Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Direct space–time manipulation mechanism for spatio-temporal coupling of ultrafast light field
Direct space–time manipulation mechanism for spatio-temporal coupling of ultrafast light field
Here the authors propose a mechanism for direct space-time manipulation of ultrafast light field and experimentally demonstrate the generation of a spatiotemporally coupling light spring with a broad topological charge bandwidth.
- Qinggang Lin
- , Fu Feng
- & Xiaocong Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient octave-spanning long-wavelength infrared generation with a 74% quantum efficiency in a χ(2) waveguide
Highly efficient octave-spanning long-wavelength infrared generation with a 74% quantum efficiency in a χ(2) waveguide
A χ(2) nonlinear micro-waveguide platform is demonstrated based on the birefringence phase matching for simple and efficient long-wavelength infrared generation, which could trigger new frontiers of MIR integrated nonlinear photonics.
- Bo Hu
- , Xuemei Yang
- & Houkun Liang
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed scanless entire bandwidth mid-infrared chemical imaging
High-speed scanless entire bandwidth mid-infrared chemical imaging
The authors present a fast mid-infrared hyperspectral chemical imaging technique that uses chirped pulse upconversion of sub-cycle pulses at the image plane, with lateral resolution of 15 µm and an adjustable field of view and large spectral range. They demonstrate identification and mapping different components in a microfluidic device, plant cell, and mouse embryo.
- Yue Zhao
- , Shota Kusama
- & Takao Fuji
-
Article
| Open Access 400nm ultra-broadband gratings for near-single-cycle 100 Petawatt lasers
400nm ultra-broadband gratings for near-single-cycle 100 Petawatt lasers
Gratings are used for pulse compression and stretching in chirped pulse amplification (CPA) or optical parametric CPA methods. Here the authors demonstrate ultra-broadband gold gratings that can compress single-cycle pulses with powers around 100 petawatts.
- Yuxing Han
- , Zhaoyang Li
- & Jianda Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental realisations of the fractional Schrödinger equation in the temporal domain
Experimental realisations of the fractional Schrödinger equation in the temporal domain
Studies on the fractional Schrödinger equation (FSE) remain mostly theoretical, due to the lack of materials supporting fractional dispersion or diffraction. Here, the authors indirectly realized the FSE using two programmable holograms acting as an optical Lévy waveguide.
- Shilong Liu
- , Yingwen Zhang
- & Ebrahim Karimi
-
Article
| Open Access Topological polarization singular lasing with highly efficient radiation channel
Topological polarization singular lasing with highly efficient radiation channel
Here the authors develop topological polarization singular lasers that feature paired radiation channels carrying distinct topological properties which leads to single mode lasing with high external quantum efficiency.
- Yun-Gang Sang
- , Jing-Yu Lu
- & Ren-Min Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-comb thin-disk oscillator
Dual-comb thin-disk oscillator
Achieving high output powers in dual-comb sources is important for possible applications like deep UV high resolution spectroscopy. Here the authors demonstrate a fully passive scheme of generating a set of high-power dual-combs from a thin-disc gain medium.
- Kilian Fritsch
- , Tobias Hofer
- & Oleg Pronin
-
Article
| Open Access Transient quantum beatings of trions in hybrid organic tri-iodine perovskite single crystal
Transient quantum beatings of trions in hybrid organic tri-iodine perovskite single crystal
Understanding photo-physics giving rise to quantum beating oscillations in hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites aids their applications in spintronics and quantum information science. Here, authors demonstrate that quantum beatings observed in single crystal perovskite at cryogenic temperatures are originating from positive and negative trions.
- Uyen N. Huynh
- , Ye Liu
- & Z. Valy Vardeny
-
Article
| Open Access Strong-field coherent control of isolated attosecond pulse generation
Strong-field coherent control of isolated attosecond pulse generation
Attosecond pulse generation needs improvements both in terms of tunability and photon flux for next level attosecond experiments. Here the authors show how to control the HHG emission and its spectral-temporal characteristics by driving the IAP generation with synthesized sub-cycle optical pulses.
- Yudong Yang
- , Roland E. Mainz
- & Franz X. Kärtner
-
Article
| Open Access Mode-locked short pulses from an 8 μm wavelength semiconductor laser
Mode-locked short pulses from an 8 μm wavelength semiconductor laser
Producing pulses in the mid-IR often requires bulky sources and has been inaccessible with compact and versatile quantum cascade lasers (QCLs). Here, the authors demonstrate actively mode-locked, mid-IR QCL operation at room temperature.
- Johannes Hillbrand
- , Nikola Opačak
- & Benedikt Schwarz
-
Article
| Open Access Optical parametric amplification of sub-cycle shortwave infrared pulses
Optical parametric amplification of sub-cycle shortwave infrared pulses
Short-wavelength infrared pulses are important for applications in strong field physics and nonlinear optics. Here the authors show multi-stage optical parametric amplification of sub-cycle SWIR pulses with carrier-envelope phase stability.
- Yu-Chieh Lin
- , Yasuo Nabekawa
- & Katsumi Midorikawa
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent master equation for laser modelocking
Coherent master equation for laser modelocking
Modelocked lasers are typically modeled using the Haus master equation which, albeit powerful, provides only a limited description in certain parameter regimes. The authors introduce another master equation formalism to describe laser modelocking that accounts for coherent effects and overcomes these limitations.
- Auro M. Perego
- , Bruno Garbin
- & Germán J. de Valcárcel
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of extremely efficient terahertz generation from mid-infrared two-color laser filaments
Observation of extremely efficient terahertz generation from mid-infrared two-color laser filaments
Powerful terahertz pulses are generated during the nonlinear propagation of ultrashort laser pulses in gases. Here, the authors demonstrate efficient sub-cycle THz pulse generation by using two-color midinfrared femtosecond laser filaments in ambient air.
- Anastasios D. Koulouklidis
- , Claudia Gollner
- & Stelios Tzortzakis
-
Article
| Open Access Free-space transfer of comb-rooted optical frequencies over an 18 km open-air link
Free-space transfer of comb-rooted optical frequencies over an 18 km open-air link
Phase-coherent transfer of optical frequencies over long open-air paths is necessary in photonic applications. Here the authors demonstrate the parallel transmission of multiple optical carriers in air up to 18 km using a stable near-infrared frequency comb.
- Hyun Jay Kang
- , Jaewon Yang
- & Seung-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral phase control of interfering chirped pulses for high-energy narrowband terahertz generation
Spectral phase control of interfering chirped pulses for high-energy narrowband terahertz generation
Optical generation of terahertz radiation is needed for many applications, but gaining high efficiency is still a challenge. The authors report a method to overcome dispersion effects in interfering chirp pulses used for THz pulse production by tuning their relative spectral phase, enabling 0.6 mJ of THz energy output.
- Spencer W. Jolly
- , Nicholas H. Matlis
- & Andreas R. Maier
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of picosecond melting and disintegration of metallic nanoparticles
Direct observation of picosecond melting and disintegration of metallic nanoparticles
Laser-matter interaction has been intensively studied in equilibrium states, but irreversible processes in a highly nonequilibrium state at nanoscales remains elusive due to experimental challenges. Here, Ihm et al. image heterogeneous melting of gold nanoparticles with nanometer and picosecond resolution.
- Yungok Ihm
- , Do Hyung Cho
- & Changyong Song
-
Article
| Open Access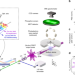 Odd electron wave packets from cycloidal ultrashort laser fields
Odd electron wave packets from cycloidal ultrashort laser fields
Laser fields can be tuned to probe electronic motion in atoms and molecules. Here the authors ionize Na atoms using bichromatic pulses to generate electron wave packets of crescent-shaped and 7-fold rotational symmetry which do not follow the field symmetry but are determined by multiphoton interference.
- S. Kerbstadt
- , K. Eickhoff
- & M. Wollenhaupt
-
Article
| Open Access High-flux ultrafast extreme-ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy at 18.4 MHz pulse repetition rate
High-flux ultrafast extreme-ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy at 18.4 MHz pulse repetition rate
Space charge effects can distort the results of photoelectron spectroscopic measurements, and usually limit the allowable photon flux in an experiment. Here, the authors present an 18.4 MHz repetition rate high harmonic source in the 25–60 eV range, with a large count rate improvement over state-of-the-art attosecond setups under identical space charge conditions.
- T. Saule
- , S. Heinrich
- & I. Pupeza
-
Article
| Open Access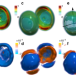 Real-time determination of enantiomeric and isomeric content using photoelectron elliptical dichroism
Real-time determination of enantiomeric and isomeric content using photoelectron elliptical dichroism
The analysis of chiral chemical mixtures is crucial for many applications. Here, the authors perform real-time analysis of samples by ionizing them with elliptically polarized femtosecond laser pulses and detecting the angular distributions of the photoelectrons.
- A. Comby
- , E. Bloch
- & Y. Mairesse
-
Article
| Open Access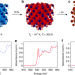 Probing warm dense matter using femtosecond X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a laser-produced betatron source
Probing warm dense matter using femtosecond X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a laser-produced betatron source
Understanding the ultrafast dynamics of materials under extreme conditions is challenging. Here the authors use a femtosecond betatron X-ray source to investigate the solid to dense plasma phase transition in copper using XAS with unprecedented time resolution.
- B. Mahieu
- , N. Jourdain
- & L. Lecherbourg
-
Article
| Open Access Micro-scale fusion in dense relativistic nanowire array plasmas
Micro-scale fusion in dense relativistic nanowire array plasmas
Neutron beams are useful studying fundamental physics problems, fusion process and material properties. Here the authors use intense laser irradiation of deuterated nanowire array targets to create high energy density plasmas capable of efficient generation of ultrafast neutron pulses.
- Alden Curtis
- , Chase Calvi
- & Jorge J. Rocca
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond recorder of the polarization state of light
Attosecond recorder of the polarization state of light
Attosecond pulses are useful in exploring processes involving ultrafast electron motion in atomic and molecular systems. Here the authors discuss a method to characterize the complex time-varying polarization state of broadband attosecond pulses by using asymmetry in photoelectron spectra.
- Álvaro Jiménez-Galán
- , Gopal Dixit
- & Misha Ivanov
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast carrier thermalization in lead iodide perovskite probed with two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy
Ultrafast carrier thermalization in lead iodide perovskite probed with two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy
Carrier-carrier scattering rates determine the fundamental limits of carrier transport and electronic coherence. Using two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy with sub-10 fs resolution, Richter and Branchi et al. extract carrier thermalization times of 10 to 85 fs in hybrid perovskites.
- Johannes M. Richter
- , Federico Branchi
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy mid-infrared sub-cycle pulse synthesis from a parametric amplifier
High-energy mid-infrared sub-cycle pulse synthesis from a parametric amplifier
Stable sub-cycle pulses in the mid-infrared region allow damage-free investigation of electron dynamics in solids. Here, the authors develop a suitable source to this end which is based on an optical parametric amplifier.
- Houkun Liang
- , Peter Krogen
- & Kyung-Han Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Self-amplified photo-induced gap quenching in a correlated electron material
Self-amplified photo-induced gap quenching in a correlated electron material
The non-equilibrium dynamics of correlated electron materials are still poorly understood. Here, the authors use time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy to show that carrier multiplication is important in initial non-equilibrium dynamics of 1T-TiSe2and depends on the size of the energy gap.
- S. Mathias
- , S. Eich
- & M. Aeschlimann
-
Article
| Open Access Pure-quartic solitons
Pure-quartic solitons
Optical solitons are pulses that propagate undistorted. Here, the authors demonstrate a class of soliton arising from the interaction of self-phase modulation with quartic dispersion, rather than with quadratic dispersion as occurs in conventional solitons.
- Andrea Blanco-Redondo
- , C. Martijn de Sterke
- & Chad Husko
-
Article
| Open Access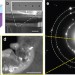 Experimental evidence of new tetragonal polymorphs of silicon formed through ultrafast laser-induced confined microexplosion
Experimental evidence of new tetragonal polymorphs of silicon formed through ultrafast laser-induced confined microexplosion
Ordinary materials can transform into exotic phases with new crystal structures at high pressure and temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate metastable phases of silicon, created by confined microexplosions initiated by ultrafast laser pulses, that are preserved for further utilisation.
- L. Rapp
- , B. Haberl
- & A.V. Rode
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency domain optical parametric amplification
Frequency domain optical parametric amplification
Optical parametric amplification is a process that amplifies the power of laser pulses. Here, Schmidt and colleagues demonstrate that performing this amplification in the frequency domain rather than the optical domain could lead to higher power outputs.
- Bruno E. Schmidt
- , Nicolas Thiré
- & François Légaré
-
Article |
 Frequency-resolved optical gating capable of carrier-envelope phase determination
Frequency-resolved optical gating capable of carrier-envelope phase determination
The time-resolved characterization of laser pulses is important in particular for the development of optical characterization techniques at ultrashort timescales. Here the authors develop a scheme that is able to characterize the electric-field evolution of femtosecond laser pulses.
- Yutaka Nomura
- , Hideto Shirai
- & Takao Fuji
-
Article |
 Probing the tunnelling site of electrons in strong field enhanced ionization of molecules
Probing the tunnelling site of electrons in strong field enhanced ionization of molecules
Molecules in intense laser fields have enhanced multiple ionization rates, caused by the ionic core and laser fields acting on the part of the molecule in the up-field. Here, direct proof of this model is presented by studying the instantaneous effect of the field direction during double ionization in ArXe.
- J. Wu
- , M. Meckel
- & R. Dörner
-
Article |
 Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network
Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network
Understanding ultrafast demagnetisation is key to manipulating magnetic structures on fast timescales, yet laser sources limit the attainable spatial resolution. Here, a soft X-ray high harmonic source enables a high temporal and spatial resolution study of domain demagnetisation in [Co/Pt]30multilayer films.
- Boris Vodungbo
- , Julien Gautier
- & Jan Lüning
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity
Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity
Stable, ultrahigh repetition rate optical clocks are critical for applications in high-speed communications, metrology and microchip computing. Pecciantiet al.present a mode-locked laser based on an integrated microcavity, with repetition rate exceeding 200 GHz and narrow linewidth pulses.
- M. Peccianti
- , A. Pasquazi
- & R. Morandotti

 Plasma electron acceleration driven by a long-wave-infrared laser
Plasma electron acceleration driven by a long-wave-infrared laser