Access Tough soldering for stretchable electronics by small-molecule modulated interfacial assemblies
Tough soldering for stretchable electronics by small-molecule modulated interfacial assemblies
“The interface mismatch of soft substrates and rigid silicon-based microelectronics frequently causes failures of integrated circuits. Here, the authors develop a stretchable solder based on liquid metal-polymer composites which enables seamless integration of electronic components with soft substrates, showcasing high conductivity and stretchability”.
- Liqing Ai
- , Weikang Lin
- & Xi Yao
-
Article
| Open Access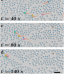 Environmental memory boosts group formation of clueless individuals
Environmental memory boosts group formation of clueless individuals
Indirect coordination among individuals through the environment typically requires some basic levels of communication and information processing. Dias et al. introduce a coordination mechanism that emerges in a population of clueless individuals, facilitated by environmental memory, culminating in group formation.
- Cristóvão S. Dias
- , Manish Trivedi
- & Giorgio Volpe
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting nucleic acid phase transitions as a mechanism of action for antimicrobial peptides
Targeting nucleic acid phase transitions as a mechanism of action for antimicrobial peptides
In this work the authors describe antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)-driven phase transitions of intracellular nucleic acids, whereby AMPs induce compaction and phase separation of nucleic acids, resulting in their sequestration and eventual cell death.
- Tomas Sneideris
- , Nadia A. Erkamp
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles

 Emergence of a short peptide based reductase via activation of the model hydride rich cofactor
Emergence of a short peptide based reductase via activation of the model hydride rich cofactor