Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked structures in polymer backbones can give interesting functionality, but can be challenging to prepare and control. Here, the authors report the development of polymers with a daisy chain unit in the backbone that are capable of shape memory behaviour.
- Shang-Wu Zhou
- , Danlei Zhou
- & Da-Hui Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable afterglow for mechanical self-monitoring 3D printing structures
Tunable afterglow for mechanical self-monitoring 3D printing structures
Organic afterglow materials have potential in self-monitoring applications but it is challenging to design materials with desired properties. Here, the authors report the development of a lifetime tunable organic afterglow system for use in mechanical self-monitoring 3D printed structures.
- Rongjuan Huang
- , Yunfei He
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access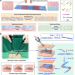 4D printed hydrogel scaffold with swelling-stiffening properties and programmable deformation for minimally invasive implantation
4D printed hydrogel scaffold with swelling-stiffening properties and programmable deformation for minimally invasive implantation
3D printing has potential in designing personalised scaffolds, but minimally invasive implantation is still challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a polyurethane material with temperature triggered shape memory and water triggered deformation that allows for transcatheter delivery.
- Bo Liu
- , Hui Li
- & Xiaoli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed nanotrap structures for efficient separation of rare earth elements over a single step
Rationally designed nanotrap structures for efficient separation of rare earth elements over a single step
Extracting rare earth elements (REEs) from wastewater is essential for the growth of an eco-friendly sustainable economy but separating individual rare earth elements remains challenging. Here, the authors report a REE nanotrap that features dense uncoordinated carboxyl groups and triazole N atoms in a two-fold interpenetrated metalorganic framework which is highly responsive to the size variation of rareearth ions.
- Qing-Hua Hu
- , An-Min Song
- & Jian-Ding Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Harmonic amide bond density as a game-changer for deciphering the crosslinking puzzle of polyamide
Relating the degree of network crosslinking as a descriptor to the desalination performance of crosslinked polymer membranes remains challenging. Here, the authors introduce a parameter based on distinct amide bonds per unit mass of polyamide, to unravel the relationship between the crosslinked networks of polyamide membranes and their desalination performance.
- Yu-Ren Xue
- , Chang Liu
- & Zhi-Kang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Complexation-driven assembly of imine-linked helical receptors showing adaptive folding and temperature-dependent guest selection
Complexation-driven assembly of imine-linked helical receptors showing adaptive folding and temperature-dependent guest selection
The development of synthetic receptors capable of selectively binding monosaccharides is highly challenging. Here, authors present the efficient synthesis of these receptors based on foldamers, achieved through complexation-induced equilibrium shifting.
- Geunmoo Song
- , Seungwon Lee
- & Kyu-Sung Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
A high-current hydrogel generator with engineered mechanoionic asymmetry
Mechanoelectric energy conversion is a potential solution for the power supply of soft devices, but the low current output for low frequency motions limits its applicability. Here, the authors report a hydrogel generator with mechanoionic current generation amplified by orders of magnitudes and its application as controlled drug-releasing system for wound healing.
- Hongzhen Liu
- , Xianglin Ji
- & Lizhi Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Circular olefin copolymers made de novo from ethylene and α-olefins
Circular olefin copolymers made de novo from ethylene and α-olefins
Although several advances have been made in chemical Polyethylene (PE) re- and upcycling, energy-efficient and selective catalytic processes are still lacking. Here, the authors show coupling of an industrially relevant coordination copolymerization olefins with a functionalized chain-transfer agent, followed by modular assembly of the resulting telechelic polyolefin building blocks by polycondensation to afford ester-linked PE-based random and block copolymers which exhibit full chemical circularity.
- Xing-Wang Han
- , Xun Zhang
- & Yong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access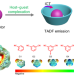 A general supramolecular strategy for fabricating full-color-tunable thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials
A general supramolecular strategy for fabricating full-color-tunable thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials
Thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials with full-colour tunability are desirable but challenging to prepare. Here, the authors report a method for preparing such materials through the design of host-guest cocrystals with through-space charge transfer.
- Nan Xue
- , He-Ye Zhou
- & Chuan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access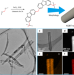 In-situ formatting donor-acceptor polymer with giant dipole moment and ultrafast exciton separation
In-situ formatting donor-acceptor polymer with giant dipole moment and ultrafast exciton separation
Donor-acceptor polymers have potential for application in photocatalysis, but often harsh synthetic conditions are required. Here, the authors report a post-synthetic method for conversion to donor-acceptor states, to give a polymer capable of enhancing photocatalytic hydrogen peroxide synthesis.
- Chang Cheng
- , Jiaguo Yu
- & Mietek Jaroniec
-
Article
| Open Access Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks
Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks
Tough hydrogels commonly utilise energy dissipation mechanisms, but this can lead to challenges in achieving low hysteresis. Here, the authors report a hydrogel with a highly entangled double network that allows reversibility following stretching.
- Ruixin Zhu
- , Dandan Zhu
- & Xinling Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic mercury immobilization by selenium functionalized polyphenylene sulfide fabric
Biomimetic mercury immobilization by selenium functionalized polyphenylene sulfide fabric
The abatement of elemental mercury remains an enormous challenge for public health and ecosystems. Here, inspired by the seleno-mercury antagonism effect in biological systems, the authors developed an ideal Hg0 adsorbent with a record-high adsorption capacity of 1621.9 mg g−1.
- Hailong Li
- , Fanyue Meng
- & Jianping Yang
-
Article
| Open Access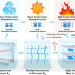 Twofold rigidity activates ultralong organic high-temperature phosphorescence
Twofold rigidity activates ultralong organic high-temperature phosphorescence
Obtaining high-temperature phosphorescence in organic materials can potentially lead to broader applications, but can be challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of rigid molecules as both host and guest to give temperature resistance and therefore high-temperature phosphorescence.
- Kaijun Chen
- , Yongfeng Zhang
- & Xiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralight crystalline hybrid composite material for highly efficient sequestration of radioiodine
Ultralight crystalline hybrid composite material for highly efficient sequestration of radioiodine
The development of effective adsorbents of radioiodine nuclear waste remains difficult due to the lack of proper material design strategies. Here the authors report an ultralight hierarchically porous crystalline multifunctional hybrid nanocomposite for ultrafast entrapment of iodine and polyiodide species under both static and dynamic condition.
- Sahel Fajal
- , Writakshi Mandal
- & Sujit K. Ghosh
-
Article
| Open Access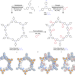 Robust links in photoactive covalent organic frameworks enable effective photocatalytic reactions under harsh conditions
Robust links in photoactive covalent organic frameworks enable effective photocatalytic reactions under harsh conditions
The development of heterogeneous photocatalysts applicable under harsh conditions is challenging. Here the authors report the conversion of imine linkages into quinoline groups in triphenylamine incorporated photosensitive covalent organic frameworks to develop robust heterogeneous photocatalysts for photocatalytic applications in harsh conditions.
- Jia-Rui Wang
- , Kepeng Song
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Melt-quenched carboxylate metal–organic framework glasses
Melt-quenched carboxylate metal–organic framework glasses
Many MOFs feature carboxylate ligands with strong coordination bonds, hindering thermal melting. Here, authors present a meltable carboxylate MOF designed with a thermodynamically favored component.
- Minhyuk Kim
- , Hwa-Sub Lee
- & Hoi Ri Moon
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced MOF synthesis enabling composite photothermal materials
Light-induced MOF synthesis enabling composite photothermal materials
Introduced here is a light-induced MOF synthesis, enabled by plasmonic nanoparticles. The method, proven to be rapid and efficient, can also promote the formation of a nanoparticle-MOF composite, imparting photothermal properties to the new material.
- Ofir Shelonchik
- , Nir Lemcoff
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article
| Open Access Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Crack formation typically results in random patterns and material failure. Inspired by plant phototropism, the authors use plasmonic absorbers to control crack propagation in colloidal films with light, showcasing a robust, programmable self-assembly process.
- Fanny Thorimbert
- , Mateusz Odziomek
- & Marco Faustini
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery
Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery
The dynamic protein corona hinders the uptake of nanocarriers in desired target cell populations, limiting their bench-to-bedside translation. Here the authors reveal that the modification of hydroxyl and amino functional groups on nanovesicles can rationally regulate the composition of protein coronas to improve the efficiency of targeted drug delivery.
- Yunqiu Miao
- , Lijun Li
- & Yong Gan
-
Article
| Open Access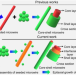 Visualizing the interfacial-layer-based epitaxial growth process toward organic core-shell architectures
Visualizing the interfacial-layer-based epitaxial growth process toward organic core-shell architectures
Organic heterostructures with controlled geometry on the micro and nanoscale are important in nanotechnology, but epitaxial growth processes with high lattice mismatching are challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report a visualisation process for morphology evolution on epitaxial growth.
- Ming-Peng Zhuo
- , Xiao Wei
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Coacervate-based compartments are attractive as potential protocells, but formation and control of the compartments can be challenging. Here, the authors report the spontaneous formation of core-shell, cell-sized coacervate compartments driven by droplet evaporation.
- Cheng Qi
- , Xudong Ma
- & Zhou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access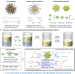 Ultra-stable and highly reactive colloidal gold nanoparticle catalysts protected using multi-dentate metal oxide nanoclusters
Ultra-stable and highly reactive colloidal gold nanoparticle catalysts protected using multi-dentate metal oxide nanoclusters
For catalytic nanoparticles there is often a trade-off between stability and activity. Here the authors report a route to ultra-stable and catalytically active colloidal small (~3 nm) gold nanoparticles using multi-dentate polyoxometalates as protecting agents in nonpolar solvents.
- Kang Xia
- , Takafumi Yatabe
- & Kosuke Suzuki
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing potassium polysulfides for high performance potassium-sulfur batteries
Optimizing potassium polysulfides for high performance potassium-sulfur batteries
Potassium-sulfur battery are promising materials for next-generation high energy, low cost batteries. Here the authors explore a tungsten based catalytic composite for optimizing potassium polysulfides and improve K-S electrochemistry in batteries
- Wanqing Song
- , Xinyi Yang
- & Wenbin Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
“Understanding the structure-property relationship of organic molecules which exhibit different properties upon aggregation is important for the field of material science. Here, the authors prepare nonconjugated rhodamine-based molecules without aggregation-induced emission building blocks yet displaying typical aggregation-induced emission behavior.”
- Lin-Lin Yang
- , Haoran Wang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Dressings for aiding in chronic wound healing can be beneficial, but often involve additional processes or leave residue. Here, the authors report a hydrogel dressing with antibiofilm and antioxidative properties for the treatment of infected diabetic wounds.
- Dicky Pranantyo
- , Chun Kiat Yeo
- & Mary B. Chan-Park
-
Article
| Open Access Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Ionic skins have potential in long-term physiological monitoring, but do not always achieve a desirable balance of viscosity and elasticity. Here, the authors report a material with hierarchical topological entanglements allowing desirable viscoelastic properties.
- Huating Ye
- , Baohu Wu
- & Peiyi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Artificial ion channels have potential in a range of applications, but achieving performance comparable to biological channels has been challenging. Here, the authors report an artificial, light-driven chloride pump, inspired by halorhodopsin, with a helical porphyrin channel array.
- Chao Li
- , Yi Zhai
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
It is desirable to be able to mimic the properties of skin with hydrogels, but challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of functionalised extracellular vesicles as crosslinkers for skin-mimicking hydrogels with good mechanical strength.
- Feng Wu
- , Yusheng Ren
- & Yan Pang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with nia nets for efficient separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures
Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with nia nets for efficient separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures
The synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with highly connected building blocks presents a significant challenge. Here, the authors report the synthesis of two 3D COFs with the nia topology, by introducing planar hexagonal and triangular prism nodes.
- Jianhong Chang
- , Fengqian Chen
- & Qianrong Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Upcycling poly(succinates) with amines to N-substituted succinimides over succinimide anion-based ionic liquids
Upcycling poly(succinates) with amines to N-substituted succinimides over succinimide anion-based ionic liquids
Ionic liquids have been employed in dissolution and chemical degradation of waste polymers. Here the authors report a cation-anion confined hydrogen-bonding catalysis strategy to deconstruct poly(succinates) into N-substituted succinimides over ionic liquids.
- Fengtian Wu
- , Yuepeng Wang
- & Zhimin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A one-two punch targeting reactive oxygen species and fibril for rescuing Alzheimer’s disease
A one-two punch targeting reactive oxygen species and fibril for rescuing Alzheimer’s disease
Toxic amyloid-beta plaque and harmful inflammation are two leading hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and precise AD therapy is elusive due to the lack of dual-targeting therapy function, limited blood-brain barrier penetration, and low imaging sensitivity. Here, the authors address these issues by designing a near-infrared-II aggregation-induced emission nanotheranostic for precise AD therapy.
- Jiefei Wang
- , Ping Shangguan
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Sublimed C60 for efficient and repeatable perovskite-based solar cells
Sublimed C60 for efficient and repeatable perovskite-based solar cells
Batch-to-batch reproducibility of device performances is crucial for perovskite photovoltaics moving towards industrialization. Here, the authors show that commercial as-received C60 source materials may coalesce during repeated thermal evaporation processes, jeopardizing such reproducibility.
- Ahmed A. Said
- , Erkan Aydin
- & Stefaan De Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing
Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing
Fabrication methods for ionic conductive hydrogel fibers are challenged by complexity and poor stability. Using a stress-induced adaptive phase transition strategy, Liu et al. fabricate self-encapsulated hydrogel fibers for depth-of-field sensing applications in a sustainable, two-step process.
- Ying Liu
- , Chan Wang
- & Zhou Li
-
Article
| Open Access Self-similar chiral organic molecular cages
Self-similar chiral organic molecular cages
To enhance the utility of organic molecular cages (OMCs), the evolution of OMCs into higher-level chiral OMCs with self-similar superstructures is meaningful yet challenging. Here, the authors report a pair of higher-level 3D tri-bladed chiral helical molecular cages, displaying self-similarity in a discrete self-similar superstructure at different levels.
- Zhen Wang
- , Qing-Pu Zhang
- & Chuan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks in solution enables continuous and high-crystalline membranes
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks in solution enables continuous and high-crystalline membranes
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks (HOFs) attract increasing attention as porous materials. Despite the widely studied solid-state properties, little research has been done on the solution state. Here, the authors demonstrate that HOFs fragment into small particles while maintaining their original assemblies upon dispersing in solvents.
- Qi Yin
- , Kuan Pang
- & Tian-Fu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Robust hydrogels offer a promising solution for the development of artificial skin for bionic robots, yet few hydrogels have a comprehensive performance comparable to real human skin. Here, the authors present a general method to convert traditional elastomers into tough hydrogels via a unique radiation-induced penetrating polymerization method.
- Yuan Tian
- , Zhihao Wang
- & Yunlong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-micro porous thin polymer membranes for discriminating H2 and CO2
Sub-micro porous thin polymer membranes for discriminating H2 and CO2
The fabrication of polymeric membranes with high permeance and remarkable selectivity for simultaneous H2 purification and CO2 capture is challenging. Here, the authors design a polymer membrane with sub-micro pores via controlled transformation of amine-linked polymer films into benzimidazole- and amine-linked polymer layers.
- Xueru Yan
- , Tianqi Song
- & Xinlei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Native spider silk has desirable mechanical properties, but these are challenging to replicate in an artificial material. Here, the authors report the use of a microfluidic system to create continuous fibers based on recombinant spidroin.
- Jianming Chen
- , Arata Tsuchida
- & Keiji Numata
-
Article
| Open Access Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Prelithiation can introduce controllable amounts of lithium within porous silicon, however it yields a highly reactive material unsuitable for biomedicine. In this study, the authors present a strategy to lithiate porous silicon nanowires, resulting in a biocompatible and bioresorbable material.
- Martti Kaasalainen
- , Ran Zhang
- & Ciro Chiappini
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-selective uranium separation by in-situ formation of π-f conjugated 2D uranium-organic framework
Ultra-selective uranium separation by in-situ formation of π-f conjugated 2D uranium-organic framework
Methodologies to achieve efficient and selective uranium separation originating from nuclear waste are desirable. Here the authors report the in-situ formation of π-f conjugated 2D uranium-organic framework for uranium separation, leading to superior performance in uranium uptake and outstanding uranium generation efficiency from seawater.
- Qing Yun Zhang
- , Lin Juan Zhang
- & Feng Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual flexibility of transparent poly(methylsilsesquioxane) aerogels by surfactant-induced mesoscopic fiber-like assembly
Unusual flexibility of transparent poly(methylsilsesquioxane) aerogels by surfactant-induced mesoscopic fiber-like assembly
Aerogels are mechanically friable despite their attractive properties such as visible-light transparency and low thermal conductivity. Here the authors show mechanically flexible, highly transparent aerogels based on fiber-like pore skeletons.
- Ryota Ueoka
- , Yosuke Hara
- & Kazuyoshi Kanamori
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Electro-active ionic soft actuators generally present slow responses and poor durability when are applied as artificial muscles. Here, the authors describe a polyelectrolyte membrane based on the assembly of Nafion molecules into micelles with efficient ionic conducting pathways for electro-ionic soft actuators and soft robotics with fast responses and long durability.
- Van Hiep Nguyen
- , Saewoong Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of core@shell catalysts guided by Tammann temperature
Synthesis of core@shell catalysts guided by Tammann temperature
The authors report a synthetic strategy to create core@shell catalysts using strong metal-support interactions and low-Tammann-temperature compounds. The resulting materials are highly stable and may be useful in industrial applications.
- Pei Xiong
- , Zhihang Xu
- & Molly Meng-Jung Li
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Nanoscale optoelectrodes hold the potential to optically stimulate individual neuron. Here, the authors form nanoscale capacitive optoelectrodes by incorporating zinc porphyrin into nanorods, coated by TiO2, a design that allows for far-field optical modulation of neurons with efficiency and negligible side effects.
- Jian Chen
- , Yanyan Liu
- & Wenbo Bu
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling nonconjugated polyesters emit full-spectrum fluorescence from blue to near-infrared
Enabling nonconjugated polyesters emit full-spectrum fluorescence from blue to near-infrared
Near-infrared luminescence is useful for advance applications, but is challenging to achieve through clusteroluminescence. Here, the authors report the use of amine-initiated polyesters for amine-ester clusters with near-infrared emission.
- Bo Chu
- , Xiong Liu
- & Xing-Hong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Understanding the surface growth mechanism of carbon nanostructures would help designing better catalysts. Here, the authors combine active machine learning force fields with time-stamped Monte Carlo methods, to dynamically predict carbon growth on metal surfaces.
- Di Zhang
- , Peiyun Yi
- & Hao Li
-
Article
| Open Access One-dimensional single atom arrays on ferroelectric nanosheets for enhanced CO2 photoreduction
One-dimensional single atom arrays on ferroelectric nanosheets for enhanced CO2 photoreduction
The authors report a study preparing single atom (M = Pt, Ag, Fe, Co, and Ni) arrays on Au/Bi4Ti3O12 nanosheets using electric field polarization techniques. Photocatalytic CO2 reduction is shown to proceed effectively over Au/Bi4Ti3O12.
- Lizhen Liu
- , Jingcong Hu
- & Hongwei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation
Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation
Soft robots have potential in a number of applications, but the self-regulated steering of the robots under static stimuli is a significant challenge. Here, the authors report the movement of knotbots by symmetry breaking and restoration to achieve tasks including gear rotation and rod climbing.
- Qing Li Zhu
- , Weixuan Liu
- & Zi Liang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Circularly polarised luminescence (CPL) is essential for asymmetric synthetic photochemistry. Here, the authors integrate white quantum dots with chiral nematic liquid crystal or liquid crystal polymer to achieve single-emitted tuneable full-colour or white CPL for enantioselective polymerization.
- Yajie Zhou
- , Yaxin Wang
- & Taotao Zhuang

 Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination
Self-regulated reversal deformation and locomotion of structurally homogenous hydrogels subjected to constant light illumination