Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access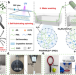 Spider-silk-inspired strong and tough hydrogel fibers with anti-freezing and water retention properties
Spider-silk-inspired strong and tough hydrogel fibers with anti-freezing and water retention properties
Hydrogel fibres have potential in a range of applications such as flexible electronics, but achieving the desired mechanical properties can be challenging. Here, the authors report spider silk-inspired hydrogel fibres with tuneable mechanical properties suitable for flexible electronics.
- Shaoji Wu
- , Zhao Liu
- & Yurong Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Cellulose nanofiber-mediated manifold dynamic synergy enabling adhesive and photo-detachable hydrogel for self-powered E-skin
Cellulose nanofiber-mediated manifold dynamic synergy enabling adhesive and photo-detachable hydrogel for self-powered E-skin
Certain devices require rapid adhesion and detachment, but achieving both can be challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a supramolecular hydrogel with reversible tough adhesion and triggered photodetachment.
- Lei Zhang
- , Lu Chen
- & Chaoji Chen
-
Article
| Open Access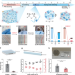 Control of polymers’ amorphous-crystalline transition enables miniaturization and multifunctional integration for hydrogel bioelectronics
Control of polymers’ amorphous-crystalline transition enables miniaturization and multifunctional integration for hydrogel bioelectronics
Soft elastic materials could be useful in the fabrication of brain-machine interfaces, but achieving the desirable material properties can be challenging. Here, the authors report control of the amorphous-crystalline transition of polymers to alter hydrogel properties and monitor mouse behaviour.
- Sizhe Huang
- , Xinyue Liu
- & Siyuan Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple hydrogen-bonding induced nonconventional red fluorescence emission in hydrogels
Multiple hydrogen-bonding induced nonconventional red fluorescence emission in hydrogels
The development of fluorescent polymer hydrogels without the use of extended pi-conjugation is challenging. Here, the authors report the use of clustering-trigger emission to give red fluorescence on boiling polymer hydrogels, with tuneable emission properties.
- Jiayu Wu
- , Yuhuan Wang
- & Feng Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Establishing superfine nanofibrils for robust polyelectrolyte artificial spider silk and powerful artificial muscles
Establishing superfine nanofibrils for robust polyelectrolyte artificial spider silk and powerful artificial muscles
Spider silk has desirable properties, but these are hard to replicate with artificial materials. Here, the authors report a polyelectrolyte artificial spider silk, with control over dissociation of the polymer chains by introduction of ions, and thermally driven supercontraction.
- Wenqian He
- , Meilin Wang
- & Zunfeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioadhesive interface for marine sensors on diverse soft fragile species
Bioadhesive interface for marine sensors on diverse soft fragile species
It is useful to be able to equip marine animals with sensors, but it can be challenging to attach these to soft marine organisms. Here, the authors use an adhesive hydrogel to achieve rapid attachment of sensors to marine life including jellyfish, squid and lobster.
- Camilo Duque Londono
- , Seth F. Cones
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printable strong and tough composite organo-hydrogels inspired by natural hierarchical composite design principles
3D printable strong and tough composite organo-hydrogels inspired by natural hierarchical composite design principles
The preparation of composite hydrogels can allow for mechanical properties to be enhanced, and hierarchical structures can be effective. Here, the authors report improved mechanical properties by the addition of ceramic platelets to an organohydrogel in direct ink writing.
- Quyang Liu
- , Xinyu Dong
- & Wei Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access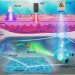 X-ray-activated polymerization expanding the frontiers of deep-tissue hydrogel formation
X-ray-activated polymerization expanding the frontiers of deep-tissue hydrogel formation
Photo-crosslinking polymerization facilitates precise control of hydrogel formation for various applications including tissue engineering, but most existing photo-crosslinking methods fail to achieve deep-tissue penetration, especially within bone structures. Here the authors report a strategy of low-dose X-ray-activated polymerization that enables deep-tissue hydrogel formation.
- Hailei Zhang
- , Boyan Tang
- & Gang Han
-
Article
| Open Access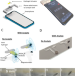 Quantitative, high-sensitivity measurement of liquid analytes using a smartphone compass
Quantitative, high-sensitivity measurement of liquid analytes using a smartphone compass
Smartphone cameras have been widely used for analysis purposes, but the use of magnetometers in smartphones is limited in this regard. In this study, the authors present a smartphone analyte sensor platform that utilizes the built in magnetometer to directly translate signals through analyte-responsive magnetic-hydrogel composites.
- Mark Ferris
- & Gary Zabow
-
Article
| Open Access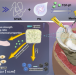 Silk fibroin hydrogel adhesive enables sealed-tight reconstruction of meniscus tears
Silk fibroin hydrogel adhesive enables sealed-tight reconstruction of meniscus tears
Suture repair is the current clinical treatment for meniscus tears, but inaccessible tears in company with re-tears susceptibility remain unresolved. Here the authors address these issues by developing a meniscus adhesive-based strategy for the seamless and dense reconstruction of torn meniscus.
- Xihao Pan
- , Rui Li
- & Hongwei Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access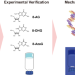 Developing a machine learning model for accurate nucleoside hydrogels prediction based on descriptors
Developing a machine learning model for accurate nucleoside hydrogels prediction based on descriptors
Supramolecular nucleoside-based hydrogels have potential in biomedical applications, but there is no model to predict what nucleoside derivatives will form hydrogels. Here, the authors report a machine learning model to predict the ability of nucleoside derivatives to form hydrogels.
- Weiqi Li
- , Yinghui Wen
- & Hang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination
Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination
Environmentally adaptive hydrogels have great potential as soft robotics but achieving self-regulated reversal shape deformation in homogenous hydrogels under a constant stimulus is challenging. Here, the authors report responsive hydrogels functionalized with two photoswitchable spiropyrans that exhibit self-regulated transient deformation reversal when subjected to constant illumination.
- Kexin Guo
- , Xuehan Yang
- & Chuang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Elasticity-controlled jamming criticality in soft composite solids
Elasticity-controlled jamming criticality in soft composite solids
Soft composite solids are building blocks for many functional and biological materials, yet it remains challenging to predict their mechanical properties. Zhao et al. propose a criticality framework to connect the mechanics to the critical behaviour near the shear-jamming transition of the dispersed inclusions.
- Yiqiu Zhao
- , Haitao Hu
- & Qin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
Mechanoelectric energy conversion is a potential solution for the power supply of soft devices, but the low current output for low frequency motions limits its applicability. Here, the authors report a hydrogel generator with mechanoionic current generation amplified by orders of magnitudes and its application as controlled drug-releasing system for wound healing.
- Hongzhen Liu
- , Xianglin Ji
- & Lizhi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Stable water splitting using photoelectrodes with a cryogelated overlayer
Stable water splitting using photoelectrodes with a cryogelated overlayer
Photoelectrodes made of earth-abundant materials can contribute to low-cost and carbon-free hydrogen production, but suffer from a short lifetime. Here the authors report cryogel overlayer to increase the operation time of the device by regulating evolving hydrogen bubble dynamics.
- Byungjun Kang
- , Jeiwan Tan
- & Hyungsuk Lee
-
Article
| Open Access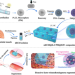 Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Elastic porous microspheres/extracellular matrix hydrogel injectable composites releasing dual bio-factors enable tissue regeneration
Injectable pro-regenerative biomaterials are vital for developing minimally invasive regenerative treatment, but impeded by brittleness and lack of biological functions. Here the authors address these issues by engineering injectable functionalized composites that facilitate the sequential release of IL-4 and IGF-1 to regulate macrophages and stem cell behavior for enhanced in situ regeneration.
- Yi Li
- , Siyang Liu
- & Meifeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks
Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks
Tough hydrogels commonly utilise energy dissipation mechanisms, but this can lead to challenges in achieving low hysteresis. Here, the authors report a hydrogel with a highly entangled double network that allows reversibility following stretching.
- Ruixin Zhu
- , Dandan Zhu
- & Xinling Wang
-
Article
| Open Access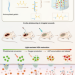 Programmed microalgae-gel promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes
Programmed microalgae-gel promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes
The treatment of infected diabetic wounds faces obstacles of bacterial infection, hypoxia, hyperexpression of reactive oxygen species, and inflammation. Here, the authors address these issues by developing a programmed treatment strategy that utilizes live Haematococcus to promote healing of diabetic wounds in a comprehensive manner.
- Yong Kang
- , Lingling Xu
- & Xiaoyuan Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Dressings for aiding in chronic wound healing can be beneficial, but often involve additional processes or leave residue. Here, the authors report a hydrogel dressing with antibiofilm and antioxidative properties for the treatment of infected diabetic wounds.
- Dicky Pranantyo
- , Chun Kiat Yeo
- & Mary B. Chan-Park
-
Article
| Open Access Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Light-responsive MXenegel via interfacial host-guest supramolecular bridging
Multifunctional composite hydrogels are promising candidates to develop smart and recyclable electronic components. Here, the authors report a reversible on-demand liquefication and solidification conductive gel formed by the self-assembly of photoresponsive host-guest complexes and MXene nanosheets which can be integrated into traditional solid-state circuits.
- Yu-Liang Lin
- , Sheng Zheng
- & Jiun-Tai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Ionic skins have potential in long-term physiological monitoring, but do not always achieve a desirable balance of viscosity and elasticity. Here, the authors report a material with hierarchical topological entanglements allowing desirable viscoelastic properties.
- Huating Ye
- , Baohu Wu
- & Peiyi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
It is desirable to be able to mimic the properties of skin with hydrogels, but challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of functionalised extracellular vesicles as crosslinkers for skin-mimicking hydrogels with good mechanical strength.
- Feng Wu
- , Yusheng Ren
- & Yan Pang
-
Article
| Open Access A wearable electrostimulation-augmented ionic-gel photothermal patch doped with MXene for skin tumor treatment
A wearable electrostimulation-augmented ionic-gel photothermal patch doped with MXene for skin tumor treatment
A wearable biological patch capable of producing multiple responses to light and electricity without interfering with daily activities is desired for skin cancer treatment but remains elusive. Herein, the authors report a skin-mountable and dual-responsive electrothermal patch for melanoma treatment by the co-therapy of photothermal and electrical stimulations.
- Xingkai Ju
- , Jiao Kong
- & Yongdong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Robust hydrogels offer a promising solution for the development of artificial skin for bionic robots, yet few hydrogels have a comprehensive performance comparable to real human skin. Here, the authors present a general method to convert traditional elastomers into tough hydrogels via a unique radiation-induced penetrating polymerization method.
- Yuan Tian
- , Zhihao Wang
- & Yunlong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation
Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation
Soft robots have potential in a number of applications, but the self-regulated steering of the robots under static stimuli is a significant challenge. Here, the authors report the movement of knotbots by symmetry breaking and restoration to achieve tasks including gear rotation and rod climbing.
- Qing Li Zhu
- , Weixuan Liu
- & Zi Liang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Shape morphing of hydrogels by harnessing enzyme enabled mechanoresponse
Shape morphing of hydrogels by harnessing enzyme enabled mechanoresponse
A change material properties on application of stimuli is a useful property for hydrogels, but mechano-responsiveness in such materials is challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report a strain-responsive hydrogel, controlled by the activity of enzymes within the material.
- Kuan Zhang
- , Yu Zhou
- & Lifei Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable adhesion and morphing of protein hydrogels for underwater robots
Programmable adhesion and morphing of protein hydrogels for underwater robots
Soft robots have potential in carrying out underwater tasks, but achieving the right level of adhesion and shape-changing ability is challenging. Here, the authors report the development of protein-based hydrogels with iron oxide nanoparticles with photothermal and magnetic responsiveness, capable of carrying out complex tasks.
- Sheng-Chen Huang
- , Ya-Jiao Zhu
- & Zhi-Gang Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Surface hydrophobization of hydrogels via interface dynamics-induced network reconfiguration
Surface hydrophobization of hydrogels via interface dynamics-induced network reconfiguration
It is useful to be able to control the surface properties of a hydrogel, but tuning the surface without altering bulk properties of the hydrogel is challenging. Here, the authors report a method for modifying the surface of a hydrogel by grafting of polymer chains to the mold.
- Bo Yi
- , Tianjie Li
- & Liming Bian
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital-flop transition of superfluid 3He in anisotropic silica aerogel
Orbital-flop transition of superfluid 3He in anisotropic silica aerogel
When imbibed in an anisotropic silica aerogel, superfluid 3He undergoes a temperature-driven “orbital flop" transition, where the orbital quantization axis rotates by 90 degrees. Here, by simulating planar and nematic aerogel, M. D. Nguyen et al. show that the orbital flop transition is driven by the distinct large- and small-scale structures of the aerogel.
- M. D. Nguyen
- , Joshua Simon
- & W. P. Halperin
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired structural hydrogels with highly ordered hierarchical orientations by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils
Bioinspired structural hydrogels with highly ordered hierarchical orientations by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils
Natural materials can combine strength and toughness, but achieving similar well-ordered structures for synthetic materials is challenging. Here, the authors report hydrogels prepared by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils, with anisotropic structure and good mechanical properties.
- Shuihong Zhu
- , Sen Wang
- & Youhui Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Organohydrogel-based transparent terahertz absorber via ionic conduction loss
Organohydrogel-based transparent terahertz absorber via ionic conduction loss
Transparent absorbers for electromagnetic interference shielding are sought in the terahertz frequency range. The authors demonstrate organohydrogel-elastomer composites based on permittivity gradients, with strong ionic conduction loss, showing high absorption in the 0.5–4.5 THz band.
- Wenke Xie
- , Qian Tang
- & Qiye Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Folk arts-inspired twice-coagulated configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors
Folk arts-inspired twice-coagulated configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors
Aerogels attract considerable attention in various emerging fields in recent decades, but low density and weak mechanical performance make their configuration-editing capability challenging. Here the authors establish an efficient twice-coagulated strategy to fabricate configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors.
- Lishan Li
- , Guandu Yang
- & Xuetong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Visible light-induced switching of soft matter materials properties based on thioindigo photoswitches
Visible light-induced switching of soft matter materials properties based on thioindigo photoswitches
Thioindigos are reversible photoswitches with spatial control over the conformational change, yet have very limited solubility in most solvents. Here, the authors report a method for the insertion of thioindigos into polymer chains, allowing the formation of visible light responsive hydrogels.
- Sarah L. Walden
- , Phuong H. D. Nguyen
- & Vinh X. Truong
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically tunable organogels from highly charged polyoxometalate clusters loaded with fluorescent dyes
Mechanically tunable organogels from highly charged polyoxometalate clusters loaded with fluorescent dyes
Functionalizing inorganic organogels is a challenge and can have a negative impact on their mechanical properties. Here, the authors present nanowire-based organogels based on highly charged polyoxometalate cluster units that are mechanically tuned and loaded with fluorescent dyes.
- Fenghua Zhang
- , Zhong Li
- & Xun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogels with tunable mechanical plasticity regulate endothelial cell outgrowth in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis
Hydrogels with tunable mechanical plasticity regulate endothelial cell outgrowth in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis
It is vital to unveil the effects of extracellular matrix cues on endothelial cell (EC) outgrowth for desirably governing vasculature formation, but the role of matrix plasticity on EC outgrowth is elusive. Here, the authors develop hydrogels with tunable mechanical plasticity independent of stiffness, and elucidate the plasticity-mediated responses of ECs during vasculogenesis and angiogenesis.
- Zhao Wei
- , Meng Lei
- & Feng Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Micro- and nanofabrication of dynamic hydrogels with multichannel information
Micro- and nanofabrication of dynamic hydrogels with multichannel information
Responsive hydrogels containing multichannel information have potential in miniature devices, but their fabrication can be challenging. Here, the authors report the creation of hydrogel materials with each pixel containing three-channel information for printing of distinct images in one location.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Yohan Lee
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access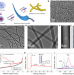 One-dimensionally oriented self-assembly of ordered mesoporous nanofibers featuring tailorable mesophases via kinetic control
One-dimensionally oriented self-assembly of ordered mesoporous nanofibers featuring tailorable mesophases via kinetic control
One-dimensional materials have interesting physiochemical properties, but control over porosity is still a significant challenge. Here, the authors report a self-assembly method for the fabrication of 1D materials with an ordered mesostructure.
- Liang Peng
- , Huarong Peng
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A click chemistry-mediated all-peptide cell printing hydrogel platform for diabetic wound healing
A click chemistry-mediated all-peptide cell printing hydrogel platform for diabetic wound healing
Diabetic wounds are challenging to heal, with vascular injury induced by high glucose a key pathological factor. Here, the authors report a hydrogel designed to interrupt the process of vascular injury, with angiogenic capacity.
- Jinjian Huang
- , Rong Yang
- & Jianan Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Achieving successful in vivo cartilage regeneration remains challenging. Here they present a cell-free, multiple hydrogen-bond crosslinked hydrogel loaded with tannic acid and Kartogenin with ultra-durable mechanical properties and stage-dependent drug release behavior to promote cartilage regeneration.
- Yuxuan Yang
- , Xiaodan Zhao
- & Xuesi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access High speed underwater hydrogel robots with programmable motions powered by light
High speed underwater hydrogel robots with programmable motions powered by light
Underwater soft robots made of stimuli-responsive shape-changing hydrogels generally present low actuation speed which is limited by the water diffusion between hydrogels and their surrounding environment. Here, the authors develop dynamic hydrogel robots with a fast and switchable actuation based on a thermally driven chain conformation change after mechanical programming.
- Chujun Ni
- , Di Chen
- & Qian Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Four-dimensional hydrogel dressing adaptable to the urethral microenvironment for scarless urethral reconstruction
Four-dimensional hydrogel dressing adaptable to the urethral microenvironment for scarless urethral reconstruction
Urethral repair can be carried out using hydrogels, but the harsh microenvironment hinders the repair. Here, the authors report the development of a 4D hydrogel dressing that can provide an early-vascularised and later-antifibrogenic microenvironment to assist in scarless reconstruction.
- Yujie Hua
- , Kai Wang
- & Kaile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access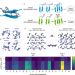 Hierarchical assembly of tryptophan zipper peptides into stress-relaxing bioactive hydrogels
Hierarchical assembly of tryptophan zipper peptides into stress-relaxing bioactive hydrogels
Rational design has endowed self-assembling peptides with structural similarities to natural materials, but recreating the dynamic functional properties inherent to natural systems remains challenging. Here the authors report the discovery of a short peptide based on the tryptophan zipper motif, that shows multiscale hierarchical ordering into hydrogels that display emergent dynamic properties.
- Ashley K. Nguyen
- , Thomas G. Molley
- & Kristopher A. Kilian
-
Article
| Open Access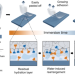 Autonomous underwater adhesion driven by water-induced interfacial rearrangement
Autonomous underwater adhesion driven by water-induced interfacial rearrangement
The underwater adhesives developed so far usually show water adsorption and lack of spontaneity as major drawbacks. Herein, the authors develop a tough, flexible and autonomous underwater adhesive based on an amphiphilic polymeric matrix swollen by hydrophobic ionic liquid.
- Le Yao
- , Chengjiang Lin
- & Qi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A biocompatible electrolyte enables highly reversible Zn anode for zinc ion battery
A biocompatible electrolyte enables highly reversible Zn anode for zinc ion battery
Aqueous zinc metal batteries utilized in wearable and implanted devices require good biosecurity, long lifespan, and high flexibility. Here, the authors proposed a biocompatible hyaluronic acid-based gel electrolyte to improve the reversibility of zinc anodes and prolong the cycle life of batteries.
- Guanjie Li
- , Zihan Zhao
- & Zaiping Guo
-
Article
| Open Access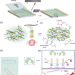 Programmable nanocomposites of cellulose nanocrystals and zwitterionic hydrogels for soft robotics
Programmable nanocomposites of cellulose nanocrystals and zwitterionic hydrogels for soft robotics
Soft robots made of hydrogels with anisotropic and shape-change properties offer interesting design opportunities. Here, the authors report zwitterionic hydrogels and anisotropic cellulose nanocrystals composites in which the shear-induced alignment of cellulose nanocrystals allows for the development of shape-change programmable miniature robots.
- Rasool Nasseri
- , Negin Bouzari
- & Hamed Shahsavan
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid–liquid phase separation within fibrillar networks
Liquid–liquid phase separation within fibrillar networks
Liquid–liquid phase separation is known in cell biology as an underlying mechanism of intracellular organization. The authors study a complex interplay between phase separation, network mechanics, and condensate capillarity, providing explanation for the phenomena in complex environments like the cellular interior.
- Jason X. Liu
- , Mikko P. Haataja
- & Rodney D. Priestley
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent Deborah number-dependent transition from homogeneity to heterogeneity
Divergent Deborah number-dependent transition from homogeneity to heterogeneity
Due to the complexity of living systems, it is challenging to identify the factors influencing the formation of native heterogeneous structures. Here, the authors employ flexible polymer networks with embedded stiff cellulose nanocrystals to simulate heterogeneous core-sheath structures interrelated with the divergence of Deborah number.
- Dan Xu
- , Yang Yang
- & Kai Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Building block aspect ratio controls assembly, architecture, and mechanics of synthetic and natural protein networks
Building block aspect ratio controls assembly, architecture, and mechanics of synthetic and natural protein networks
Fibrous networks constructed from high aspect ratio protein building blocks are ubiquitous in nature, but the functional advantage of such building blocks over globular proteins is not understood. Here, using shear rheology and small-angle neutron scattering, the authors characterise the mechanical and structural properties of photochemically crosslinked protein L and fibrin networks and show that aspect ratio is a crucial property that defines network architecture and mechanics.
- Matt D. G. Hughes
- , Sophie Cussons
- & Lorna Dougan
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale assembly of isotropic nanofiber aerogels based on columnar-equiaxed crystal transition
Large-scale assembly of isotropic nanofiber aerogels based on columnar-equiaxed crystal transition
In this work, the authors present an ice-templating strategy to produce large-scale isotropic nanofiber aerogels using a unique process of freezing the material on a rotating cryogenic drum surface, crushing it, and then re-casting the nanofiber slurry enabling high-throughput and design flexibility.
- Lei Li
- , Yiqian Zhou
- & Hui Wu

 Skin-inspired, sensory robots for electronic implants
Skin-inspired, sensory robots for electronic implants